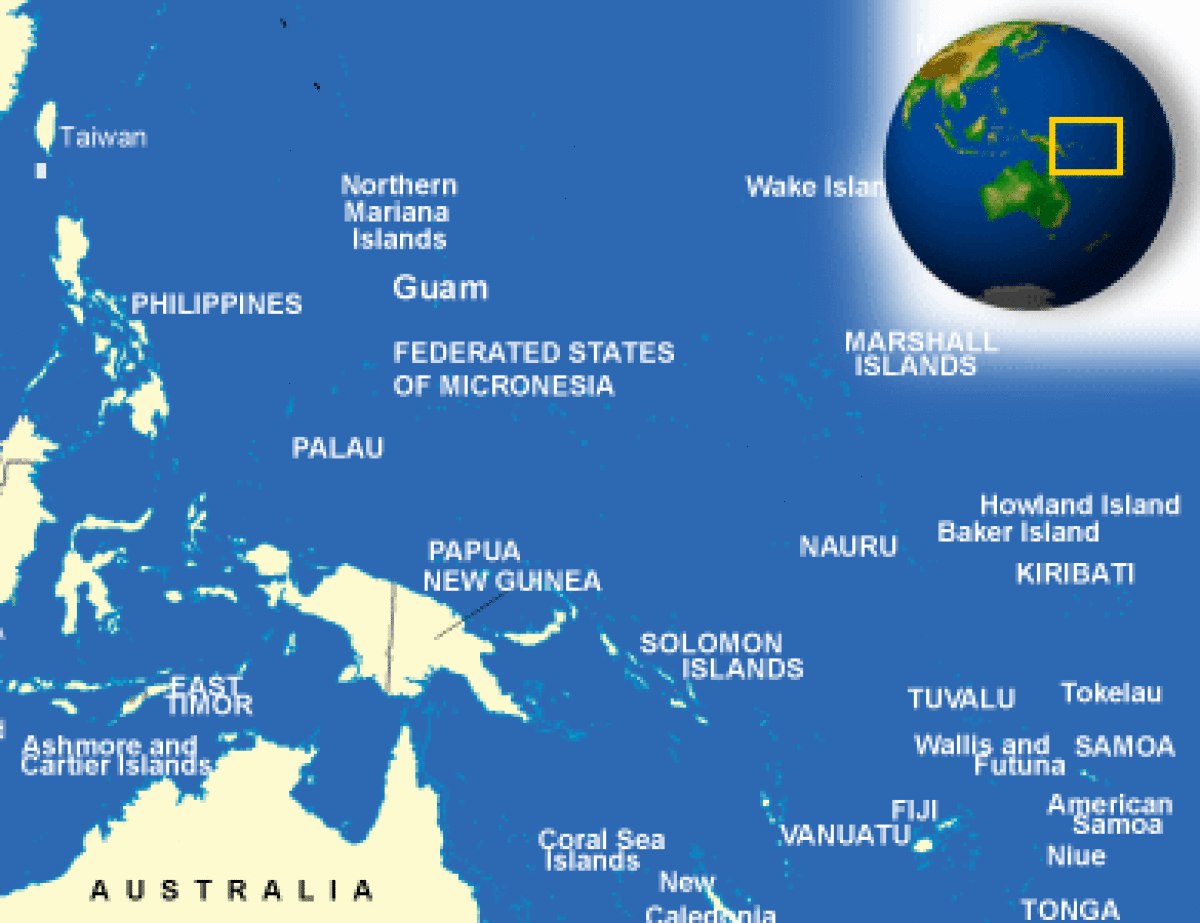
Where is Guam located?
What countries border Guam?
Guam Weather
What is the current weather in Guam?
Guam Facts and Culture
What is Guam famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Guam, a small island territory in the western Pacific Ocean, is home to a vibrant and unique culture that is... More
- Personal Apperance: The people of Guam have a unique style of dress that reflects the island's cultural heritage and climate. From traditional... More
- Recreation: Guam is an island paradise that offers a wide range of recreational activities for locals and tourists alike. From water... More
- Diet: The diet in Guam is influenced by its unique cultural history and location. Chamorro cuisine, which is the traditional cuisine... More
Guam Facts
What is the capital of Guam?
| Capital | Hagatna (Agana) |
| Government Type | Unincorporated organized territory of the US with local self-government; republican form of territorial government with separate executive, legislative, and judicial branches |
| Currency | US Dollar (USD) |
| Total Area |
210 Square Miles 544 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Oceania, island in the North Pacific Ocean, about three-quarters of the way from Hawaii to the Philippines |
| Language | English, Chamorro, Japanese |
| GDP - real growth rate | 0.6% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $30,500.00 (USD) |
Guam Demographics
What is the population of Guam?
| Ethnic Groups | Chamorro 37%, Filipino 26%, white 10%, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and other 27% |
| Nationality Noun | Guamanian(s) |
| Population | 168,485 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.34% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | HAGATNA (capital) 169,000 |
| Urban Population | 93.200000 |
Guam Government
What type of government does Guam have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Donald J. TRUMP (since 20 January 2025) head of government: Governor Lourdes LEON GUERRERO (since 7 January 2019) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the governor with the consent of the Legislature election/appointment process: president and vice president indirectly elected on the same ballot by an Electoral College of electors chosen from each state to serve a 4-year term (eligible for a second term); under the US Constitution, residents of unincorporated territories, such as Guam, do not vote in elections for US president and vice president, but they can vote in Democratic and Republican presidential primary elections; governor and lieutenant governor elected on the same ballot by absolute majority vote in 2 rounds, if needed, for a 4-year term (eligible for 2 consecutive terms) most recent election date: gubernatorial: 8 November 2022 election results: 2022: Lourdes LEON GUERRERO reelected governor; percent of vote - Lourdes LEON GUERRERO (Democratic Party) 55%, Felix CAMACHO (Republican Party) 44%; Josh TENORIO (Democratic Party) elected lieutenant governor 2018: Lourdes LEON GUERRERO elected governor; percent of vote - Lourdes LEON GUERRERO (Democratic Party) 50.7%, Ray TENORIO (Republican Party) 26.4%; Josh TENORIO (Democratic Party) elected lieutenant governor expected date of next election: gubernatorial: 3 November 2026 |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal; note - Guamanians are US citizens but do not vote in US presidential elections |
| Citizenship | See United States |
| National Holiday | Discovery Day (or Magellan Day), first Monday in March (1521) |
| Constitution |
History: Effective 1 July 1950 (Guam Act of 1950 serves as a constitution) Amendments: Amended many times, last in 2015 |
| Independence | None (territory of the US) |
Guam Video
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Guam Geography
What environmental issues does Guam have?
| Climate | Tropical marine; generally warm and humid, moderated by northeast trade winds; dry season from January to June, rainy season from July to December; little seasonal temperature variation |
| Environment - Current Issues | Extirpation of native bird population by the rapid proliferation of the brown tree snake, an exotic, invasive species |
| Terrain | Volcanic origin, surrounded by coral reefs; relatively flat coralline limestone plateau (source of most fresh water), with steep coastal cliffs and narrow coastal plains in north, low hills in center, mountains in south |
Guam Economy
How big is the Guam economy?
| Economic Overview | US national defense spending is the main driver of Guam’s economy, followed closely by tourism and other services. Guam serves as a forward US base for the Western Pacific and is home to thousands of American military personnel. Total federal spending (defense and non-defense) amounted to $1.988 billion in 2016, or 34.2 of Guam’s GDP. Of that total, federal grants and cover-over payments amounted to $3444.1 million in 2016, or 35.8% of Guam’s total revenues for the fiscal year. In 2016, Guam’s economy grew 0.3%. Despite slow growth, Guam’s economy has been stable over the last decade. National defense spending cushions the island’s economy against fluctuations in tourism. Service exports, mainly spending by foreign tourists in Guam, amounted to over $1 billion for the first time in 2016, or 17.8% of GDP. |
| Industries | US military, tourism, construction, transshipment services, concrete products, printing and publishing, food processing, textiles |
| Currency Name and Code | US Dollar (USD) |
| Export Partners | Japan 81.6%, South Korea 5.3%, Canada 2.6% |
| Import Partners | Singapore 39.2%, South Korea 21%, Japan 20.8%, Hong Kong 7.8% |
Guam News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Guam?
Source: Google News
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
