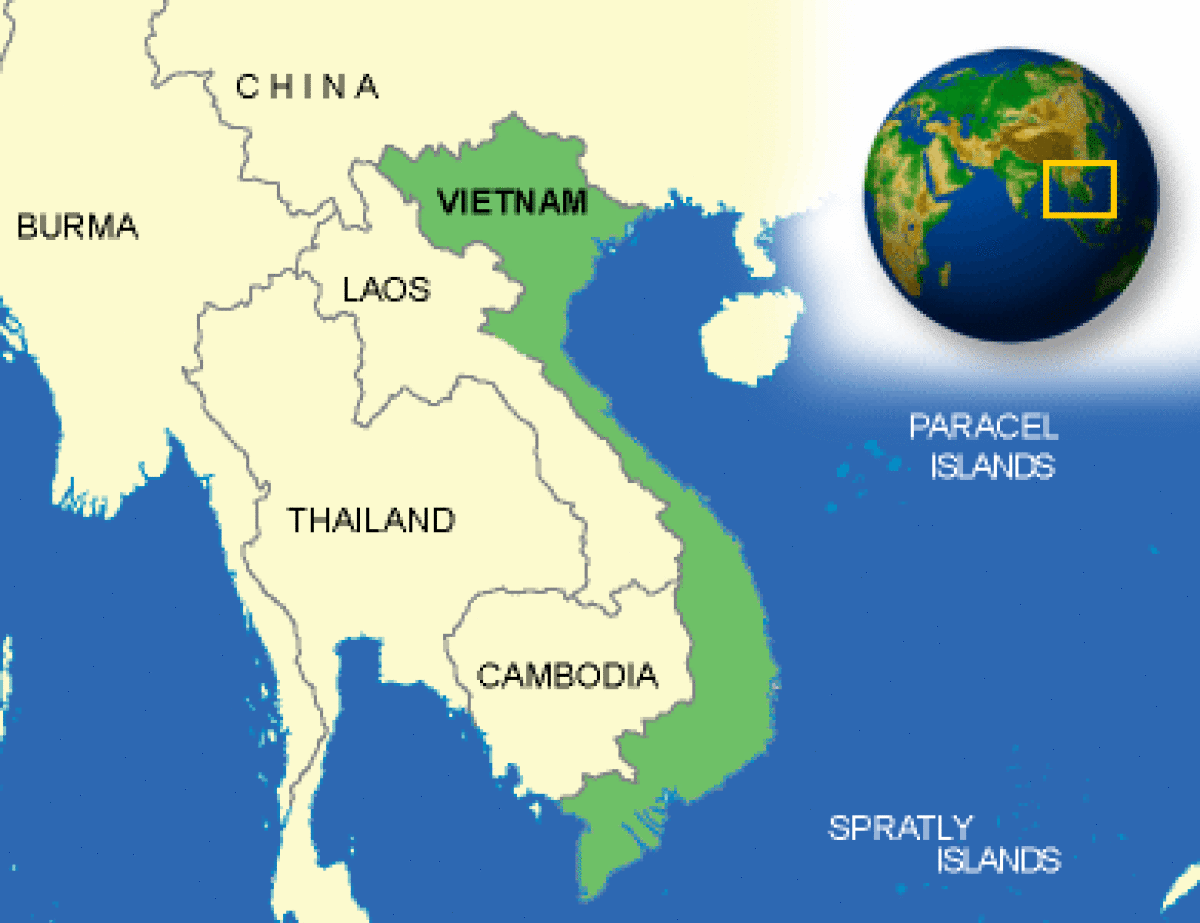
Where is Vietnam located?
What countries border Vietnam?
Vietnam Weather
What is the current weather in Vietnam?
Vietnam Facts and Culture
What is Vietnam famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: The Vietnamese people use the experience of it's history to re-create the future. There is inequality between urban and rural... More
- Family: Rank in the family denotes status, which carries responsibilities as well as rights. In an extended family (group) culture,... More
- Personal Apperance: Women sometimes wear the traditional "ao dai", which is a long dress with panels in the front and back worn... More
- Recreation: Men and women often relax after work by going to a café for companionship. Older men may play chess or... More
- Diet: Rice is the staple food of Vietnam. A fermented fish sauce called nuoc mam is the main seasoning used to... More
- Food and Recipes: The Vietnamese use rice bowls and chopsticks for the majority of meals. Eating from a rice bowl that is... More
- Visiting: In Vietnam, because the majority of people do not have telephones, people drop in on one another all the time.... More
- Dating: Socializing in public varies depending upon upbringing and the degree of Western influence. In rural Vietnam, young men and women... More
Vietnam Facts
What is the capital of Vietnam?
| Capital | Hanoi (Ha Noi) |
| Government Type | communist state |
| Currency | Vietnamese Dong (VND) |
| Total Area |
127,880 Square Miles 331,210 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southeastern Asia, bordering the Gulf of Thailand, Gulf of Tonkin, and South China Sea, as well as China, Laos, and Cambodia |
| Language | Vietnamese (official), English (as a second language), some French, Chinese, and Khmer; mountain area languages (Mon-Khmer and Malayo-Polynesian) |
| GDP - real growth rate | 6.5% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $6,100.00 (USD) |
Vietnam Demographics
What is the population of Vietnam?
| Ethnic Groups | Vietnamese 85%-90%, Chinese, Hmong, Thai, Khmer, Cham, mountain groups |
| Languages | Vietnamese is the official language. There are distinct northern, central, and southern dialects and accents. The most popular foreign languages taught in schools are English, Russian, and French. |
| Nationality Noun | Vietnamese (singular and plural) |
| Population | 98,721,275 |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.03% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | Ho Chi Minh City 6.405 million; HANOI (capital) 2.955 million; Haiphong 925,000; Da Nang 834,000 |
| Urban Population | 31.000000 |
Vietnam Government
What type of government does Vietnam have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Luong CUONG (since 21 Oct 2024) head of government: Prime Minister Pham Minh CHINH (since 26 July 2021) cabinet: Cabinet proposed by the prime minister, confirmed by the National Assembly, and appointed by the president election/appointment process: president indirectly elected by the National Assembly from among its members for a single 5-year term; prime minister recommended by the president and confirmed by the National Assembly; deputy prime ministers appointed by the president and confirmed by the National Assembly note: in August 2024, To LAM was elected general secretary of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam, the country’s most powerful position |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Vietnam dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day (National Day), 2 September (1945) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest adopted 28 November 2013, effective 1 January 2014 amendments: proposed by the president, by the National Assembly’s Standing Committee, or by at least two thirds of the National Assembly membership; a decision to draft an amendment requires approval by at least a two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly membership, followed by the formation of a constitutional drafting committee to write a draft and collect citizens’ opinions; passage requires at least two-thirds majority of the Assembly membership; the Assembly can opt to conduct a referendum |
| Independence | 2 September 1945 (from France) |
Vietnam Video
YouTube, ClubTravelie Hanoi, the City of Lakes
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Vietnam Geography
What environmental issues does Vietnam have?
| Overview |
Like a dragon floating in the sea, Vietnam winds its way some 1,030 miles up from the South China Sea to the Gulf of Tonkin, with its head caressing the border of China to the north and its back resting snuggly against her Southeast Asian neighbors, Laos and Cambodia, to the west. The total land area of Vietnam covers about 128,000 square miles. Vietnam’s main cities, for population and importance, are Hanoi, Haiphong, Hue, and Ho Chi Minh City (formerly Saigon). Vietnam’s northern terrain is mostly mountainous or hilly, with some highland areas covered by a thick green blanket of jungle (about half the total land area). The Red River Delta and coastal plains in the lowland part of the North are heavily populated and intensively cultivated (almost entirely by rice fields). Although much of this Delta Region is seasonally flooded, a complex network of dikes and levees helps to prevent serious flood damage. The southern part of Vietnam is dominated by the estuary of the Mekong River system and is low, flat, and frequently marshy. The rich soil in the Mekong Delta is the most fertile in the country. Areas immediately north and east of Ho Chi Minh City in the Mekong Delta are much more varied with low-lying tropical rain forest, upland forest, and the rugged Annamite Mountain chain. |
| Climate |
Vietnam is largely a tropical monsoon country. In the north, a hot rainy season prevails from May to September. The average temperature in Hanoi is about 86°F during this period, with very high humidity. During the cooler, dry season in the north from December to March, the average temperature is 68°F, with overnight minimums sometimes around 40°–42°F. In the south, Ho Chi Minh City and the Mekong Delta experience a year-round tropical climate with daily temperatures normally exceeding 88°F. The rainy season in Danang and Hue in the center of the country lasts from October to March. |
| Border Countries | Cambodia 1,228 km, China 1,281 km, Laos 2,130 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | logging and slash-and-burn agricultural practices contribute to deforestation and soil degradation; water pollution and overfishing threaten marine life populations; groundwater contamination limits potable water supply; growing urban industrialization and population migration are rapidly degrading environment in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | low, flat delta in south and north; central highlands; hilly, mountainous in far north and northwest |
Vietnam Economy
How big is the Vietnam economy?
| Economic Overview |
Vietnam is a densely populated developing country that has been transitioning since 1986 from the rigidities of a centrally planned, highly agrarian economy to a more industrial and market based economy, and it has raised incomes substantially. Vietnam exceeded its 2017 GDP growth target of 6.7% with growth of 6.8%, primarily due to unexpected increases in domestic demand, and strong manufacturing exports. Vietnam has a young population, stable political system, commitment to sustainable growth, relatively low inflation, stable currency, strong FDI inflows, and strong manufacturing sector. In addition, the country is committed to continuing its global economic integration. Vietnam joined the WTO in January 2007 and concluded several free trade agreements in 2015-16, including the EU-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (which the EU has not yet ratified), the Korean Free Trade Agreement, and the Eurasian Economic Union Free Trade Agreement. In 2017, Vietnam successfully chaired the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) Conference with its key priorities including inclusive growth, innovation, strengthening small and medium enterprises, food security, and climate change. Seeking to diversify its opportunities, Vietnam also signed the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for the Transpacific Partnership in 2018 and continued to pursue the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership. To continue its trajectory of strong economic growth, the government acknowledges the need to spark a ‘second wave’ of reforms, including reforming state-owned-enterprises, reducing red tape, increasing business sector transparency, reducing the level of non-performing loans in the banking sector, and increasing financial sector transparency. Vietnam’s public debt to GDP ratio is nearing the government mandated ceiling of 65%. In 2016, Vietnam cancelled its civilian nuclear energy development program, citing public concerns about safety and the high cost of the program; it faces growing pressure on energy infrastructure. Overall, the country’s infrastructure fails to meet the needs of an expanding middle class. Vietnam has demonstrated a commitment to sustainable growth over the last several years, but despite the recent speed-up in economic growth the government remains cautious about the risk of external shocks. |
| Industries | food processing, garments, shoes, machine-building, mining, cement, chemical fertilizer, glass, tires, oil, coal, steel, paper |
| Currency Name and Code | Vietnamese Dong (VND) |
| Export Partners | US 15%, Japan 14.6%, Australia 7.5%, China 6.4%, Germany 6.4%, Singapore 5.4%, UK 4.2% |
| Import Partners | Taiwan 12.6%, South Korea 12.3%, China 11.8%, Japan 11.7%, Singapore 11.4%, Thailand 5.2%, Hong Kong 4.2% |
Vietnam News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Vietnam?
Source: Google News
Vietnam Travel Information
What makes Vietnam a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Vietnam is a developing, mainly agrarian country that is moving from a centrally-planned economy to a market economy. Political control rests with the Communist Party. Tourist facilities can be basic in rural areas but are increasingly well established in Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City, and some beach and mountain resorts.
Crime
Pick-pocketing and other petty crimes occur regularly. Although violent crimes such as armed robbery are still relatively rare in Vietnam, perpetrators have grown increasingly bold, and both the U.S. Consulate General and the U.S. Embassy have recently received reports of pipes, knives and razors being used in attempted robberies in Ho Chi Minh City and Hanoi. Thieves congregate around hotels frequented by foreign tourists and business people and areas such as Hanoi’s Old Quarter and Ho Chi Minh City’s Ben Thanh Market, and assaults have been reported in outlying areas at night. Do not resist theft attempts and report them immediately to local police and to the U.S. Embassy in Hanoi or the U.S. Consulate General in Ho Chi Minh City.Motorcyclists are known to snatch bags, cameras, and other valuables from pedestrians or passengers riding in "cyclos" (pedicabs) or on the back of motorcycles. Serious injuries resulted when thieves snatched purses or bags that were strapped across the victim's body, resulting in the victim being dragged along the ground by the thief's motorcycle.
Passengers riding in cyclos (pedicabs) may be especially prone to theft of personal possessions by snatch-and-grab thieves, because they ride in a semi-reclining position that readily exposes their belongings and does not allow good visibility or movement. Some cyclo drivers have reportedly kidnapped passengers and extorted money; it may be risky to hire cyclos not associated with reputable hotels or restaurants.
The use of motorcycle taxis (known as “xe omsâ€) is strongly discouraged. Motorcycle taxis are unregulated and unsafe, and the helmets provided to riders offer little to no protection against injury in the case of an accident. In one instance, a U.S. citizen was sexually assaulted after hiring what was believed to be a legitimate motorcycle taxi near Ho Chi Minh City. Keep your passport and other important valuables in your hotel in a safe or another secured location at all times. You should carry at least two photocopies of your U.S. passport. Hotels are required to obtain a copy of your passport (please refer to "Special Circumstances" below), and you should carry a photocopy of your passport with you. You should immediately report the loss or theft of your U.S. passport to the local police and the U.S. Embassy or the U.S. Consulate General. You must obtain a police report from the local police office in order to apply for a replacement passport and a Vietnamese exit visa.
You should take precautions in choosing ground transportation when you arrive at the airport in Hanoi or Ho Chi Minh City. Some travelers reported being robbed by drivers who greeted them upon arrival with a placard showing the traveler's name. If you are expecting to be picked up, ask the company for the drivers name, phone number, and license plate number before you travel. You should use only airport taxis (currently Noi Bai taxi in Hanoi and Mai Linh or Vinasun in HCMC) or vehicles provided by hotels. Several times in the past year in Hanoi, taxi drivers detoured travelers en route from the airport to flophouses masquerading as hotels. You should be familiar with the basics of the hotel you have chosen, such as address and neighboring landmarks. This information can be found on the Internet. We have received complaints of taxi drivers overcharging fares by using rigged meters. In one case a driver locked the passenger in the cab to extort a higher fare. You should try to write down the name of the taxi company, plate number and any other identifying information in any incident so that it can be reported to the local authorities.
Some scams target tourists. Specifically, tourists have been victims of gambling scams in the Pham Ngu Lao neighborhood of Ho Chi Minh City. This scam usually starts with a friendly invitation to someone's home to meet a relative interested in visiting or studying in the U.S. While waiting for this individual, a casual game of cards will start. Victims have reported starting the game with only a small wager but losing thousands of dollars over the course of an evening. Be aware that gambling outside of licensed casinos is illegal in Vietnam.
The U.S. Embassy has also received occasional reports of incidents in which an unknown substance was used to taint drinks, leaving the victim unconscious or in a state similar to inebriation and unable to make appropriate decisions. To date, reports have included theft, but sexual assaults are also possible. Do not leave drinks or food unattended, and don't go to unfamiliar venues alone. You should also avoid purchasing liquor from street vendors, as the authenticity of the contents cannot be assured.
Recreational drugs available in Vietnam can be extremely potent. Three U.S. citizens died in 2010 from accidental overdoses of drugs. Drug suppliers will often misrepresent the substances they are selling, such as heroin for cocaine and vice versa. Penalties for possession or use of drugs of any kind are severe (please refer to the Criminal Penalties section below).
Some U.S. citizens have reported threats of death or physical injury related to personal business disputes. The U.S. Embassy and the U.S. Consulate General cannot provide personal protection services. If you do not have confidence in the ability of the local police to protect you, you may wish to depart the country as soon as possible.
Do not buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Vietnam, you are subject to the laws of Vietnam even if you are a U.S. citizen. The Vietnamese legal system and some Vietnamese laws can be vastly different from our own. While you are in Vietnam, U.S. laws do not apply. If you do something illegal in Vietnam, your U.S. passport will not help.In some places in Vietnam, you may be taken in for questioning if you do not have your passport with you. In some places, it is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings (see Special Circumstances below). Driving under the influence of alcohol in Vietnam can result in fines, confiscation of your driving permit, or imprisonment. There are also some actions that might be legal in Vietnam but still illegal in the United States. Be aware that you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods, engage in child pornography, or have sex with minors.
Notification and Access: A 1994 agreement between the United States and Vietnam provides that Vietnamese officials should notify the U.S. Embassy of the detainment of a U.S. citizen within 96 hours of the arrest and that they give U.S. officials access to those citizens within 48 hours after notification of the arrest. For purposes of notification and access, the U.S. government considers a U.S. citizen to be anyone — including a U.S. citizen of Vietnamese origin -- who enters Vietnam on a U.S. passport. Therefore, we encourage you to carry photocopies of your U.S. passport data and photo pages at all times so that, if questioned by Vietnamese officials, you have proof of your U.S. citizenship readily available.
Despite the 1994 agreement, Vietnamese officials do not always notify U.S. consular officers in Vietnam in a timely manner when they arrest or detain a U.S. citizen. There have also been very significant delays in U.S. consular officers obtaining access to some incarcerated U.S. citizens. This has been particularly true when the U.S. citizen is being held during the investigatory stage, which Vietnamese officials do not consider covered by the bilateral agreement. The investigatory stage can last up to one year, and often proceeds without the formal filing of any charges. U.S. citizens should note that the problem of access has been particularly evident when the Vietnamese government considers the U.S. citizen to be a citizen of Vietnam, irrespective of proof of U.S. citizenship. According to the 1994 agreement, U.S. citizens, even dual citizens, have the right to consular access if they were admitted into Vietnam as a U.S. citizen with their U.S. passport. If detained or arrested, U.S. citizens should insist upon contact with the U.S. Embassy or the U.S. Consulate General.
Based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements with certain countries, and customary international law, if you are arrested in Vietnam, you have the option to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate of your arrest, and to have communications from you forwarded to the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate.
Languages
Vietnamese is the official language. There are distinct northern, central, and southern dialects and accents. The most popular foreign languages taught in schools are English, Russian, and French.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities in Vietnam do not meet international standards and frequently lack medicines and supplies. Medical personnel in Vietnam, particularly outside Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City, may speak little or no English. Doctors and hospitals expect immediate cash payment for health services. International health clinics in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City can provide acceptable care for minor illnesses and injuries, but more serious problems will often require medical evacuation to Bangkok or Singapore. Although you can purchase many medications at pharmacies without having a prescription, some common U.S. medications are not available in Vietnam. You should bring adequate supplies of medications for the duration of your stay in Vietnam. You may obtain lists of local English-speaking physicians from the U.S. Embassy in Hanoi or the U. S. Consulate General in Ho Chi Minh City. Neither the Embassy nor the Consulate may recommend specific medical practitioners or hospitals. Emergency medical response services are generally unresponsive, unreliable, or completely unavailable.Be cautious about drinking non-bottled water and about using ice cubes in drinks. You may wish to drink only bottled or canned beverages or beverages that have been boiled (such as hot tea and coffee).
In July 2012, the Government of Vietnam reported outbreaks of rabies in the northern mountainous provinces of Son La, Lai Chau, Dien Bien, Lao Cai (Sapa) and Yen Bai. Rabies is a preventable viral disease of mammals most often transmitted through the bite of a rabid animal. The most important global source of rabies in humans is from uncontrolled rabies in dogs. In Vietnam, monkeys also pose a risk. Children are often at greatest risk from rabies. They are more likely to be bitten by rabid animals, and are also more likely to be severely exposed through multiple bites in high-risk sites on the body. Travelers in Vietnam should exercise caution around unfamiliar animals and seek immediate medical attention if bitten.
Avian influenza (H5N1) continues to be a concern in Vietnam. In Vietnam and other Southeast Asian countries affected by avian influenza, you should avoid poultry farms, contact with animals in live food markets, and any surfaces that appear to be contaminated with feces from poultry or other animals.
Safety and Security
The Government of Vietnam may not allow or authorize you to travel to certain areas of Vietnam deemed sensitive. These travel limitations may also hinder the ability of the U.S. Government to provide assistance to you in those areas. U.S. citizens have been detained after traveling in areas close to the Vietnamese borders with China, Cambodia, and Laos. These areas are not always marked, and there are no warnings about prohibited travel. You should avoid such areas unless you obtain written permission in advance from local authorities. You should check with travel agencies before going to border areas to see if you need to obtain a travel permit issued by local authorities.Tourists who visit Ha Long Bay, Quang Ninh and want to spend the night on a boat should take caution. A boat sinking accident in Feb 2011 resulted in the deaths of 12 people, including 2 U.S. citizens, and revealed weaknesses in the management of some boat companies. You should consider taking overnight tours only with large, reputable companies. Smaller companies operating poorly equipped and managed boats may offer cheap prices, but can lead to unsafe tours.
At any time, you should avoid large gatherings, such as those forming at the scene of traffic accidents, which can become violent with little or no warning.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Vietnam, you will encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Vietnam is provided for general reference only and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Traffic in Vietnam is chaotic. Traffic accidents occur frequently. The most common victims are motorbike riders and pedestrians. At least 30 people die each day from transportation-related injuries and many more are injured, often with traumatic head injuries. Traffic accident injuries are the leading cause of death, severe injury, and emergency evacuation of foreigners in Vietnam. Traffic accidents, including those involving a pedestrian and a motorized vehicle, are the single greatest health and safety risk you will face in Vietnam.
Traffic moves on the right, although drivers frequently cross to the left to pass or turn, and motorcycles and bicycles often travel (illegally) against the flow of traffic. Drivers honk their horns constantly, often for no apparent reason. Streets in major cities are choked with motorcycles, cars, buses, trucks, bicycles, pedestrians, and cyclos. Outside the cities, livestock compete with vehicles for road space. Sudden stops by motorcycles and bicycles make driving particularly hazardous. Nationwide, drivers do not follow basic traffic principles, vehicles do not yield right of way, and there is little adherence to traffic laws or enforcement by traffic police. The number of traffic lights in Hanoi and Ho Chi Minh City is increasing, but red lights are often not obeyed. Most Vietnamese ride motorcycles; often an entire family rides on one motorcycle. The urban speed limit ranges from 30 to 40 km/h (or 19-25 miles/h). The rural speed limit ranges from 40 to 60 km/h (or 25 - 37 miles/h). Both speed limits are routinely ignored.
If you are walking, you should be careful, as sidewalks are extremely uneven and congested, and drivers of bicycles, motorcycles and other vehicles routinely ignore traffic signals and traffic flows, and even drive on sidewalks. For safety, you should always look carefully in both directions before crossing streets, even when using a marked crosswalk with a green "walk" light illuminated.
Road conditions are poor nationwide. Numerous accidents occur due to poor road conditions. U.S. citizen travelers have lost their lives on the roads while traveling in northern provinces during the rainy season due to landslides. You should exercise extra caution in the countryside, as road conditions are particularly poor in rural areas.
Driving at night is especially dangerous, and you should exercise extreme caution. Roads are poorly lit, and there are few road signs. Buses and trucks often travel at high speed with bright lights that they rarely dim. Some motor vehicles don't use any lights, and vehicles of all types often stop in areas of the road that have no illumination. Livestock are often in the road.
A law mandating the use of motorcycle helmets on all roads went into effect on December 15, 2007, and is strictly enforced. We strongly urge you to wear a helmet when you ride a motorcycle or a bicycle. Vietnamese vehicles often are not equipped with working seatbelts; however, when a seatbelt is available, you should always use it, including in taxis. Child car seats are not available in Vietnam.
Penalties for driving under the influence of alcohol or causing an accident resulting in injury or death can include fines, confiscation of driving permits, and imprisonment. U.S. citizens involved in traffic accidents have been barred from leaving Vietnam until they have paid compensation (often determined arbitrarily) for property damage or injuries.
Emergency roadside help is theoretically available nationwide by dialing 113 for police, 114 for fire brigade, and 115 for an ambulance. The efficiency of these services is well below U.S. standards, and public telephones are generally not available. Trauma care is not widely available.
International driving permits and U.S. drivers' licenses are not valid in Vietnam. Foreigners renting vehicles risk prosecution and/or imprisonment for driving without a Vietnamese license endorsed for the appropriate vehicle. If you wish to drive in Vietnam, you should contact any office of the Provincial Public Transportation Service of the Vietnamese Department of Communications and Transport to obtain a Vietnamese driver's license. The U.S. Embassy in Hanoi and Consulate General in Ho Chi Minh City cannot assist you in obtaining Vietnamese driver's permits or notarize U.S. drivers' licenses for use in Vietnam.
Most Vietnamese travel within Vietnam by long-distance bus or train. Both are slow, and safety conditions fall below U.S. standards. Local buses and taxis are available in some areas, particularly in the larger cities. Safety standards vary widely depending on the individual company operating the service, but are generally much lower than what you would find in the United States.
