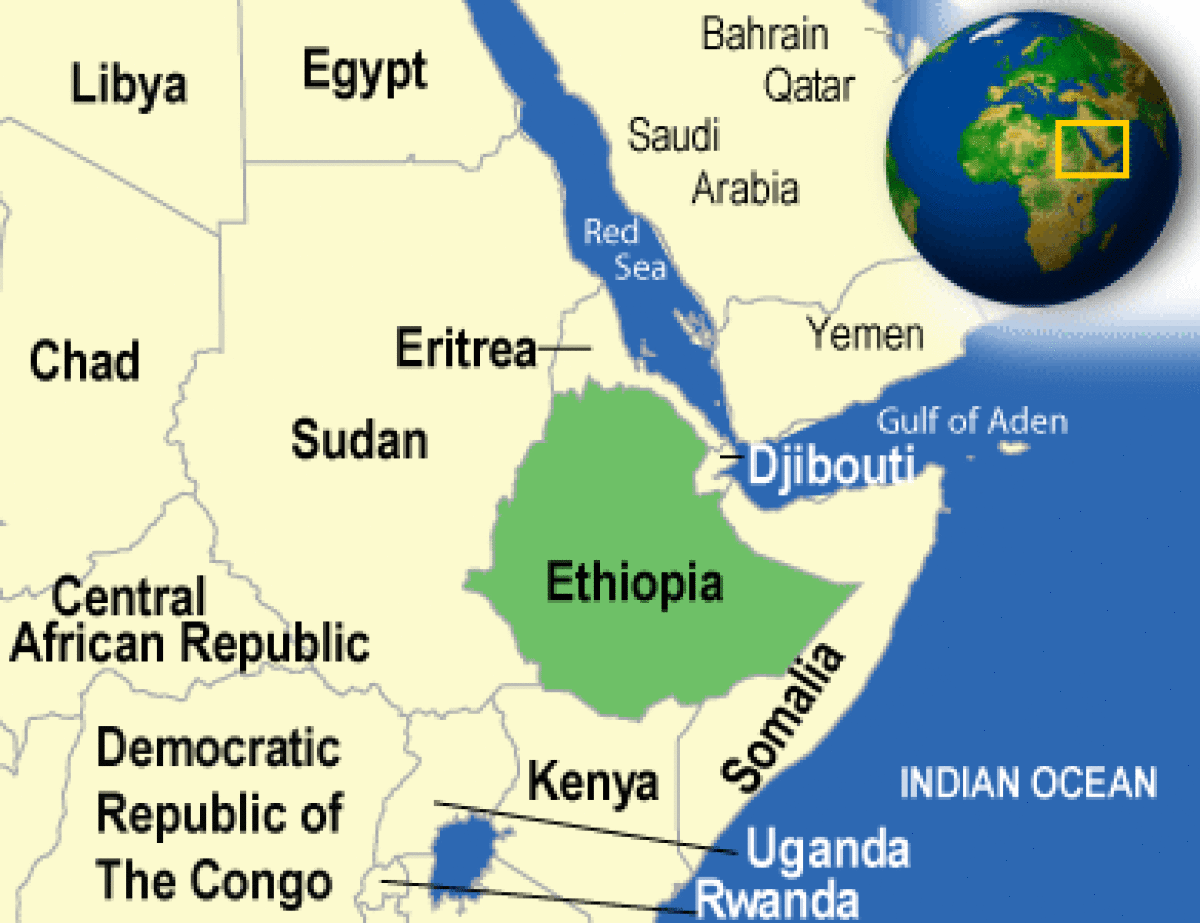
Where is Ethiopia located?
What countries border Ethiopia?
Ethiopia Weather
What is the current weather in Ethiopia?
Ethiopia Facts and Culture
What is Ethiopia famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: All people of Ethiopia, whether Christian or Muslim, tend to be somewhat complacent and passive, enduring adversity with stoicism unknown... More
- Family: The Amharic family is strongly patriarchal, a pattern typical throughout Ethiopia. Sons usually bring their brides to live with or... More
- Personal Apperance: In larger cities, most people wear Western-style clothing under the traditional white shamma (toga). Men in some ethnic groups wear... More
- Recreation: Ethiopians enjoy football (soccer) and it is the most popular sport. Long distance running is also popular. Traditional sports include... More
- Diet: The Ethiopian diet includes lamb, goat, and fowl. Ethiopians do not usually eat pork, turkey, or ham. Common foods include... More
- Food and Recipes: Amhara hosts take pride in offering guests the best meal they are capable of providing, whether at a public restaurant... More
- Visiting: The Amharic home is a highly private and personal domain. Visits are not made without invitation. If one is going... More
- Dating: Western-style dating is not common in Ethiopia as traditional norms are still strong in most areas. Because marriage represents the... More
Ethiopia Facts
What is the capital of Ethiopia?
| Capital | Addis Ababa |
| Government Type | Federal parliamentary republic |
| Currency | birr (ETB) |
| Total Area |
426,370 Square Miles 1,104,300 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Eastern Africa, west of Somalia |
| Language | Amharic, Tigrinya, Oromigna, Guaragigna, Somali, Arabic, other local languages, English |
| GDP - real growth rate | 6.5% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $1,900.00 (USD) |
Ethiopia Demographics
What is the population of Ethiopia?
| Ethnic Groups | Oromo 40%, Amhara and Tigre 32%, Sidamo 9%, Shankella 6%, Somali 6%, Afar 4%, Gurage 2%, other 1% |
| Languages |
Amharic, a Semitic language related to Hebrew and Arabic is the official national language and is used in commerce and administration. Tigrinya is the most widely spoken daily language and Orominga is also used. The liturgical language (Geéz) of the Ethiopian Orthodox church has produced a large and vibrant literature of considerable importance. English is taught in most schools, making it the most widely understood foreign language. The Amharic alphabet has thirty-three(33) root letters or constants with seven(7) phonetics (vowels) or 231 symbols or letters. Additionally there are 40 characters that are use as combinations or shortenings of the 231 characters. |
| Nationality Noun | Ethiopian(s) |
| Population | 108,113,150 |
| Population - note | Note: Estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.9% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | ADDIS ABABA (capital) 2.979 million |
| Urban Population | 17.000000 |
Ethiopia Government
What type of government does Ethiopia have?
| Executive Branch |
Chief of State: President SAHLE-WORK Zewde (since 25 October 2018) Head of Government: Prime Minister ABIY Ahmed Ali (since April 2018); Deputy Prime Minister and Minister of Foreign Affairs DEMEKE Mekonnen Hassen (since 29 November 2012) Cabinet: Council of Ministers selected by the prime minister and approved by the House of People's Representatives Elections/Appointments: President indirectly elected by both chambers of Parliament for a 6-year term (eligible for a second term); election held on 21 June 2021 and 30 September 2021 (the scheduled 29 August 2020 election was postponed by Prime Minister ABIY due to the COVID-19 pandemic); prime minister designated by the majority party following legislative elections Election results: 2021: SAHLE-WORK Zewde reelected president during joint session of Parliament, vote - 659 (unanimous); ABIY confirmed Prime Minister by House of Peoples' Representatives (4 October 2021) 2018: SAHLE-WORK Zewde elected president during joint session of Parliament, vote - 659 (unanimous); note - snap election held on 25 October 2018 due to resignation of President MULATA Teshome Note: SAHLE-WORK Zewde is the first female elected head of state in Ethiopia; she is currently the only female president in Africa. |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
Citizenship by birth: No Citizenship by descent only: At least one parent must be a citizen of Ethiopia Dual citizenship recognized: No Residency requirement for naturalization: 4 years |
| National Holiday | Derg Downfall Day (defeat of MENGISTU regime), 28 May (1991) |
| Constitution |
History: Several previous; latest drafted June 1994, adopted 8 December 1994, entered into force 21 August 1995 Amendments: Proposals submitted for discussion require two-thirds majority approval in either house of Parliament or majority approval of one-third of the State Councils; passage of amendments other than constitutional articles on fundamental rights and freedoms and the initiation and amendment of the constitution requires two-thirds majority vote in a joint session of Parliament and majority vote by two thirds of the State Councils; passage of amendments affecting rights and freedoms and amendment procedures requires two-thirds majority vote in each house of Parliament and majority vote by all the State Councils |
| Independence | Oldest independent country in Africa and one of the oldest in the world - at least 2,000 years (may be traced to the Aksumite Kingdom, which coalesced in the first century B.C.) |
Ethiopia Video
YouTube: TrekkingThePlanetNet Trekking in the Simien Mountains, Ethiopia
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Ethiopia Geography
What environmental issues does Ethiopia have?
| Overview |
Ethiopia, part of the Horn of Africa, borders Eritrea, Sudan, Kenya, Somalia, and Djibouti. It has an area of 1,127,127 square kilometers, slightly less than twice the size of Texas. Only 12% of the total land area is arable, with about 85% of the people dependent on agriculture or animal husbandry for subsistence. The terrain consists of high plateaus, mountains, and dry lowland plains. Ethiopia has some of the world’s most rugged and beautiful scenery. Changes in vegetation and terrain offer striking differences and are readily apparent when traveling in any direction from Addis Ababa. Fertile farmland, high mountains with crater lakes, deep canyons and abysses, low-lying savannas, and deserts are some of the many aspects of Ethiopia’s topography. |
| Climate |
The climate varies from temperate in the highlands to hot in the lowlands. Addis Ababa's altitude is above 8,000 feet. Addis Ababa has two primary seasons: a dry season from October to February, and for the rest of the year, a rainy season, divided into "small rains" and "big rains." The small rains, February through April, are generally intermittent showers. The big rains, June through September or longer, usually bring heavy daily precipitation. The big rains are rarely continuous, and sunny mornings or afternoons can be expected on many days. Average annual rainfall in Addis Ababa is 50 inches. Daytime temperatures are fairly constant throughout the year. The dry season has bright, sunny days with moderate to cool temperatures; nights are chilly. The average daily temperature in Addis Ababa is 62.9°F. Daytime temperatures are rarely above 80°F. Sharp drops in temperature occur in late afternoon, sometimes making outside entertainment uncomfortable after 5 p.m. Night temperatures drop to the low 40’s from November to January and are warmer in the period from February to May. |
| Border Countries | Djibouti 349 km, Eritrea 912 km, Kenya 861 km, Somalia 1,600 km, Sudan 1,606 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; desertification; water shortages in some areas from water-intensive farming and poor management |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection Signed, but not ratified: Environmental Modification, Law of the Sea |
| Terrain | High plateau with central mountain range divided by Great Rift Valley |
Ethiopia Economy
How big is the Ethiopia economy?
| Economic Overview |
Ethiopia - the second most populous country in Africa - is a one-party state with a planned economy. For more than a decade before 2016, GDP grew at a rate between 8% and 11% annually – one of the fastest growing states among the 188 IMF member countries. This growth was driven by government investment in infrastructure, as well as sustained progress in the agricultural and service sectors. More than 70% of Ethiopia’s population is still employed in the agricultural sector, but services have surpassed agriculture as the principal source of GDP. Ethiopia has the lowest level of income-inequality in Africa and one of the lowest in the world, with a Gini coefficient comparable to that of the Scandinavian countries. Yet despite progress toward eliminating extreme poverty, Ethiopia remains one of the poorest countries in the world, due both to rapid population growth and a low starting base. Changes in rainfall associated with world-wide weather patterns resulted in the worst drought in 30 years in 2015-16, creating food insecurity for millions of Ethiopians. The state is heavily engaged in the economy. Ongoing infrastructure projects include power production and distribution, roads, rails, airports and industrial parks. Key sectors are state-owned, including telecommunications, banking and insurance, and power distribution. Under Ethiopia's constitution, the state owns all land and provides long-term leases to tenants. Title rights in urban areas, particularly Addis Ababa, are poorly regulated, and subject to corruption. Ethiopia’s foreign exchange earnings are led by the services sector - primarily the state-run Ethiopian Airlines - followed by exports of several commodities. While coffee remains the largest foreign exchange earner, Ethiopia is diversifying exports, and commodities such as gold, sesame, khat, livestock and horticulture products are becoming increasingly important. Manufacturing represented less than 8% of total exports in 2016, but manufacturing exports should increase in future years due to a growing international presence. The banking, insurance, telecommunications, and micro-credit industries are restricted to domestic investors, but Ethiopia has attracted roughly $8.5 billion in foreign direct investment (FDI), mostly from China, Turkey, India and the EU; US FDI is $567 million. Investment has been primarily in infrastructure, construction, agriculture/horticulture, agricultural processing, textiles, leather and leather products. To support industrialization in sectors where Ethiopia has a comparative advantage, such as textiles and garments, leather goods, and processed agricultural products, Ethiopia plans to increase installed power generation capacity by 8,320 MW, up from a capacity of 2,000 MW, by building three more major dams and expanding to other sources of renewable energy. In 2017, the government devalued the birr by 15% to increase exports and alleviate a chronic foreign currency shortage in the country. |
| Industries | Food processing, beverages, textiles, leather, garments, chemicals, metals processing, cement |
| Currency Name and Code | birr (ETB) |
| Export Partners | Switzerland 14.3%, China 11.7%, US 9.5%, Netherlands 8.8%, Saudi Arabia 5.9%, Germany 5.7% |
| Import Partners | China 20.4%, US 9.2%, Saudi Arabia 6.5%, India 4.5% |
Ethiopia News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Ethiopia?
Source: Google News
Ethiopia Travel Information
What makes Ethiopia a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
The Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia is a developing country in East Africa. It is comprised of nine states and two city administrations (Addis Ababa and Dire Dawa). The capital is Addis Ababa. Tourism facilities can be found in the most populous regions of Ethiopia, but infrastructure is basic. The government is led by the Ethiopian People's Revolutionary Democratic Front (EPRDF) and Prime Minister Hailemariam Desalegn. Despite several years of high economic growth, the country remains vulnerable to external economic shocks.
Crime
U.S. citizens are strongly advised to review their personal safety and security posture, to remain vigilant and to be cautious when frequenting prominent public places and landmarks. Varying your travel times and routes is advised. Pick-pocketing, “snatch and run” thefts, including from occupied vehicles and other petty crimes are common in Addis Ababa. These are generally crimes of opportunity rather than planned attacks. Beginning in 2011, purse snatchings and harassment by gangs of youths in the Bole area of Addis Ababa have increased. These incidents have occurred in both the daytime and nighttime. There were also beatings and stabbings of expats in the area. The number of residential burglaries has also increased. Travelers should exercise caution in crowded areas, and especially in the Mercato in Addis Ababa, a large open-air market. You should limit the amount of cash you carry and leave valuables, such as passports, jewelry, and airline tickets in a hotel safe or other secure place. You should keep wallets and other valuables where they will be less susceptible to pick-pockets. If you have a cellular phone, carry it with you.You should be cautious at all times when traveling on roads in Ethiopia. Highway robbery by armed bandits in some border areas has been reported. Some of these incidents have been accompanied by violence. You are cautioned to limit road travel outside major towns or cities to daylight hours and travel in convoys, if possible, in case of breakdowns. When driving, be wary of other motorists warning you of a mechanical problem or loose tire. This may be a ruse used by thieves to get you to stop the vehicle. Most of all be alert and aware of your surroundings at all times to ensure that you aren't being followed.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in another country, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. Criminal penalties vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in your host country, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not where you are going.Ethiopian law strictly prohibits the photographing of military installations, police/military personnel, industrial facilities, government buildings, and infrastructure (roads, bridges, dams, airfields, etc.). Such sites are rarely marked clearly. Travel guides, police, and Ethiopian officials can advise if a particular site may be photographed. Photographing prohibited sites may result in the confiscation of film and camera and arrest.
Persons violating Ethiopian laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Ethiopia are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines.
If you are arrested in Ethiopia, you have the right to request that authorities alert the U.S. Embassy of your detention or arrest in accordance with the 1951 Treaty of Amity and Economic Relations between the United States and Ethiopia. If you are detained or arrested in Ethiopia you should use whatever means of communication available to alert the U.S. Embassy of your situation. Please be aware that the Government of Ethiopia does not recognize dual nationality, so U.S. citizens born in Ethiopia are accorded the same rights as any other U.S. citizens in the case of arrest or detention.
Languages
Amharic, a Semitic language related to Hebrew and Arabic is the official national language and is used in commerce and administration. Tigrinya is the most widely spoken daily language and Orominga is also used. The liturgical language (Geéz) of the Ethiopian Orthodox church has produced a large and vibrant literature of considerable importance. English is taught in most schools, making it the most widely understood foreign language.The Amharic alphabet has thirty-three(33) root letters or constants with seven(7) phonetics (vowels) or 231 symbols or letters. Additionally there are 40 characters that are use as combinations or shortenings of the 231 characters.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Health facilities in Ethiopia are very limited and are generally inadequate outside the capital. Even the best hospitals in Addis Ababa suffer from inadequate facilities, antiquated equipment, and shortages of supplies (particularly medicines). There is a shortage of physicians. Emergency assistance is limited. Psychiatric services and medications are practically nonexistent. Serious illnesses and injuries often require travelers to be medically evacuated from Ethiopia to a location where adequate medical attention is available. Such “medevac” services are very expensive and are generally available only to travelers who either have travel insurance that covers medevac services or who are able to pay for the service in advance (often in excess of USD 40,000). See Medical Insurance information below. Travelers must carry their own supplies of prescription drugs and preventive medicines, as well as a doctor's note describing the medication. If the quantity of drugs exceeds that which would be expected for personal use, a permit from the Ministry of Health is required.Malaria is prevalent in Ethiopia outside of the highland areas. Travelers who become ill with a fever or flu-like illness while traveling in a malaria-risk area and up to one year after returning home should seek prompt medical attention and explain to the health care provider their travel history and which anti-malarials they have been taking. For additional information on malaria, protection from insect bites, and anti-malarial drugs, please visit the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention malaria website.
Ethiopia is a mountainous country and the high altitude may cause health problems, even for healthy travelers. Addis Ababa is the third highest capital city in the world, at an altitude of 8,300 feet. Travelers may experience shortness of breath, fatigue, nausea, headaches and an inability to sleep. Individuals with respiratory (including asthma) or heart conditions should consult with a health care professional before traveling to Ethiopia. Travelers to Ethiopia should also avoid swimming in any lakes, rivers, or still bodies of water (other than Lake Langano). Most bodies of water have been found to contain parasites. Travelers should be aware that Ethiopia has a high prevalence of HIV/AIDS.
Ethiopia has had outbreaks of acute watery diarrhea, possible cholera, typhoid, and other bacterial diarrhea in the recent past, and the conditions for reoccurrences continue to exist in both urban and rural settings. Further information on prevention and treatment of cholera and other diarrheal diseases can be found at the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Foodborne, Bacterial and Mycotic Diseases webpage.
Safety and Security
U.S. citizens are strongly advised to review their personal safety and security posture, to remain vigilant, and to be cautious when frequenting prominent public places and landmarks. While Ethiopia is generally stable, domestic insurgent groups, extremists from Somalia, and the heavy military presence along the border with Eritrea pose risks to safety and security.A number of al-Qaida operatives and other extremists are believed to be operating in and around Africa. Since the July 11, 2010, terrorist bombings in Kampala, Uganda, for which the Somalia-based, U.S. government-designated Foreign Terrorist Organization al-Shabaab has claimed responsibility, there have been increased threats against public areas across East Africa. Current information suggests that al-Qaida and affiliated organizations continue to plan terrorist attacks against US interests in multiple regions, including Africa. In February 2012, leaders of al-Shabaab and al-Qaida announced a merger of the two groups.
U.S. citizens should strongly consider the risk of attending or being near large public gatherings, or venues where westerners gather on a routine or predictable basis, and which have no visible security presence. Such gatherings or venues can provide vulnerable targets for extremist or terrorist groups. U.S. citizens should avoid, if possible, using public transportation, including mini-buses, and should vary their travel times and routes to the extent possible. You are advised to avoid unattended baggage or packages left in any location, including in taxis.
There are periodic attacks on civilians as well as security forces in the Somali region of Ethiopia. In 2011, Kenyan and Ethiopian forces initiated an offensive against al-Shabab in Somalia, together with the African Union Mission in Somalia (AMISOM) which has been in Mogadishu since 2007, resulting in an increase in the threat level in Ethiopia and neighboring countries.
In southern Ethiopia, along the Kenyan border, banditry and incidents involving ethnic conflicts are also common. You should exercise caution when traveling to any remote area of the country, including the borders with Eritrea, Somalia, Kenya, Sudan, and South Sudan, and avoid travel outside of the major towns in these border areas.
U.S. citizens are advised that, due to serious safety and security concerns, U.S. government personnel and their families are presently restricted from traveling to the following areas:
Ethiopia/Eritrea Border (Northern Ethiopia): Ethiopia and Eritrea signed a peace agreement in December 2000 that ended their border war. However, the border remains an active issue of contention between the governments of Ethiopia and Eritrea. The border area is a militarized zone where the possibility of armed conflict between Ethiopian and Eritrean forces continues. U.S. government personnel are restricted from travel north of the Shire (Inda Silassie)-Axum-Adigrat road in the Tigray region of Ethiopia. Personnel are further restricted from travel north of the road from Dessie through Semera to the Galafi border crossing with Djibouti, including the Danakil Depression and the Erta Ale volcano. In January 2012, a group of foreign tourists were attacked near the Erta Ale volcano in the Afar region near the Eritrean border, approximately 100 miles southeast of Adigrat in the Danakil Depression. The attack resulted in five deaths, three wounded, and four people kidnapped. The victims were European and Ethiopian citizens. The two Europeans who were kidnapped were subsequently released. On February 15, 2012, Ethiopia, which blamed Eritrea for the attack, retaliated by striking military camps in Eritrea where the attackers were allegedly trained. This episode illustrates the continuing volatility of the border area.
Somali Region (Eastern Ethiopia): Travel to Ethiopia's Somali regional state is restricted for U.S. government employees, although essential travel to the region is permitted on a case-by-case basis. Since the mid-1990's, members of the Ogaden National Liberation Front (ONLF) have conducted attacks on civilian targets in parts of the Somali regional state, particularly in the Ogaden zones. Expatriateshave been killed in these attacks. In 2010, the Government of Ethiopia initiated peace talks with the ONLF, which are ongoing. Despite these talks, there have been isolated incidents of violence continues. In May 2011, gunmen affiliated with the ONLF attacked a vehicle belonging to the United Nations World Food Program (WFP), killing the vehicle’s driver, wounding one other, and kidnapping two other WFP employees. The kidnapped employees were later released.
Gambella Region (Western Ethiopia): Sporadic inter-ethnic clashes are a concern throughout the Gambella region of western Ethiopia. While the security situation in the town of Gambella is generally calm, it remains unpredictable throughout the rest of the region. Intensified conflict between Sudan and the Republic of South Sudan has increased refugee flows into Western Ethiopia. Travel to the border areas in the Beneshangul (Asosa) region is restricted to major towns.
Important Note: The Government of Ethiopia rarely informs the Embassy of arrested or detained U.S. citizens, even those detained at the airport by immigration or customs authorities. In some instances, U.S. citizens have been detained for weeks or even months without Embassy notification. If you are arrested or detained in Ethiopia, you have the right to request that Ethiopian authorities alert the U.S. Embassy of your detention or arrest in accordance with the 1951 Treaty of Amity and Economic Relations between the United States and Ethiopia . If you are detained or arrested in Ethiopia you should use whatever means of communication available to alert the U.S. Embassy of your situation.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in a foreign country, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States.According to the World Health Organization (WHO), Ethiopia has the highest rate of traffic fatalities per vehicle in the world. Roads in Ethiopia are poorly maintained, inadequately marked, and poorly lighted. Road travel after dark outside Addis Ababa and other cities is dangerous and discouraged due to hazards posed by broken-down vehicles left in the road, pedestrians walking in the road, stray animals, and the possibility of armed robbery. Road lighting in cities is inadequate at best and nonexistent outside of cities. Excessive speed, unpredictable local driving habits, pedestrians and livestock in the roadway, and the lack of adherence to basic safety standards for vehicles are daily hazards on Ethiopian roads. Many vehicles are unlicensed and many drivers lack basic driver training or insurance. Emergency services are limited or nonexistent in many parts of the country. Drivers should always carry spare tires, fuel, and tools on long trips as there is no roadside assistance. USG personnel must limit road travel outside towns or cities to daylight hours and travel in convoys, if possible, in case of breakdowns. Public transport is unregulated and unsafe; if travelers do use public transport, they should use taxis, not minibuses or large buses and should ensure they are the only passengers in the vehicle.
While travel during daylight hours on both paved and unpaved roads is generally considered safe, land mines and other anti-personnel devices can be encountered on isolated dirt roads that were targeted during various conflicts, especially along the Eritrean border. Before undertaking any off-road travel, it is advisable to inquire of local authorities to ensure that the area has been cleared of mines.
It is unlawful to use a cell phone or other electronic communications device while driving in Ethiopia (even if it has a hands-free feature), and use of seat belts is required. Be sure to carry your valid Ethiopian driver’s license with you, as well as proof of comprehensive local insurance coverage, and your Ethiopian Identification card. While in a vehicle, keep your doors locked and the windows rolled up at all times. Keep bags, purses, and valuables out of sight — in the trunk, on the floor, or in the glove compartment. Do not carry unnecessary items in your bag; leave your credit cards, social security card, etc., at home. Do not open your doors or windows to give to beggars. Police can fine people for giving money to beggars.
If you are in a traffic accident, do not leave the scene unless you fear for your personal safety. Special units of the traffic police investigate traffic accidents. Normal investigative procedures require the police to conduct on on-scene investigation, after which all involved parties go to the Traffic Department for a vehicle inspection and to provide details about the accident for a final report. If possible, obtain the names and contact information of all persons involved in the accident and make a note of the extent of any injuries; make a note of any registration information (tag number) of other vehicle(s) involved; and obtain the other driver’s permit data, and give similar information or registration/permit data to the other driver and to the police upon request.
