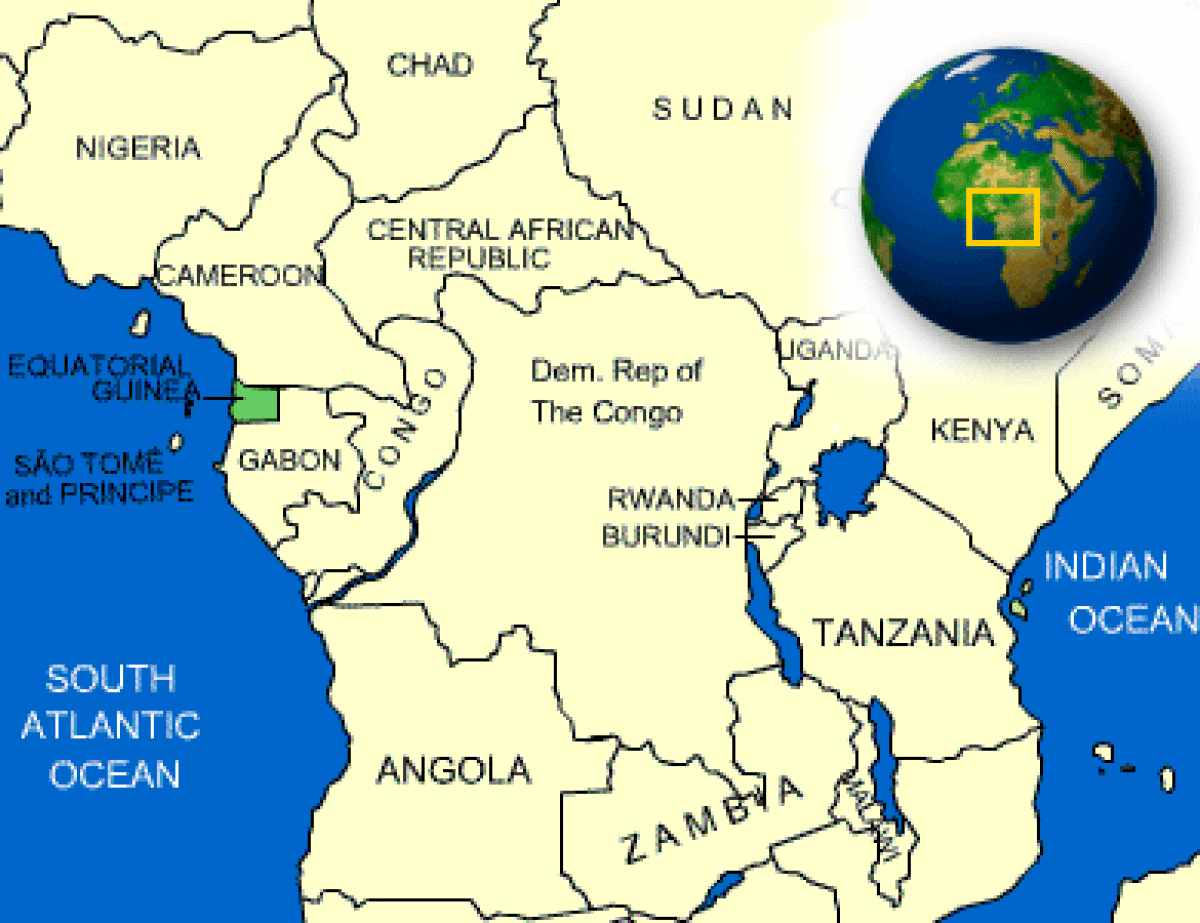
Where is Equatorial Guinea located?
What countries border Equatorial Guinea?
Equatorial Guinea Weather
What is the current weather in Equatorial Guinea?
Click for weather forecast
Equatorial Guinea Facts and Culture
What is Equatorial Guinea famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: People who live on Bioko Island, or the Bubi society divides people by function farmers, hunters, and fishers. More
- Family: The family and the clan are very important in Equatorial Guinea. Fang men may have more than one wife and... More
- Personal Apperance: Equatorial Guineans try to look good in public, In Urban areas Western style clothes are worn. Women and girls wear... More
-
Recreation: Soccer is a favorite pastime as well as table tennis that was learned from Chinese aid workers.
Equatorial Guineans enjoy socializing... More - Food and Recipes: Staple foods include cocoyams, plantains, rice and peanuts. People eat little meat. Many people only eat what they can... More
Equatorial Guinea Facts
What is the capital of Equatorial Guinea?
| Capital | Malabo; note - Malabo is on the island of Bioko; some months of the year, the government operates out of Bata on the mainland region. |
| Government Type | Presidential republic |
| Currency | Cooperation Financiere en Afrique Centrale francs (XAF) |
| Total Area |
10,830 Square Miles 28,051 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Central Africa, bordering the Bight of Biafra, between Cameroon and Gabon |
| Language | Spanish (official), French (official), pidgin English, Fang, Bubi, Ibo |
| GDP - real growth rate | -9.9% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $38,700.00 (USD) |
Equatorial Guinea Demographics
What is the population of Equatorial Guinea?
| Ethnic Groups | Bioko (primarily Bubi, some Fernandinos), Rio Muni (primarily Fang), Europeans less than 1,000, mostly Spanish |
| Nationality Noun | Equatorial Guinean(s) or Equatoguinean(s) |
| Population | 1,795,834 |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.58% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | MALABO (capital) 137,000 |
| Urban Population | 39.500000 |
Equatorial Guinea Government
What type of government does Equatorial Guinea have?
| Executive Branch |
Chief of state: President OBIANG Nguema Mbasogo (since 3 August 1979 when he seized power in a military coup); First Vice President Teodoro Nguema OBIANG Mangue (since 20 November 2022) Head of Government: Prime Minister Manuela ROKA Botey (since 1 February 2023); First Deputy Prime Minister Clemente Engonga NGUEMA Onguene (since 23 June 2016); Second Deputy Prime Minister Angel MESIE Mibuy (since 5 February 2018); Third Deputy Prime Minister Alfonso Nsue MOKUY (since 23 June 2016) Cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president and overseen by the prime minister Elections/Appointments: president directly elected by simple majority popular vote for a 7-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 20 November 2022 (next to be held in 2029); prime minister and deputy prime ministers appointed by the president Election results: 2022: OBIANG Nguema Mbasogo reelected president; percent of vote - OBIANG Nguema Mbasogo (PDGE) 95%, other 6.1% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
Citizenship by birth: No Citizenship by descent only: At least one parent must be a citizen of Equatorial Guinea Dual citizenship recognized: No Residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 12 October (1968) |
| Constitution |
History: Previous 1968, 1973, 1982; approved by referendum 17 November 1991 Amendments: Proposed by the president of the republic or supported by three-fourths of the membership in either house of the National Assembly; passage requires a three-fourths majority vote by both houses of the Assembly and approval in a referendum if requested by the president; amended several times, last in 2012 |
| Independence | 12 October 1968 (from Spain) |
Equatorial Guinea Video
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Equatorial Guinea Geography
What environmental issues does Equatorial Guinea have?
| Climate | Tropical; always hot, humid |
| Border Countries | Cameroon 189 km, Gabon 350 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Tap water is not potable; deforestation |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands Signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | Coastal plains rise to interior hills; islands are volcanic |
Equatorial Guinea Economy
How big is the Equatorial Guinea economy?
| Economic Overview |
Exploitation of oil and gas deposits, beginning in the 1990s, has driven economic growth in Equatorial Guinea; a recent rebasing of GDP resulted in an upward revision of the size of the economy by approximately 30%. Forestry and farming are minor components of GDP. Although preindependence Equatorial Guinea counted on cocoa production for hard currency earnings, the neglect of the rural economy since independence has diminished the potential for agriculture-led growth. Subsistence farming is the dominant form of livelihood. Declining revenue from hydrocarbon production, high levels of infrastructure expenditures, lack of economic diversification, and corruption have pushed the economy into decline in recent years and limited improvements in the general population’s living conditions. Equatorial Guinea’s real GDP growth has been weak in recent years, averaging -0.5% per year from 2010 to 2014, because of a declining hydrocarbon sector. Inflation remained very low in 2016, down from an average of 4% in 2014. As a middle income country, Equatorial Guinea is now ineligible for most low-income World Bank and the IMF funding. The government has been widely criticized for its lack of transparency and misuse of oil revenues and has attempted to address this issue by working toward compliance with the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative. US foreign assistance to Equatorial Guinea is limited in part because of US restrictions pursuant to the Trafficking Victims Protection Act. Equatorial Guinea hosted two economic diversification symposia in 2014 that focused on attracting investment in five sectors: agriculture and animal ranching, fishing, mining and petrochemicals, tourism, and financial services. Undeveloped mineral resources include gold, zinc, diamonds, columbite-tantalite, and other base metals. In 2017 Equatorial Guinea signed a preliminary agreement with Ghana to sell liquefied natural gas (LNG); as oil production wanes, the government believes LNG could provide a boost to revenues, but it will require large investments and long lead times to develop. |
| Industries | Petroleum, natural gas, sawmilling |
| Currency Name and Code | Cooperation Financiere en Afrique Centrale francs (XAF) |
| Export Partners | China 16.6%, South Korea 15.1%, Spain 9%, Brazil 8.2%, Netherlands 6.8%, South Africa 6.6%, India 5.8%, UK 5.7%, France 5.7% |
| Import Partners | Netherlands 16.9%, Spain 16.3%, China 14.8%, US 8.9%, Cote dIvoire 6%, France 4.8% |
Equatorial Guinea News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Equatorial Guinea?
Source: Google News
Equatorial Guinea Travel Information
What makes Equatorial Guinea a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Equatorial Guinea is an oil-rich, developing country on the western coast of central Africa. Its capital and main port, Malabo, is located on the island of Bioko, off the coast of Cameroon. A secondary port, Luba, is also on Bioko. The mainland territory of Equatorial Guinea is bordered by Cameroon and Gabon. The principal city on the mainland is Bata. Official languages are Spanish, which is widely spoken, and French, which is not widely understood, but sometimes used in business dealings.Equatorial Guinea is nominally a multiparty constitutional republic. In practice, however, all branches of government are dominated by President Teodoro Obiang Nguema Mbasogo, who has ruled since 1979. In November 2009, he was declared the winner of the presidential election with more than 95 percent of the vote.
Facilities for tourism are limited but growing. Cash machines are rare and often out of service. The cash machine located at Malabo’s airport and one at the SGBGE Bank in downtown Malabo are open to the public; other cash machines that do exist require membership in the local bank. There are no ATMs outside of Malabo and Bata. Equatorial Guinea is a beautiful country with many interesting sites and beautiful beaches, but there is little tourism information to assist in planning a vacation. There is no public transportation and renting a vehicle is difficult. Rental vehicle choices are limited and can be expensive. Taxis are readily available in the larger cities and are generally inexpensive. Unless you pay a significantly higher price, drivers will pick up additional people until the vehicle is full. Passengers are delivered to their destinations at the convenience of the driver, not the passenger.
Crime
Violent crime is rare and the overall level of criminal activity is low in comparison to other countries in the region. However, there has been a rise in non-violent street crime and residential burglaries. You should exercise prudence and normal caution, including avoiding dark alleys, remote locations, and traveling alone. Sexual assault is either rare or not reported (there are no crime statistics or studies) and there is no specific group of people specifically targeted. There is little evidence of racially motivated hate crimes and U.S. citizens are not specifically targeted. There is also limited evidence of scams or confidence schemes.In many countries around the world, counterfeit and pirated goods are widely available. You will find such products widely available on the streets, local shops, and in market places. Transactions involving such products may be illegal under local law. In addition, carrying them back to the United States may result in forfeitures and/or fines.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Equatorial Guinea, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In some places you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you. In some places, it is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings. In some places driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. Persons violating Equatoguinean laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested or imprisoned. Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Equatorial Guinea are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States.If you break local laws in Equatorial Guinea, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not where you are going.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities are very limited. Pharmacies in Malabo and Bata stock basic medicines including antibiotics, but cannot becounted on to supply advanced medications. Outside of these cities, many medicines are unavailable. You are advised to carry a supply of properly-labeled prescription drugs and other medications that you require for your entire stay; an adequate supply of prescription or over-the-counter drugs in local stores or pharmacies is generally not available. The sanitation levels in hospitals are very low, except for the new La Paz Hospitals in Bata and Malabo, which meet the medical standards of a modern hospital in a developed country. Doctors and hospitals often require immediate payment for health services, and patients are sometimes expected to supply their own bandages, linen, and toiletries.Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease. The national government, along with international oil companies in the country, has taken aggressive steps to control the mosquito population and limit the impact of malaria on the population centers in Malabo and Bata. Plasmodium falciparum malaria, the type that predominates in Equatorial Guinea, is resistant to the anti-malarial drug chloroquine. Travelers to the country are at high risk for contracting malaria; the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advise that you take one of the following anti-malarial drugs: mefloquine,doxycycline, or atovaquone/proguanil (Malarone™). If you become ill with a fever or flu-like illness while traveling in a malaria-risk area, and up to one year after returning home, you should seek prompt medical attention and tell your physician your travel history and what anti-malarials you have been taking. Visit the CDC's Travelers' Health page for additional information on malaria, including protective measures.
There are periodic outbreaks of cholera in Equatorial Guinea. Yellow fever can cause serious medical problems, but the vaccine, required for entry, is very effective in preventing the disease. Tuberculosis is an increasingly serious health concern in Equatorial Guinea. For further information, please consult the CDC's information on TB.
Many insect-borne illnesses are present. Insect precautions are encouraged at all times. Avoid non-chlorinated freshwater contact on the mainland to lessen the risk of Schistosomiasis.
Safety and Security
Although large public demonstrations are uncommon, you should avoid large crowds, political rallies, and street demonstrations.In February 2009, approximately 50 gunmen arriving by speedboats attacked government buildings in Malabo but were repelled by Equatoguinean military and police.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in a foreign country, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Equatorial Guinea is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Generally, Equatorial Guinea's road networks are increasingly well developed. Nevertheless, livestock and pedestrians still create road hazards. New road construction and repair is taking place all over the country, and road conditions have improved markedly over the course of the past year. If you plan on staying in Equatorial Guinea and driving around the country for any length of time, you should attempt to purchase a cell phone for assistance in case of an emergency.
Travelers outside the limits of Malabo and Bata will encounter military roadblocks. You should be prepared to show proper identification (for example, a U.S. passport) and to explain your reason for being at that particular location. The personnel staffing these checkpoints normally do not speak or understand English or French; travelers who do not speak Spanish should have their reason for being in the country and their itinerary written down in Spanish before venturing into the countryside. Please refer to our Road Safety page for more information.
There are currently no distracted driving laws in effect in the Equatorial Guinea, but police may pull over drivers who talk or text while driving for not following unspecific safe driving procedures.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
