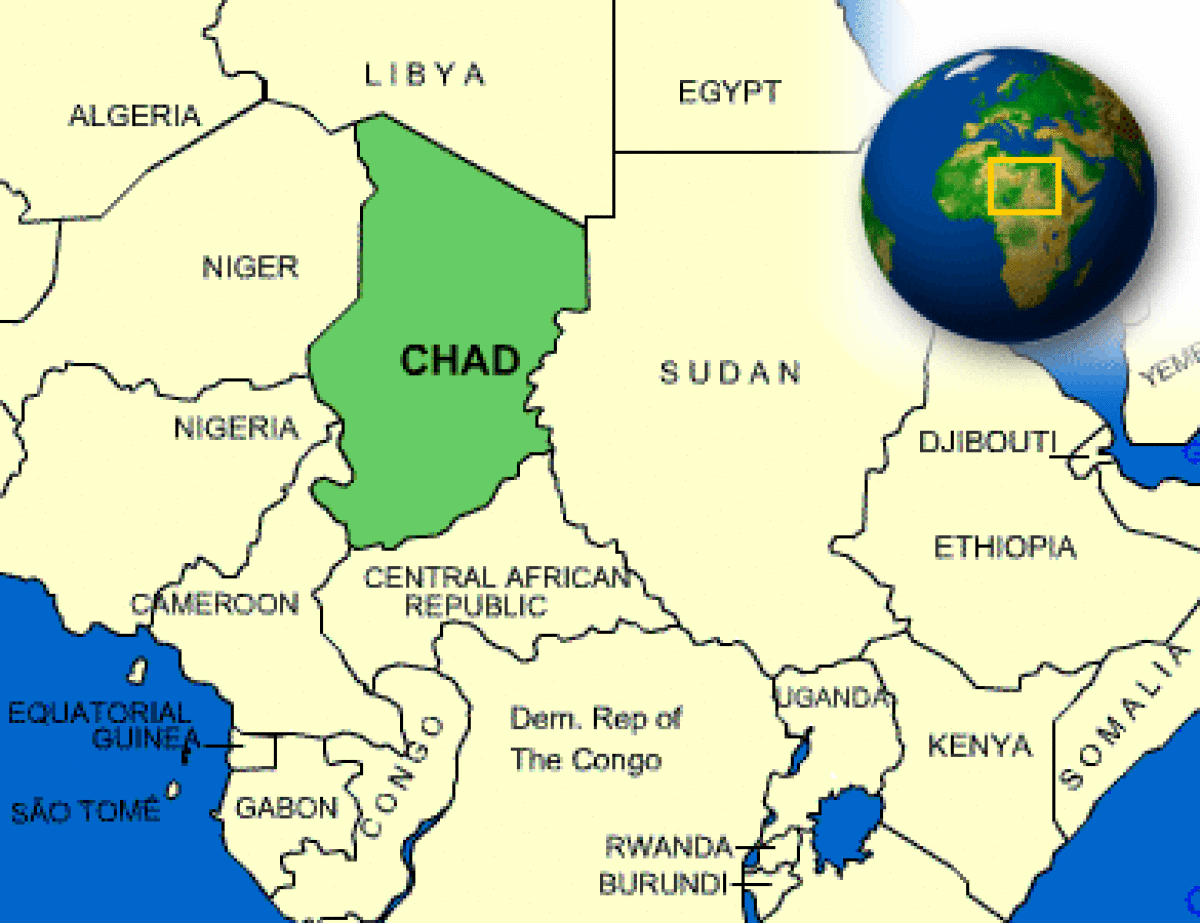
Where is Chad located?
What countries border Chad?
Chad Weather
What is the current weather in Chad?
Chad Facts and Culture
What is Chad famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Because Chad is a former French colony and many of its citizens speak French. The people of Chad include more... More
- Family: Gorane families are small, consisting of parents, children, and sometimes one or two other relatives. The clan is the most... More
- Personal Apperance: Chadians generally place great emphasis on clothing. Women often wear a loose top and a length of cloth (pagne) around... More
- Recreation: Soccer is the most popular sport in Chad. Basketball is widely played in the cities. Children in Chad often build... More
- Diet: Fish abound in Chad's lakes and rivers. The most common fish is the Nile perch, called capitaine in Chad. Other... More
- Food and Recipes: Chad has several geographical zones reflected in the diet like this: in the South, the diet is dominated by roots... More
Chad Facts
What is the capital of Chad?
| Capital | N'Djamena |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | Cooperation Financiere en Afrique Centrale francs (XAF) |
| Total Area |
495,752 Square Miles 1,284,000 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Central Africa, south of Libya |
| Language | French (official), Arabic (official), Sara (in the south), and more than 120 different languages and dialects |
| GDP - real growth rate | -1.1% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $2,600.00 (USD) |
Chad Demographics
What is the population of Chad?
| Ethnic Groups | Sara (Ngambaye/Sara/Madjingaye/Mbaye) 30.5%, Kanembu/Bornu/Buduma 9.8%, Arab 9.7%, Wadai/Maba/Masalit/Mimi 7%, Gorane 5.8%, Masa/Musseye/Musgum 4.9%, Bulala/Medogo/Kuka 3.7%, Marba/Lele/Mesme 3.5%, Mundang 2.7%, Bidiyo/Migaama/Kenga/Dangleat 2.5%, Dadjo/Kibet/Muro 2.4%, Tupuri/Kera 2%, Gabri/Kabalaye/Nanchere/Somrai 2%, Fulani/Fulbe/Bodore 1.8%, Karo/Zime/Peve 1.3%, Baguirmi/Barma 1.2%, Zaghawa/Bideyat/Kobe 1.1%, Tama/Assongori/Mararit 1.1%, Mesmedje/Massalat/Kadjakse 0.8%, other Chadian ethnicities 3.4%, Chadians of foreign ethnicities 0.9%, foreign nationals 0.3%, unspecified 1.7% |
| Languages | French (official), Arabic (official), Sara (in south), more than 120 different languages and dialects |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Chadian(s) adjective: Chadian |
| Population | 19,093,595 |
| Population Growth Rate | 3.01% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 1.592 million N'DJAMENA (capital) |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 24.4% of total population rate of urbanization: 4.1% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 9,464,699 female: 9,628,896 |
Chad Government
What type of government does Chad have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Mahamat Idriss DÉBY (since 6 May 2024) head of government: Prime Minister Allamaye HALINA (since 23 May 2024) cabinet: Council of Ministers election/appointment process: president directly elected by absolute-majority popular vote in 2 rounds, if needed, for a 5-year term (no term limits) most recent election date: 6 May 2024 election results: 2024: Mahamat Idriss DÉBY elected president; percent of vote - Mahamat Idriss DÉBY (MPS) 61%, Succes MASRA (Transformers) 18.5%, Albert PADACKE 16.9%, other 3.6% 2021: Lt. Gen. Idriss DÉBY reelected transitional president; percent of vote - Lt. Gen. Idriss DÉBY (MPS) 79.3%, Pahimi PADACKET Albert (RNDT) 10.3%, Lydie BEASSEMDA (Party for Democracy and Independence) 3.2%, other 7.2% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: both parents must be citizens of Chad dual citizenship recognized: Chadian law does not address dual citizenship residency requirement for naturalization: 15 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 11 August (1960) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest adopted by National Transitional Council 27 June 2023, approved by referendum 17 December, verified by Chad Supreme Court 28 December, promulgated 1 January 2024 amendments: previous process: proposed as a revision by the president of the republic after a Council of Ministers (cabinet) decision or by the National Assembly; approval for consideration of a revision requires at least three-fifths majority vote by the Assembly; passage requires approval by referendum or at least two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly |
| Independence | 11 August 1960 (from France) |
Chad Video
YouTube: City Travel Reviews Top 14 Things To Do In Chad
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Chad Geography
What environmental issues does Chad have?
| Overview |
Chad is a land-locked country in north-central Africa measuring 496,000 square miles (1,284,000 square km), roughly the size of Texas, Oklahoma and New Mexico combined. Most of its ethnically and linguistically diverse population of about 7.6 million to 8 million lives in the south, with densities ranging from 54 persons per square km. in the Logone River basin to 0.1 persons in the northern B.E.T. desert region which is larger than France. The capital city of N’Djamena, situated at the confluence of the Chari and Logone Rivers, is cosmopolitan in nature, with a current population in excess of 700,000 persons. Chad has four bioclimatic zones. The northernmost Saharan Zone averages less than 200 mm (8 inches) of rainfall annually. Its sparse human population is largely nomadic, with cattle, small ruminants, and camels. The central Sahelian Zone receives between 200mm and 600 mm (24 inches) of rainfall and has vegetation ranging from grass/shrub-steppe to thorny, open savannah. Livestock production is the most important economic activity there, but with significant agriculture that is high risk due to irregular rainfall. The Southern Zone, often referred to as the Sudanian Zone, receives between 600 mm and 1,000 mm (39 inches), with woodland savannah and deciduous forests for vegetation. A surplus of coarse grains, cassava, cotton, and fruits are produced here. Rainfall in the Guinea Zone, located in Chad’s southwestern tip, ranges between 1,000 mm and 1,200 mm (47 inches). The country’s topography is generally flat, with the elevation gradually rising as one moves north and east away from Lake Chad. The highest point in Chad is Emi Koussi, a mountain that rises 3,400 meters (11,200 feet) in the northern Tibesti Mountains. The Ennedi Plateau and the Ouaddaï highlands in the east complete the image of a gradually sloping basin, which descends toward Lake Chad. There are also central highlands in the Guera region rising to 1,500 meters (4,900 feet). Lake Chad is the second-largest lake in west Africa and is one of the most important wetlands on the continent. Home to 120 species of fish and at least that many species of birds, the lake has shrunk dramatically in the last 4 decades due to increased water use and low rainfall. Bordered by Chad, Niger, Nigeria, and Cameroon, Lake Chad currently covers only 1,350 square km. down from 25,000 square km. in 1963. The Chari and Logone Rivers, both of which originate in the Central African Republic and flow northward, provide most of the water entering Lake Chad. |
| Climate | The capital, N'Djamena, which is located in the Sahelian Zone, has a rainy season extending from June to October, characterized by sporadic, heavy rains and increased humidity with high temperatures in excess of 90°F. The remaining 8 months of the year are dry and generally hot, with a brief respite from November to February when daytime temperatures seldom exceed 90°F and lows at night descend to the 60s. Northeasterly winds off the desert, called the "harmattan," blow regularly during the dry season and envelop the town in a shroud of thick dust. April/May temperatures regularly exceed 110°F. |
| Border Countries | Cameroon 1,094 km, Central African Republic 1,197 km, Libya 1,055 km, Niger 1,175 km, Nigeria 87 km, Sudan 1,360 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Inadequate supplies of potable water; improper waste disposal in rural areas contributes to soil and water pollution; desertification |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party To: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping |
| Terrain | Broad, arid plains in the center, desert in the north, mountains in the northwest, lowlands in the south |
Chad Economy
How big is the Chad economy?
| Economic Overview |
Chad’s landlocked location results in high transportation costs for imported goods and dependence on neighboring countries. Oil and agriculture are the mainstays of Chad’s economy. Oil provides about 60% of export revenues, while cotton, cattle, livestock, and gum arabic provide the bulk of Chad's non-oil export earnings. The services sector contributes less than one-third of GDP and has attracted foreign investment mostly through telecommunications and banking. Nearly all of Chad’s fuel is provided by one domestic refinery, and unanticipated shutdowns occasionally result in shortages. The country regulates the price of domestic fuel, providing an incentive for black market sales. Although high oil prices and strong local harvests supported the economy in the past, low oil prices now stress Chad’s fiscal position and have resulted in significant government cutbacks. Chad relies on foreign assistance and foreign capital for most of its public and private sector investment. Investment in Chad is difficult due to its limited infrastructure, lack of trained workers, extensive government bureaucracy, and corruption. Chad obtained a three-year extended credit facility from the IMF in 2014 and was granted debt relief under the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries Initiative in April 2015. In 2018, economic policy will be driven by efforts that started in 2016 to reverse the recession and repair damage to public finances and exports. The government is implementing an emergency action plan to counterbalance the drop in oil revenue and diversify the economy. Chad’s national development plan (NDP) cost just over $9 billion with a financing gap of $6.7 billion. The NDP emphasized the importance of private sector participation in Chad’s development, as well as the need to improve the business environment, particularly in priority sectors such as mining and agriculture. The Government of Chad reached a deal with Glencore and four other banks on the restructuring of a $1.45 billion oil-backed loan in February 2018, after a long negotiation. The new terms include an extension of the maturity to 2030 from 2022, a two-year grace period on principal repayments, and a lower interest rate of the London Inter-bank Offer Rate (Libor) plus 2% - down from Libor plus 7.5%. The original Glencore loan was to be repaid with crude oil assets, however, Chad's oil sales were hit by the downturn in the price of oil. Chad had secured a $312 million credit from the IMF in June 2017, but the release of those funds hinged on restructuring the Glencore debt. Chad had already cut public spending to try to meet the terms of the IMF program, but that prompted strikes and protests in a country where nearly 40% of the population lives below the poverty line. Multinational partners, such as the African Development Bank, the EU, and the World Bank are likely to continue budget support in 2018, but Chad will remain at high debt risk, given its dependence on oil revenue and pressure to spend on subsidies and security. |
| Industries | Oil, cotton textiles, brewing, natron (sodium carbonate), soap, cigarettes, construction materials |
| Currency Name and Code | Cooperation Financiere en Afrique Centrale francs (XAF) |
| Export Partners | United States 58.5%, India 13.3%, Japan 11.3%, China 4.1% |
| Import Partners | France 16.5%, China 14.2%, Cameroon 11%, United States 6.4%, India 6%, Belgium 5.7%, Italy 4.8% |
Chad News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Chad?
Source: Google News
Chad Travel Information
What makes Chad a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Chad is a developing country in north-central Africa with one of the lowest per capita incomes in the world and has historically faced challenges in the areas of political stability and economic development. Years of war, drought, and regional instability have severely damaged the country's infrastructure and hampered the development of its institutions. Facilities for tourism are limited. The capital is N'Djamena. French and Arabic are the official languages.
Crime
U.S. citizens and many foreigners are perceived to be wealthy and should take precautions to avoid becoming crime victims. You should not leave cash or valuables unsecured in your hotel room, nor should you wear expensive jewelry or show large amounts of cash. You should dress modestly, walk outside only during daylight hours, and lock your car doors. Petty crimes such as purse snatching, pick-pocketing, and theft from vehicles do occur, particularly in areas frequented by expatriates. The potential for violent crime against expatriates remains a concern. Carjacking, burglary, and vehicle thefts increase during times of political instability. Historically, expatriate residences have been targeted for armed robbery, and some foreigners have been assaulted in the process, although there have been no recent incidents reported.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Chad, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In some places, you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you. In some places, it is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings. In some places driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States. You can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Chad, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not where you are going.Based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements with certain countries, and customary international law, if you are arrested in Chad, you have the option to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate of your arrest, and to have communications from you forwarded to the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate.
Languages
French (official), Arabic (official), Sara (in south), more than 120 different languages and dialects
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities in Chad are extremely limited. Medicines are in short supply or unavailable, including many over-the-counter preparations sold in the United States. Travelers should carry any needed, properly labeled, medicines with them. In the event of major injury or illness, visitors generally will require medical evacuation.There are two medical clinics in the capital of N’Djamena which offer "international standard" medical care: International SOS and Europ-Assistance. These are not walk-in clinics and advance membership is required to access services. This information is provided for informational purposes only and in no way constitutes an endorsement, expressed or implied, by the United States Department of State
Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease. Plasmodium falciparum malaria, the type that predominates in Chad, is resistant to the antimalarial drug chloroquine. Because travelers to Chad are at high risk for contracting malaria, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) advise that travelers should take one of the following antimalarial drugs: mefloquine (Lariam - TM), doxycycline, or atovaquone/proguanil (Malarone -TM). Travelers who become ill with a fever or flu-like illness while traveling in a malaria-risk area, and up to one year after returning home, should seek prompt medical attention and tell the physician their travel history and what antimalarials they have been taking. For additional information on malaria, including protective measures, visit the CDC Travelers’ Health website.
Other widespread illnesses in Chad include diarrhea and upper respiratory infections. HIV/AIDS is becoming an increasingly serious problem as infection rates are at alarming levels (up to 25 percent in high-risk groups). Meningitis outbreaks usually occur annually and several other diseases (cholera, diphtheria, chicken pox, typhoid) periodically appear.
Safety and Security
U.S. citizens planning to travel to Chad should read the current Worldwide Caution Travel Alert and the Travel Warning for Chad, which warns U.S. citizens of the risks of traveling to Chad. Due to the insecurity caused by high levels of violent crime, the potential risk of clashes between Chadian security forces and criminal or other armed groups, and the risk of a sudden, unanticipated outbreak of conflict among the populations living in these areas, we caution against all travel to eastern Chad, the Chad/Sudan border area, and the Chad/Central African Republic border area. The U.S. Embassy in Chad reviews each request for official government travel outside the capital and prohibits travel to eastern Chad and most border regions without express authorization. If you are affiliated with humanitarian relief efforts, you should review security precautions and consider measures to mitigate your exposure to violent crime. The Government of Chad requires travel authorization (autorisation de circuler) for anyone traveling to a humanitarian zone or refugee camp. If you are residing in Chad, you should exercise caution throughout the country.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in a foreign country, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Chad is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Roads are in poor condition and dangerous. In the capital city of N'Djamena, only the main roads are paved; although the government continues with its construction program, hard surface highways are still limited in number and distance in Chad; the rest of the roads are either hard-packed dirt or looser dirt and sand. During the rainy season (mid-June to mid-September) many roads become impassable or are restricted by rain barriers, while during the dryer season, clouds of dust rising from the roads reduce visibility.
Visitors should take great care while driving. Both paved and unpaved roads are poorly maintained, and often have large ruts and potholes. All drivers should adjust their speed accordingly. At night, streets are not lit and drivers frequently operate cars or motorcycles without lighting headlights; it is imperative to watch for pedestrians, bicyclists, motorcyclists, and livestock, as they may not be visible until they are in very close proximity.
Driving in Chad tends to be erratic both in cities and in rural areas. In cities, particularly N'Djamena, motorists share the roads with bicycles, motor scooters, pedestrians, and non-motorized wheelchairs. Lanes are not marked, and it is not uncommon for a normally two-lane thoroughfare to become a four-lane road during rush hours (generally 7:00 a.m. - 9:00 a.m. and 3:00 p.m. - 6:00 p.m. Monday - Thursday; 7:00 a.m. - 9:00 a.m. and 11:00 a.m. - 12:30 p.m. on Friday). Drivers are urged to be particularly observant at these times because motorists often attempt to overtake slower traffic by moving into oncoming lanes, usually at high speeds. There are only a few traffic lights in N'Djamena, they are often out of service, and drivers frequently do not obey those traffic lights that are in service. Drivers yield to traffic on their right, particularly when entering the many traffic circles.
In rural areas, drivers should watch for livestock crossing the roads, and for large hawks that rest on the roads. These birds can be fearless, and cause damage by smashing into drivers' windshields; drivers may avoid this by slowing down when approaching the hawks and allowing them sufficient time to fly away. Finally, drivers should be alert to older transport trucks traveling between cities, which do not always have functioning headlights.
No emergency services exist, so drivers should exercise extreme caution. Travelers should always wear seat belts. When traveling by car, be sure to carry a spare tire. Roadside service is limited to good Samaritans and children who will help push cars to the side or out of holes. When traveling outside the capital, it is imperative to carry sufficient quantities of drinking water. Drivers should ensure that their gas tanks are at least half-full at all times, as gas stations are not widely available. Gas may be purchased in an emergency in bottles from roadside stands, but it is generally of poor quality.
Travelers on roads in all areas of the country are subject to attack by armed bandits.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
