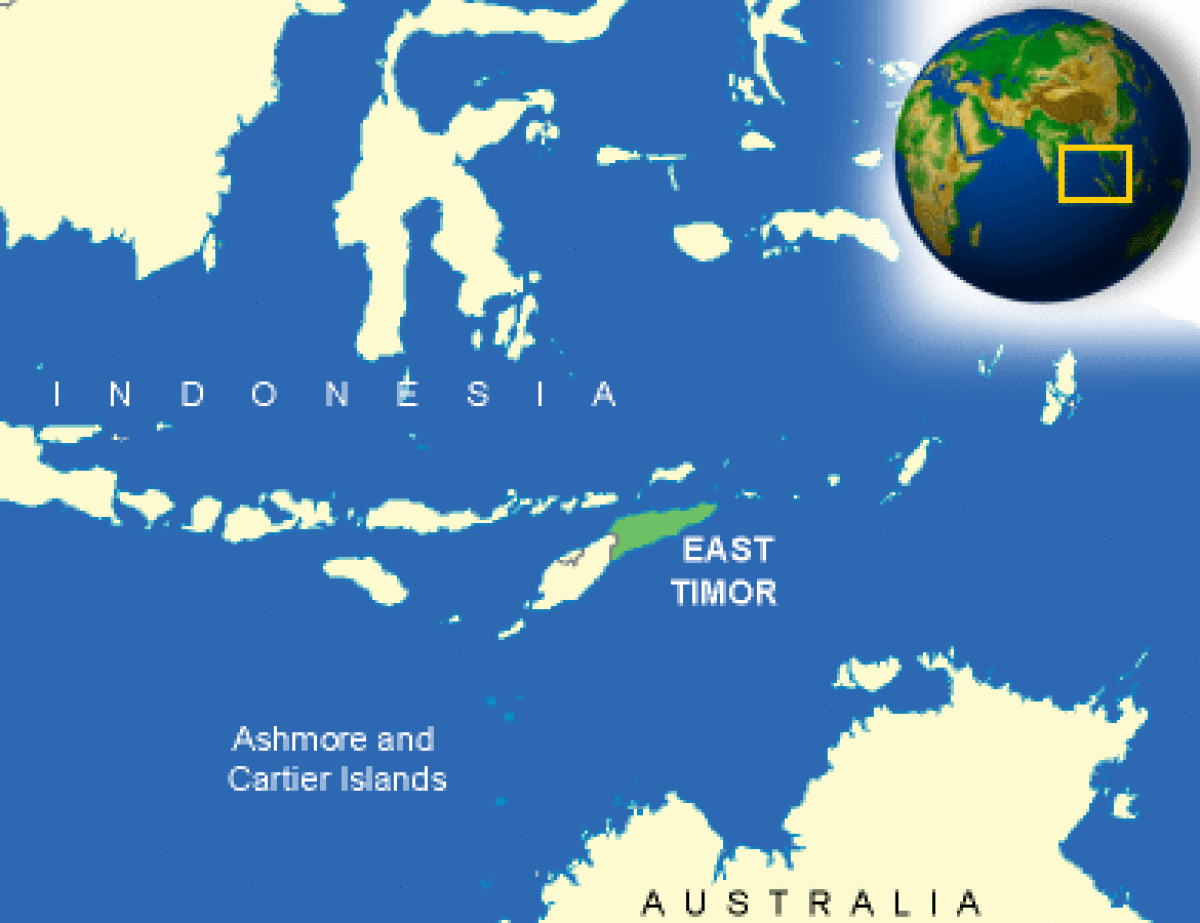
Where is Timor-Leste located?
What countries border Timor-Leste?
Timor-Leste Weather
What is the current weather in Timor-Leste?
Timor-Leste Facts and Culture
What is Timor-Leste famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: The East Timorese people are sometimes shy with strangers, but very loyal to people considered friends. As a people, East... More
- Family: The extended family is paramount in the lives of East Timorese, though families have been split by the recent conflict,... More
- Personal Apperance: East Timorese dress casually, including loose pants and patterned shirts for both men and women. In villages, people wear hand-made... More
- Recreation: he people of Timor-Leste engage in a variety of recreational activities, including: Traditional dances and music: Timor-Leste has a rich cultural... More
- Diet: The East Timor diet is affected by the short supply of many staples since the conflict. The cuisine shares elements... More
- Food and Recipes: Typically, breakfast is served by 7 AM, lunch between noon and 2: 00 PM, and dinner between 6 and 8... More
- Visiting: Visiting informally between friends and family is enjoyed. An invitation is usual for new acquaintances or strangers. Before entering a... More
- Dating: Young people do not generally date couples until they are engaged. They go out in groups together, or with a... More
Timor-Leste Facts
What is the capital of Timor-Leste?
| Capital | Dili |
| Government Type | semi-presidential republic |
| Currency | US dollar (USD) |
| Total Area |
5,743 Square Miles 14,874 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southeastern Asia, northwest of Australia in the Lesser Sunda Islands at the eastern end of the Indonesian archipelago; note - Timor-Leste includes the eastern half of the island of Timor, the Oecussi (Ambeno) region on the northwest portion of the island of Timor, and the islands of Pulau Atauro and Pulau Jaco |
| Language |
Tetum (official), Portuguese (official), Indonesian, English note: there are about 16 indigenous languages; Tetum, Galole, Mambae, and Kemak are spoken by significant numbers of people |
| GDP - real growth rate | 4.3% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $5,800.00 (USD) |
Timor-Leste Demographics
What is the population of Timor-Leste?
| Ethnic Groups | Austronesian (Malayo-Polynesian), Papuan, small Chinese minority |
| Languages | Portuguese and Tetum, the local language, are both official languages. Bahasa-Indonesia and English are also used in commercial and government spheres. English is often used in academic and non-government spheres. In school, it is still debated whether to focus on written Tetum, or Portuguese. |
| Nationality Noun | Timorese |
| Population | 1,383,723 |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.47% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | DILI (capital) 180,000 |
| Urban Population | 28.300000 |
Timor-Leste Government
What type of government does Timor-Leste have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President José RAMOS-HORTA (since 20 May 2022); note - the president is commander in chief of the military and can veto legislation, dissolve parliament, and call national elections head of government: Prime Minister Kay Rala Xanana GUSMAO (since 1 July 2023) cabinet: Council of Ministers; ministers proposed to the prime minister by the coalition in the Parliament and sworn in by the President of the Republic elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); last election held on 19 March 2022 with a runoff on 19 April 2022 (next to be held in April 2027); following parliamentary elections, the president appoints the leader of the majority party or majority coalition as the prime minister election results: 2022: José RAMOS-HORTA elected president in second round - RAMOS-HORTA (CNRT) 62.1%, Francisco GUTERRES (FRETILIN) 37.9% 2017: Francisco GUTERRES elected president; Francisco GUTERRES (FRETILIN) 57.1%, António da CONCEICAO (PD) 32.5%, other 10.4% |
| Suffrage | 17 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Timor-Leste dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years |
| National Holiday | Restoration of Independence Day, 20 May (2002); Proclamation of Independence Day, 28 November (1975) |
| Constitution |
history: drafted 2001, approved 22 March 2002, entered into force 20 May 2002 amendments: proposed by Parliament and parliamentary groups; consideration of amendments requires at least four-fifths majority approval by Parliament; passage requires two-thirds majority vote by Parliament and promulgation by the president of the republic; passage of amendments to the republican form of government and the flag requires approval in a referendum |
| Independence | 20 May 2002 (from Indonesia); note - 28 November 1975 was the date independence was proclaimed from Portugal; 20 May 2002 was the date of international recognition of Timor-Leste's independence from Indonesia |
Timor-Leste Video
YouTube- The Travel Guide TIMOR LESTE OR EAST TIMOR | ULTIMATE TRAVEL GUIDE | ASIA EDITION
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Timor-Leste Geography
What environmental issues does Timor-Leste have?
| Climate | tropical; hot, humid; distinct rainy and dry seasons |
| Border Countries | Indonesia 228 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | widespread use of slash and burn agriculture has led to deforestation and soil erosion |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | mountainous |
Timor-Leste Economy
How big is the Timor-Leste economy?
| Economic Overview |
The economy of Timor-Leste is primarily driven by the oil and gas industry, which has been the main source of revenue for the country since the early 2000s. According to the World Bank, Timor-Leste has a population of around 1.3 million people and a GDP of $2.6 billion (2020 est.). Its economy is classified as lower-middle-income, with a per capita income of $1,956. While the country has made progress in reducing poverty over the past two decades, around 41% of the population still lives below the poverty line, with limited access to basic services such as healthcare and education. The oil and gas industry accounts for over 90% of Timor-Leste's exports and more than half of its GDP. The country's main oil and gas fields are located in the Timor Sea, and its main oil and gas production companies include ConocoPhillips, Eni, and Woodside Petroleum. However, the country's reliance on oil and gas revenue has also made it vulnerable to fluctuations in global oil prices, and the COVID-19 pandemic has further impacted its economy. To diversify its economy and reduce its reliance on oil and gas, Timor-Leste has also been focusing on developing its agriculture and tourism sectors. The country has a tropical climate and fertile land, which makes it suitable for a variety of crops, including coffee, rice, corn, and cassava. The government has been providing support to farmers to improve their yields and increase production. The country also has a growing tourism industry, with attractions such as beaches, diving spots, and historical sites. Despite the efforts to diversify the economy, Timor-Leste faces several challenges in achieving sustainable economic growth. One of the main challenges is the limited infrastructure, including roads, ports, and airports, which makes it difficult to transport goods and services within the country and to other markets. The country also has a high unemployment rate, particularly among young people, and a low level of human capital, which hinders its ability to compete in the global market. To address these challenges, the government of Timor-Leste has been implementing various policies and programs to improve the business environment and attract foreign investment. In 2020, the government launched a new investment law that aims to simplify the process of doing business in the country and provide incentives for foreign investors. The government has also been investing in education and training programs to improve the skills of its workforce and increase productivity. |
| Industries | printing, soap manufacturing, handicrafts, woven cloth |
| Currency Name and Code | US dollar (USD) |
| Export Partners | NA |
Timor-Leste News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Timor-Leste?
Source: Google News
Timor-Leste Travel Information
What makes Timor-Leste a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Occupying 5,743 square miles on the eastern half of an island in the Timor Sea between Indonesia and Australia, Timor-Leste has a population of approximately 1.1 million people. Timor-Leste became independent on May 20, 2002, and is a democratically-governed, independent nation with an elected President and Parliament. Following successful presidential and parliamentary elections and a peaceful change of government in 2012, UN and Australian-led peacekeepers departed Timor Leste.Decades of occupation and periodic eruptions of post-independence violence – most recently in April 2006 – have left Timor-Leste with extremely poor infrastructure and limited economic opportunities. Electricity, telephone and telecommunications, roads, and lodging remain unreliable, particularly outside of the capital. Timor-Leste's economy relies largely on revenues from offshore oil and gas production.
Crime
Crimes such as pick pocketing, purse snatchings, residential and automobile break-ins, and theft occur throughout the country but are more frequent in Dili, the capital. These crimes often occur in recreational areas and facilities frequented by foreigners. If you become a victim of these crimes but resist, you may end up facing physical violence by perpetrators. There is occasional gang-related violence, which, at times, has affected foreign nationals. Stone-throwing attacks on vehicles occur during periods of gang conflicts and civil unrest and have resulted in serious injury and death in the past. You should avoid travel at night or alone in unfamiliar areas. Women should avoid traveling alone, especially at night, because sexual assault or banditry is possible. Timor-Leste is socially conservative and you should avoid wearing revealing clothing, particularly in crowded public areas such as markets.Don’t buy counterfeit or pirated goods, even if they are widely available.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Timor-Leste, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own, and criminal penalties vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States. You can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Timor-Leste, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not where you are.Based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements with certain countries, and customary international law, if you are arrested in Timor-Leste, you have the option to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the U.S. embassy of your arrest, and to have communications from you forwarded to the U.S. embassy.
Languages
Portuguese and Tetum, the local language, are both official languages. Bahasa-Indonesia and English are also used in commercial and government spheres. English is often used in academic and non-government spheres. In school, it is still debated whether to focus on written Tetum, or Portuguese.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Although limited emergency medical care is available in Dili, options for routine medical care throughout the rest of country are extremely limited. Serious medical problems require hospitalization and/or medical evacuation to Australia, the nearest point with acceptable medical care, to Singapore, or to the United States, and can cost thousands of dollars.
Safety and Security
If you are in Timor-Leste, you should exercise caution, use common sense, avoid large gatherings, remain alert with regard to your personal security, and avoid travel after dark to the extent possible. Exercise caution in public places, including, but not limited to, clubs, restaurants, bars, schools, places of worship, outdoor recreational events, hotels, resorts and beaches, and other locations frequented by foreigners.You should maintain a high level of security awareness while moving around in Dili, be alert to the potential for violence, and avoid demonstrations, large political gatherings, and areas where disturbances have occurred. Demonstrations can occur at or near symbols and institutions of the Government of Timor-Leste, including government buildings, police stations, and houses belonging to prominent politicians. Even demonstrations intended to be peaceful can turn confrontational and escalate into violence with little or no warning.
Timor-Leste has experienced several episodes of violence since independence. The most serious was in April 2006, when civil order broke down and the government requested the return of international security forces to help restore order. More recent instances of unrest included sporadic, localized violence following national elections in August 2007, and an attempt to assassinate former President Ramos-Horta and Prime Minister Xanana Gusmao in February 2008. There have been no major country-wide civil disturbances since 2008 and international peacekeepers departed from the country at the end of 2012.
Timorese security forces occasionally establish security checkpoints along roads. These legitimate checkpoints are intended to enhance security and should be respected. There are also occasional illegal checkpoints which you should avoid but which to date have been primarily targeted at Timorese. If you are traveling in Timor-Leste, you should remember that despite its small size, much of the territory is isolated and can be difficult to reach by available transportation or communication links.
All U.S. citizens should always ensure that passports and important personal papers are in order in the event it becomes necessary to leave the country quickly for any reason. The U.S. Embassy in Dili is not able to issue emergency passports and has only limited capacity to process passport renewals.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Timor-Leste, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States.All traffic operates on the left side of the road, and most vehicles use right-hand drive. Roads are often poorly maintained, and four-wheel drive may be required in some areas. Non-existent lighting and poor road conditions make driving at night hazardous. Driving in Dili is especially hazardous, with large trucks and military vehicles sharing the streets with vendors, pedestrians, and livestock. Many cars and, especially, motorcycles operate at night without lights.
Taxis, small buses, and mini-vans provide public transportation in Dili and elsewhere. However, public transportation is generally overcrowded, uncomfortable, and below international safety standards. Public transportation operators have been known to unexpectedly drop passengers at locations other than their destination due to the operators’ fears about certain areas or hours. Disagreement about fares has occasionally led to hostilities. Public transport is generally inadvisable and is generally unavailable after dark, although there is a growing presence of night taxis at select locations.
During the rainy season from November to May, rain showers can severely damage cross-island roadways, making roads particularly risky. You should use caution when traveling on the cross-island roadways in the mountain areas of Aileu, Ermera, Manatuto, Ainaro, and Manufahi provinces.
Accidents occur frequently. When there is an accident, you should contact the police. Bystanders sometimes attack the driver perceived to be responsible for a traffic accident. This is more common in rural areas and in accidents involving Timorese drivers, but crowds have occasionally attacked expatriate drivers at the scene of an accident. If you are involved in an accident and believe that there is a threat of bodily harm from people at the scene of the accident, it is advisable to drive to the nearest police station before stopping.
While it is required to obtain insurance for vehicles in Timor-Leste, compliance with this rule is limited and many drivers are uninsured. Most traffic accidents are settled informally between those involved.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
