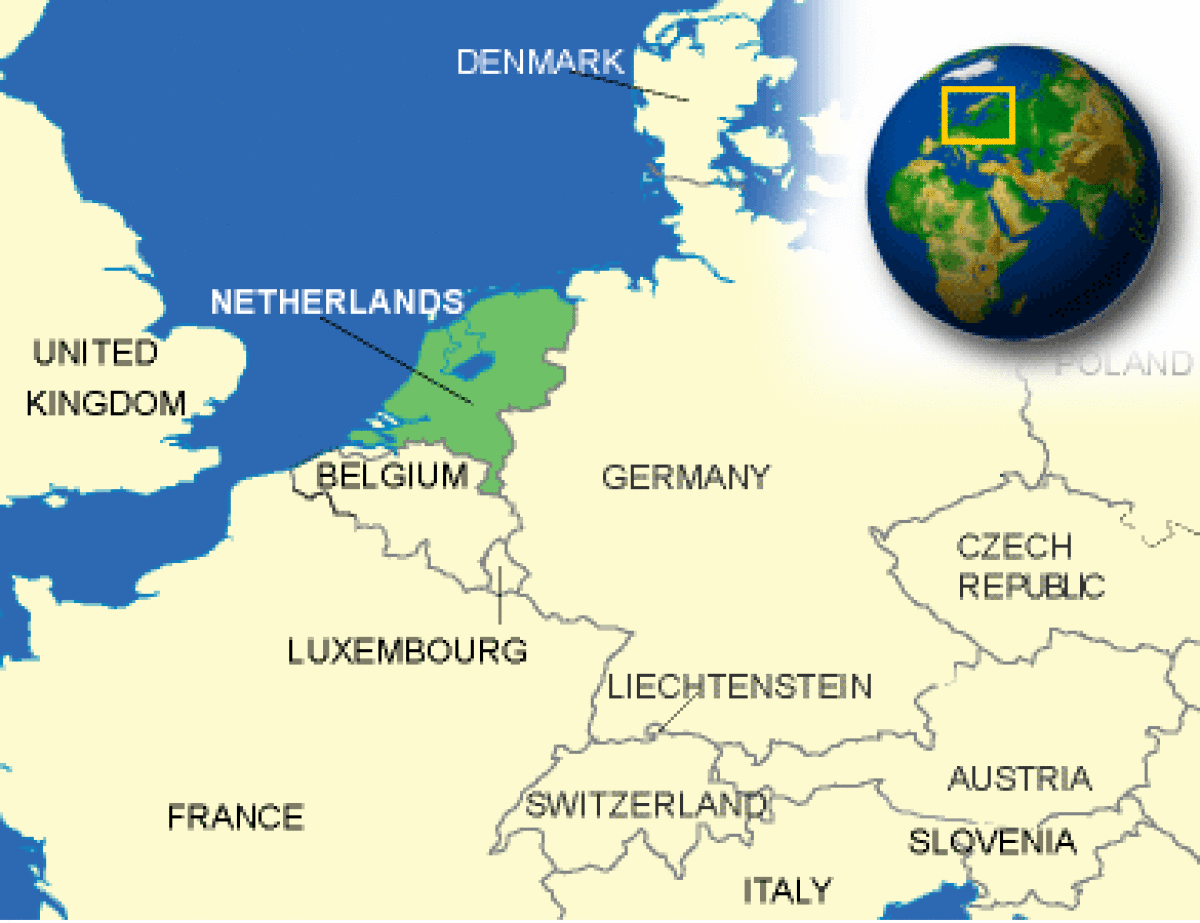
Where is Netherlands located?
What countries border Netherlands?
Netherlands Weather
What is the current weather in Netherlands?
Netherlands Facts and Culture
What is Netherlands famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: The Netherlands has a strong tradition of involvement in international affairs. Dutch openness to the world has made them no... More
- Family: Dutch families are moderate in size. Both parents typically work outside the home. Couples usually live close to relatives.... More
- Personal Apperance: On a typical day, people's clothing depends very much on their jobs. Some organizations, like banks, require formal suits and... More
- Recreation: Cycling is a popular activity for commuting, recreation, and sport involving at least half the population. Other favorite sports include... More
- Diet: Bread or toast with jelly or jam, Dutch cheese, or meats are the most common foods for a Dutch breakfast.... More
- Food and Recipes: Breakfast is eaten between 7:30 and 8:15 AM with lunch at about 12:30 PM. Dinner is between 5:30 and 7:30... More
- Visiting: When visiting, it is customary to shake hands with everyone present, including children. Dinner guests usually bring flowers or another... More
- Dating: It is common for couples to live together before getting married. It is not uncommon for couples to live... More
Netherlands Facts
What is the capital of Netherlands?
| Capital | Amsterdam; note - The Hague is the seat of government |
| Government Type | parliamentary constitutional monarchy; part of the Kingdom of the Netherlands |
| Currency | Euro (EUR) |
| Total Area |
16,040 Square Miles 41,543 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Western Europe, bordering the North Sea, between Belgium and Germany |
| Language | Dutch (official language), Frisian (official language) |
| GDP - real growth rate | 1.8% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $49,300.00 (USD) |
Netherlands Demographics
What is the population of Netherlands?
| Ethnic Groups | Dutch 83%, other 17% (of which 9% are non-Western origin mainly Turks, Moroccans, Antilleans, Surinamese and Indonesians) |
| Nationality Noun | Dutchman(men), Dutchwoman(women) |
| Population | 17,280,397 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.44% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | AMSTERDAM (capital) 1.056 million; Rotterdam 1.014 million; The Hague (seat of government) 635,000 |
| Urban Population | 83.200000 |
Netherlands Government
What type of government does Netherlands have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: King WILLEM-ALEXANDER (since 30 April 2013); Heir Apparent Princess CATHARINA-AMALIA (daughter of King WILLEM-ALEXANDER, born 7 December 2003) head of government: Prime Minister Mark RUTTE (since 14 October 2010); Deputy Prime Ministers Sigrid KAAG and Wopke HOEKSTRA (since 10 January 2022), Carola SCHOUTEN (since 26 October 2017); note - Mark RUTTE's ruling coalition collapsed on 8 July 2023; he is serving as prime minister in a caretaker status until a new prime minister is named following the 22 November 2023 cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the monarch elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; following Second Chamber elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition is usually appointed prime minister by the monarch; deputy prime ministers are appointed by the monarch |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of the Netherlands dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | King's Day (birthday of King WILLEM-ALEXANDER), 27 April (1967); note - King's or Queen's Day is observed on the ruling monarch's birthday; currently celebrated on 26 April if 27 April is a Sunday |
| Constitution |
history: many previous to adoption of the "Basic Law of the Kingdom of the Netherlands" on 24 August 1815; revised 8 times, the latest in 1983 amendments: proposed as an Act of Parliament by or on behalf of the king or by the Second Chamber of the States General; the Second Chamber is dissolved after its first reading of the Act; passage requires a second reading by both the First Chamber and the newly elected Second Chamber, followed by at least two-thirds majority vote of both chambers, and ratification by the king; amended many times, last in 2018 |
| Independence | 26 July 1581 (the northern provinces of the Low Countries formally declared their independence with an Act of Abjuration; however, it was not until 30 January 1648 and the Peace of Westphalia that Spain recognized this independence) |
Netherlands Video
YouTube, Expoza Travel Holland Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Netherlands Geography
What environmental issues does Netherlands have?
| Overview | The Netherlands is situated in Northwest Europe,reclaimed in part from the waters of the North Sea, The Netherlands is an artificially created land, half of which lies at or below sea level. The country possesses a flat terrain compromising mostly of coastal lowland, farmland, grassy dunes, and sandy beaches. The country is crisscrossed by numerous rivers and canals. |
| Climate | The Netherlands lies in the temperate zone of the Northern Hemisphere, and for the most part possesses a maritime climate. The summers are cool while winters are quite cold. The warmest months fall between July and September with temperatures ranging from 60-75°F. The winter months are long and dreary with strong winds and some snow. Temperatures range from 20-35°F. Due to the proximity of the sea, rain is quite common and spread pretty evenly all year round. |
| Border Countries | Belgium 450 km, Germany 577 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Water pollution in the form of heavy metals, organic compounds, and nutrients such as nitrates and phosphates; air pollution from vehicles and refining activities; acid rain. |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | mostly coastal lowland and reclaimed land (polders); some hills in southeast |
Netherlands Economy
How big is the Netherlands economy?
| Economic Overview |
The Netherlands boasts a robust and diverse economy that strongly emphasizes international trade, innovation, and a highly developed infrastructure. International Trade: The Netherlands has a long history of international trade dating back to its strategic location and its tradition as a maritime nation. Today, it remains one of the world's top exporters of goods and services. Rotterdam, Europe's largest port, is central in facilitating trade flows, particularly in Europe. Highly Developed Infrastructure: The Dutch economy benefits from a well-developed infrastructure, including an extensive network of roads, railways, waterways, and airports. This infrastructure supports domestic economic activities and facilitates international trade and logistics. Innovation and Technology: The Netherlands is known for its innovative and knowledge-based economy. It is home to several world-renowned technology companies and research institutions. The government actively promotes research and development through investment in education, science parks, and innovation hubs. Agriculture and Agribusiness: Despite being a relatively small country, the Netherlands is one of the world's leading agricultural producers, particularly in sectors such as horticulture, dairy, and floriculture. The country is known for its advanced agricultural techniques and sustainable practices. Financial Services: Amsterdam is a central financial hub in Europe, hosting the headquarters of several multinational financial institutions and serving as an important center for banking, insurance, and asset management activities. Manufacturing: The manufacturing sector in the Netherlands is diverse and includes machinery, electronics, chemicals, and food processing. The country is known for its high-quality manufacturing and engineering capabilities. Tourism: The Netherlands attracts millions of tourists annually, drawn by its rich cultural heritage, picturesque landscapes, and vibrant cities like Amsterdam, Rotterdam, and Utrecht. Tourism plays a significant role in the Dutch economy, contributing to job creation and revenue generation. Sustainability and Renewable Energy: The Netherlands is committed to sustainability and renewable energy initiatives, with ambitious targets for reducing carbon emissions and increasing the share of renewable energy in its energy mix. Investments in wind power, solar energy, and sustainable transportation are driving the transition towards a greener economy. Challenges: Like many other advanced economies, the Netherlands faces challenges such as an aging population, labor market reforms, and adapting to technological disruptions. External factors such as geopolitical tensions and trade uncertainties can also impact the Dutch economy. |
| Industries | agroindustries, metal and engineering products, electrical machinery and equipment, chemicals, petroleum, construction, microelectronics, fishing |
| Currency Name and Code | Euro (EUR) |
| Export Partners | Germany 25.1%, Belgium 12.7%, UK 10.7%, France 10.2%, Italy 6%, US 4.6% |
| Import Partners | Germany 17.9%, Belgium 9.7%, US 9.1%, UK 6.9%, France 5.5%, China 5.1%, Japan 4% |
Netherlands News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Netherlands?
Source: Google News
Netherlands Travel Information
What makes Netherlands a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
The Netherlands is a highly developed, stable democracy. Tourist facilities are available throughout the country.
Crime
While the rate of violent crime in the Netherlands is low, tourists are often targeted by thieves. Visitors frequently fall prey to pickpockets, bag snatchers, and other petty thieves who target automobiles and hotel rooms. You should use your room or hotel safe, and keep your baggage locked or secured when you’re away.While thieves may operate anywhere, the U.S. Consulate General in Amsterdam receives frequent reports of thefts from specific areas. Within Amsterdam, thieves and pickpockets are very active in and around train and tram stations, in the city center, and aboard public transportation. Theft is especially common on trains to and from Amsterdam’s Schiphol Airport and international destinations, where hand luggage and laptop computers are often targeted. Thieves often work in pairs; one distracts you, often by asking for directions, while the accomplice moves in on your momentarily unguarded property. The timing of these thefts usually coincides with train stops, enabling the thieves to escape. In addition, many U.S. citizens have reported the theft of purses and briefcases while eating in downtown restaurants, including hotel breakfast rooms. Never leave your personal items or baggage unattended when going to the restroom, buffet table, etc.
Although still relatively limited, electronic theft has increased dramatically in the Netherlands in recent years. In March 2012, the Dutch Banking Association reported 2011 losses at 92 million euros – nearly double that of 2010. Most of the theft involved “skimming,” a technique that copies bank card information. ATM and credit card users are advised to keep an eye on their cards at all times. If you feel uncomfortable using your card for any reason, use cash. Contact your credit card provider for further guidance.
Confidence artists have victimized U.S. citizens around the world, including in the Netherlands. Typically, a U.S. citizen is notified via email of a winning lottery ticket, an inheritance, or other offer requiring his or her assistance and cooperation. The U.S. citizen is asked to forward advance payments for alleged “official expenses,” “taxes,” etc. and, often, to come to Amsterdam to conclude the operation. Another common scam involves an Internet friend or partner who is reported to have been detained by immigration authorities in the Netherlands en route to the United States, and will not be released unless additional funds are paid to the “traveler.” In every case, these reports have been determined to be confidence schemes. Several U.S. citizens have lost tens of thousands of dollars in such scams. Funds transferred in response to such offers can rarely be recovered. Information on fraud schemes can be found on the U.S. Consulate General's website, and the Department of State's International Financial Scams page. If you suspect you have been targeted by a scam based in the Netherlands, you may report it to Dutch law enforcement authorities by email at voorlichting@klpd.politie.nl, or at the following address:
KLPD, Financial Crimes Unit
PO Box 3016
2700 KX Zoetermeer
The Netherlands
Attention: Project Apollo
The Dutch Embassy in Washington, D.C. has a prepared letter that can be used to inform the Dutch Police of fraud.
Do not buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal to bring back into the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in the Netherlands, you are subject to its laws even though you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own. Under Dutch law, for example, you may be taken in for questioning if you are unable to present your passport to local authorities. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not in the country you are visiting.Note that your U.S. passport will not help you avoid arrest or prosecution if you break local laws. If you are arrested in the Netherlands, however, you do have theright to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the Consulate General of your arrest, and to havecommunications from you forwarded to the Consulate General. This accommodation is based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements with certain countries, and customary international law.
While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested in a foreign country, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Good medical facilities are widely available. Emergency medical response can be accessed by dialing 112. Pharmacies (“Apotheek”) are widely available and can assist with emergency prescription needs. Some common medications are not available in the Netherlands without a prescription, and some prescription drugs cannot be sent to the country. Travelers are urged to carry an adequate supply of prescription drugs in their original container, in their carry-on luggage. Please carry a letter from your pharmacist or medical doctor with you, as some drugs are subject to confiscation by local custom agents. Those traveling with any pre-existing medical problems should bring a letter from the attending physician, describing the medical condition and any prescription medications, including the generic name of prescribed drugs.Vaccinations are not required for travel to the Netherlands.
Safety and Security
Since 2004, Dutch government security measures have been in place in response to concerns about terrorist activity in the Netherlands by international and domestic extremist groups. The Dutch Government has determined the current terrorist threat level to be "substantial." According to the Dutch National Coordinator for Counterterrorism, this level, the second-highest of four levels, means that “there is a realistic possibility that an attack will take place in the Netherlands.”We encourage you to keep up with the latest news while in the Netherlands and to take steps to increase your security awareness. As with other countries in the Schengen area, the Netherlands’ open borders with its European neighbors allow for the possibility of terrorist groups entering/exiting the country with anonymity.
Demonstrations are commonplace in the Netherlands and may range in number from a few demonstrators to several thousand. Prior police notice is required for public demonstrations, and police oversight is routinely provided. Nonetheless, even demonstrations intended to be peaceful can turn confrontational and possibly escalate into violence. We urge you to avoid areas of demonstrations if possible, and to exercise caution if near one. Visitors should stay informed about demonstrations from local news sources and hotel security.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in the Netherlands, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States.In the Netherlands, travel in, around, and between cities is possible via a highly developed national public transportation system, an extensive system of bike paths, and by automobile and motorcycle on a modern highway system. Rail is often a convenient alternative to driving, particularly in the areas around Amsterdam, The Hague, and Rotterdam, where road congestion is frequent. Rail network information is available online. Intercity travel by road is relatively safe in comparison to some other European countries.
A valid driver’s license issued by a Department of Motor Vehicles in the United States is valid for use in the Netherlands for up to 180 days while in tourist or visitor status. You must use seat belts and child seats. Driving is on the right side of the road, as in the United States. Speed limits are strictly enforced via radar. Traffic cameras are pervasive throughout the Netherlands and tickets for traveling even 2-5 km/h over the limit are common. The maximum speed limit on highways is 120 km/h, with a highway speed limit of 100 km/h posted in most urban areas. Secondary roads and some urban-area highways have a speed limit of 80 km/h. The speed limit in towns and cities is 50 km/h, with 30 km/h zones in residential areas. The Dutch Government has reduced speed limits on certain roads near cities in an effort to reduce air pollution. You should be aware that speed limit signs are electronic, and therefore speed limits may be changed remotely by authorities depending on traffic conditions. Drivers must yield the right-of-way to drivers and bicyclists coming from the right at intersections or traffic circles unless otherwise posted. The maximum allowable blood-alcohol content in the Netherlands is 0.05%. Use of cellular telephones while driving without the use of a hands-free device is prohibited, and is punishable by severe fines.
Lanes in the center of many urban two-way streets are reserved for buses, trams, and taxis. In cities, pedestrians should be mindful of trams, which often cross or share bicycle and pedestrian paths. Serious – and sometimes fatal – accidents involving pedestrians or bicyclists colliding with trams occur each year. Motorists should be especially mindful that bicyclists have the right-of-way; motorists must yield to bicyclists. Pedestrians should not walk along bicycle paths, which are often adjacent to the sidewalk and usually designated by red pavement.
Bicyclists and pedestrians should be particularly cautious during the winter months, when paths, roads, and especially bridges can be icy and extremely slippery.
Taxi service in the Netherlands is safe but expensive. Trams and buses are both convenient and economical, but are often frequented by pickpockets.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
