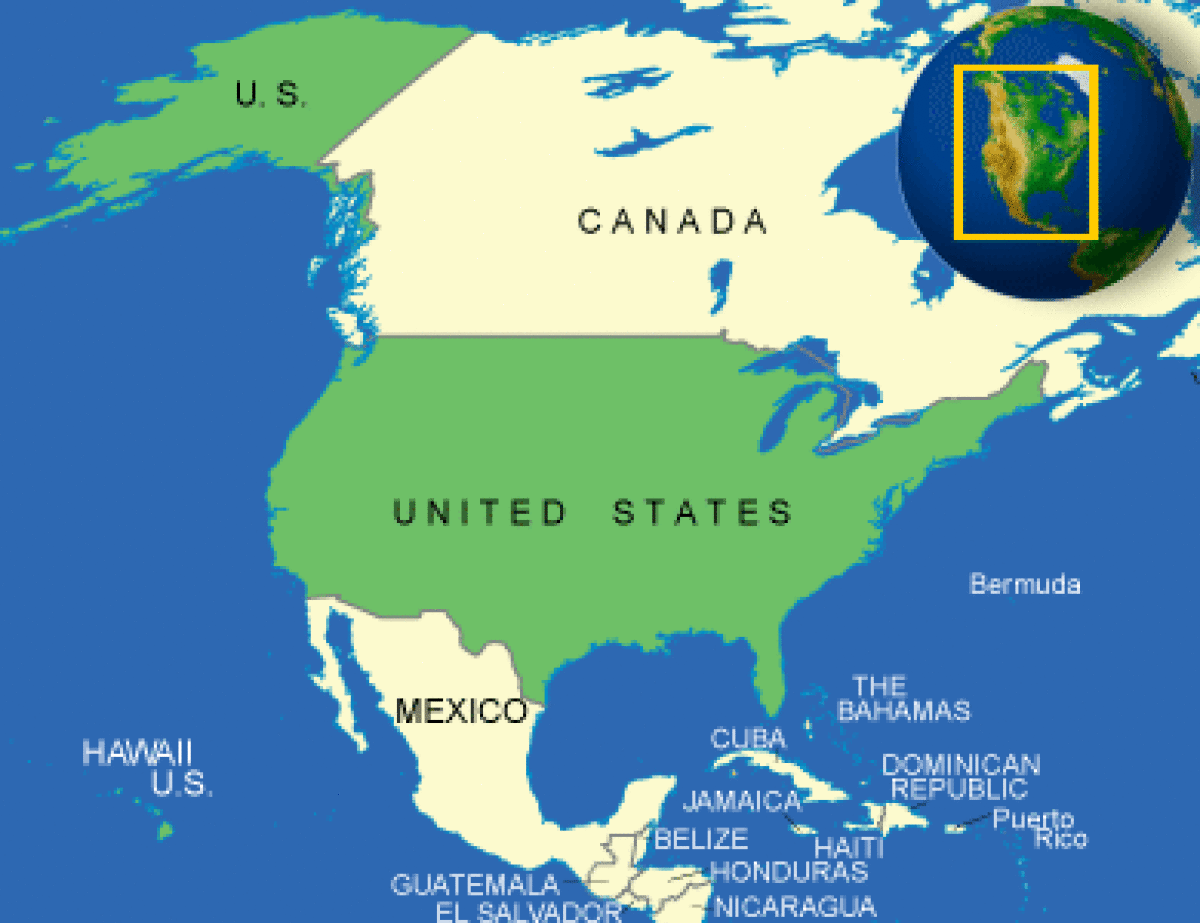
Where is United States (US) located?
What countries border United States (US)?
United States (US) Weather
What is the current weather in United States (US)?
United States (US) Facts and Culture
What is United States (US) famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Americans strongly value their freedom and see America as a country that defends democracy. People in the United States cherish... More
- Family: Perhaps more than in any other country in the world, the dream of the typical family in the United States... More
- Personal Apperance: In general, residents of the United States tend towards more informal, casual dress, particularly in areas outside the eastern seaboard.... More
- Recreation: Sports and recreation play a major role in the social fabric of the United States. Popular national sports include basketball,... More
- Diet: Fast food is found in abundance in America reflecting the on-the-go lifestyle of Americans. Many dishes are adopted from the... More
- Food and Recipes: The typical family in the United States eats three meals per day. Breakfast for adults might often consist of a... More
- Visiting: When visiting an American home or family, you should not worry as much about doing the right thing as being... More
United States (US) Facts
What is the capital of United States (US)?
| Capital | Washington, DC |
| Government Type | constitutional federal republic |
| Currency | US Dollar (USD) |
| Total Area |
3,794,079 Square Miles 9,826,675 Square Kilometers |
| Location | North America, bordering both the North Atlantic Ocean and the North Pacific Ocean, between Canada and Mexico |
| Language |
English 82.1%, Spanish 10.7%, other Indo-European 3.8%, Asian and Pacific islands 2.7%, other 0.7% Note: the US has no official national language, but English has acquired official status in 28 of the 50 states; Hawaiian is an official language in the state of Hawaii |
| GDP - real growth rate | 2.6% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $56,300.00 (USD) |
United States (US) Demographics
What is the population of United States (US)?
| Ethnic Groups |
White 79.96%, black 12.85%, Asian 4.43%, Amerindian and Alaska native 0.97%, native Hawaiian and other Pacific islander 0.18%, two or more races 1.61% Note: a separate listing for Hispanic is not included because the US Census Bureau considers Hispanic to mean persons of Spanish/Hispanic/Latino origin including those of Mexican, Cuban, Puerto Rican, Dominican Republic, Spanish, and Central or South American origin living in the US who may be of any race or ethnic group (white, black, Asian, etc.); about 15.1% of the total US population is Hispanic |
| Nationality Noun | American(s) |
| Population | 332,639,102 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.9% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | New York-Newark 20.352 million; Los Angeles-Long Beach-Santa Ana 13.395 million; Chicago 9.676 million; Miami 6.061 million; Philadelphia 5.927 million; WASHINGTON, D.C. (capital) 4.705 million |
| Urban Population | 82.400000 |
United States (US) Government
What type of government does United States (US) have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Joseph R. BIDEN, Jr. (since 20 January 2021); Vice President Kamala D. HARRIS (since 20 January 2021); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government head of government: President Joseph R. BIDEN, Jr. (since 20 January 2021); Vice President Kamala D. HARRIS (since 20 January 2021) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president, approved by the Senate elections/appointments: president and vice president indirectly elected on the same ballot by the Electoral College of 'electors' chosen from each state; president and vice president serve a 4-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 3 November 2020 (next to be held on 5 November 2024) election results: 2020: Joseph R. BIDEN, Jr. elected president; electoral vote - Joseph R. BIDEN, Jr. (Democratic Party) 306, Donald J. TRUMP (Republican Party) 232; percent of direct popular vote - Joseph R. BIDEN Jr. 51.3%, Donald J. TRUMP 46.9%, other 1.8% 2016: Donald J. TRUMP elected president; electoral vote - Donald J. TRUMP (Republican Party) 304, Hillary D. CLINTON (Democratic Party) 227, other 7; percent of direct popular vote - Hillary D. CLINTON 48.2%, Donald J. TRUMP 46.1%, other 5.7% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: yes citizenship by descent only: yes dual citizenship recognized: no, but the US government acknowledges such situtations exist; US citizens are not encouraged to seek dual citizenship since it limits protection by the US residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 4 July (1776) |
| Constitution |
history: previous 1781 (Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union); latest drafted July - September 1787, submitted to the Congress of the Confederation 20 September 1787, submitted for states' ratification 28 September 1787, ratification completed by nine of the 13 states 21 June 1788, effective 4 March 1789 amendments: proposed as a "joint resolution" by Congress, which requires a two-thirds majority vote in both the House of Representatives and the Senate or by a constitutional convention called for by at least two thirds of the state legislatures; passage requires ratification by three fourths of the state legislatures or passage in state-held constitutional conventions as specified by Congress; the US president has no role in the constitutional amendment process; amended many times, last in 1992 |
| Independence | 4 July 1776 (declared independence from Great Britain); 3 September 1783 (recognized by Great Britain) |
United States (US) Video
YouTube: DeFreesProductions ND-IA 4:24 / 5:13 Drivelapse USA - 5 Minute Roadtrip Timelapse Tour Around America
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)United States (US) Geography
What environmental issues does United States (US) have?
| Climate | Mostly temperate, but tropical in Hawaii and Florida, arctic in Alaska, semi-arid in the great plains west of the Mississippi River, and arid in the Great Basin of the southwest; low winter temperatures in the northwest are ameliorated occasionally in January and February by warm chinook winds from the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains. |
| Border Countries |
Canada 8,893 km (including 2,477 km with Alaska), Mexico 3,141 km Note: United States Naval Base at Guantanamo Bay, Cuba is leased by the United States and is part of Cuba; the base boundary is 28 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | air pollution; large emitter of carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels; water pollution from runoff of pesticides and fertilizers; declining natural freshwater resources in much of the western part of the country require careful management; deforestation; mining; desertification; species conservation; invasive species (the Hawaiian Islands are particularly vulnerable) |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party To: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Seals, Antarctic Treaty, Climate Change, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Biodiversity, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Hazardous Wastes |
| Terrain | Vast central plain, mountains in the west, hills and low mountains in the east; rugged mountains and broad river valleys in Alaska; rugged, volcanic topography in Hawaii |
United States (US) Economy
How big is the United States (US) economy?
| Economic Overview |
The United States has the most technologically powerful economy in the world, with a per capita GDP of $59,500. US firms are at or near the forefront of technological advances, especially in computers, pharmaceuticals, and medical, aerospace, and military equipment; however, their advantage has narrowed since the end of World War II. Based on a comparison of GDP measured at purchasing power parity conversion rates, the US economy in 2014, having stood as the largest in the world for more than a century, slipped into second place behind China, which has more than tripled the US growth rate for each year of the past four decades. In the United States, private individuals and business firms make most of the decisions, and the federal and state governments buy needed goods and services predominantly in the private marketplace. US business firms enjoy greater flexibility than their counterparts in Western Europe and Japan in decisions to expand capital plants, lay off surplus workers, and develop new products. At the same time, businesses face higher barriers to enter their rivals' home markets than foreign firms face entering US markets. Long-term problems for the US include stagnation of wages for lower-income families, inadequate investment in deteriorating infrastructure, rapidly rising medical and pension costs of an aging population, energy shortages, and sizable current account and budget deficits. The onrush of technology has been a driving factor in the gradual development of a "two-tier" labor market in which those at the bottom lack the education and the professional/technical skills of those at the top and, more and more, fail to get comparable pay raises, health insurance coverage, and other benefits. But the globalization of trade, and especially the rise of low-wage producers such as China, has put additional downward pressure on wages and upward pressure on the return to capital. Since 1975, practically all the gains in household income have gone to the top 20% of households. Since 1996, dividends and capital gains have grown faster than wages or any other category of after-tax income. Imported oil accounts for more than 50% of US consumption and oil has a major impact on the overall health of the economy. Crude oil prices doubled between 2001 and 2006, the year home prices peaked; higher gasoline prices ate into consumers' budgets and many individuals fell behind in their mortgage payments. Oil prices climbed another 50% between 2006 and 2008, and bank foreclosures more than doubled in the same period. Besides dampening the housing market, soaring oil prices caused a drop in the value of the dollar and a deterioration in the US merchandise trade deficit, which peaked at $840 billion in 2008. Because the US economy is energy-intensive, falling oil prices since 2013 have alleviated many of the problems the earlier increases had created. The sub-prime mortgage crisis, falling home prices, investment bank failures, tight credit, and the global economic downturn pushed the US into a recession by mid-2008. GDP contracted until the third quarter of 2009, the deepest and longest downturn since the Great Depression. To help stabilize financial markets, the US Congress established a $700 billion Troubled Asset Relief Program in October 2008. The government used some of these funds to purchase equity in US banks and industrial corporations, much of which had been returned to the government by early 2011. In January 2009, Congress passed and former President Barack OBAMA signed a bill providing an additional $787 billion fiscal stimulus to be used over 10 years - two-thirds on additional spending and one-third on tax cuts - to create jobs and to help the economy recover. In 2010 and 2011, the federal budget deficit reached nearly 9% of GDP. In 2012, the Federal Government reduced the growth of spending and the deficit shrank to 7.6% of GDP. US revenues from taxes and other sources are lower, as a percentage of GDP than those of most other countries. Wars in Iraq and Afghanistan required major shifts in national resources from civilian to military purposes and contributed to the growth of the budget deficit and public debt. Through FY 2018, the direct costs of the wars will have totaled more than $1.9 trillion, according to US Government figures. In March 2010, former President OBAMA signed into law the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA), a health insurance reform that was designed to extend coverage to an additional 32 million Americans by 2016, through private health insurance for the general population and Medicaid for the impoverished. Total spending on healthcare - public plus private - rose from 9.0% of GDP in 1980 to 17.9% in 2010. In July 2010, the former president signed the DODD-FRANK Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, a law designed to promote financial stability by protecting consumers from financial abuses, ending taxpayer bailouts of financial firms, dealing with troubled banks that are "too big to fail," and improving accountability and transparency in the financial system - in particular, by requiring certain financial derivatives to be traded in markets that are subject to government regulation and oversight. The Federal Reserve Board (Fed) announced plans in December 2012 to purchase $85 billion per month of mortgage-backed and Treasury securities in an effort to hold down long-term interest rates, and to keep short-term rates near zero until unemployment dropped below 6.5% or inflation rose above 2.5%. The Fed ended its purchases during the summer of 2014 after the unemployment rate dropped to 6.2%, inflation stood at 1.7%, and public debt fell below 74% of GDP. In December 2015, the Fed raised its target for the benchmark federal funds rate by 0.25%, the first increase since the recession began. With continued low growth, the Fed opted to raise rates several times since then, and in December 2017, the target rate stood at 1.5%. In December 2017, Congress passed and President Donald TRUMP signed the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, which, among its various provisions, reduces the corporate tax rate from 35% to 21%; lowers the individual tax rate for those with the highest incomes from 39.6% to 37%, and by lesser percentages for those at lower income levels; changes many deductions and credits used to calculate taxable income; and eliminates in 2019 the penalty imposed on taxpayers who do not obtain the minimum amount of health insurance required under the ACA. The new taxes took effect on 1 January 2018; the tax cut for corporations are permanent, but those for individuals are scheduled to expire after 2025. The Joint Committee on Taxation (JCT) under the Congressional Budget Office estimates that the new law will reduce tax revenues and increase the federal deficit by about $1.45 trillion over the 2018-2027 period. This amount would decline if economic growth were to exceed the JCT’s estimate. |
| Industries | Highly diversified, world-leading, high-technology innovator, second-largest industrial output in the world; petroleum, steel, motor vehicles, aerospace, telecommunications, chemicals, electronics, food processing, consumer goods, lumber, mining |
| Currency Name and Code | US Dollar (USD) |
| Export Partners | Canada 19%, Mexico 13.3%, China 7%, Japan 4.5% |
| Import Partners | China 18.4%, Canada 14.2%, Mexico 11.7%, Japan 5.8%, Germany 4.4% |
United States (US) News and Current Events
What current events are happening in United States (US)?
Source: Google News
United States (US) Travel Information
What makes United States (US) a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
The United States is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Native American reservations.It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and Mexico to its south and maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The capital of the United States is Washington, D.C., and its most populous city and principal financial center is in New York City.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
