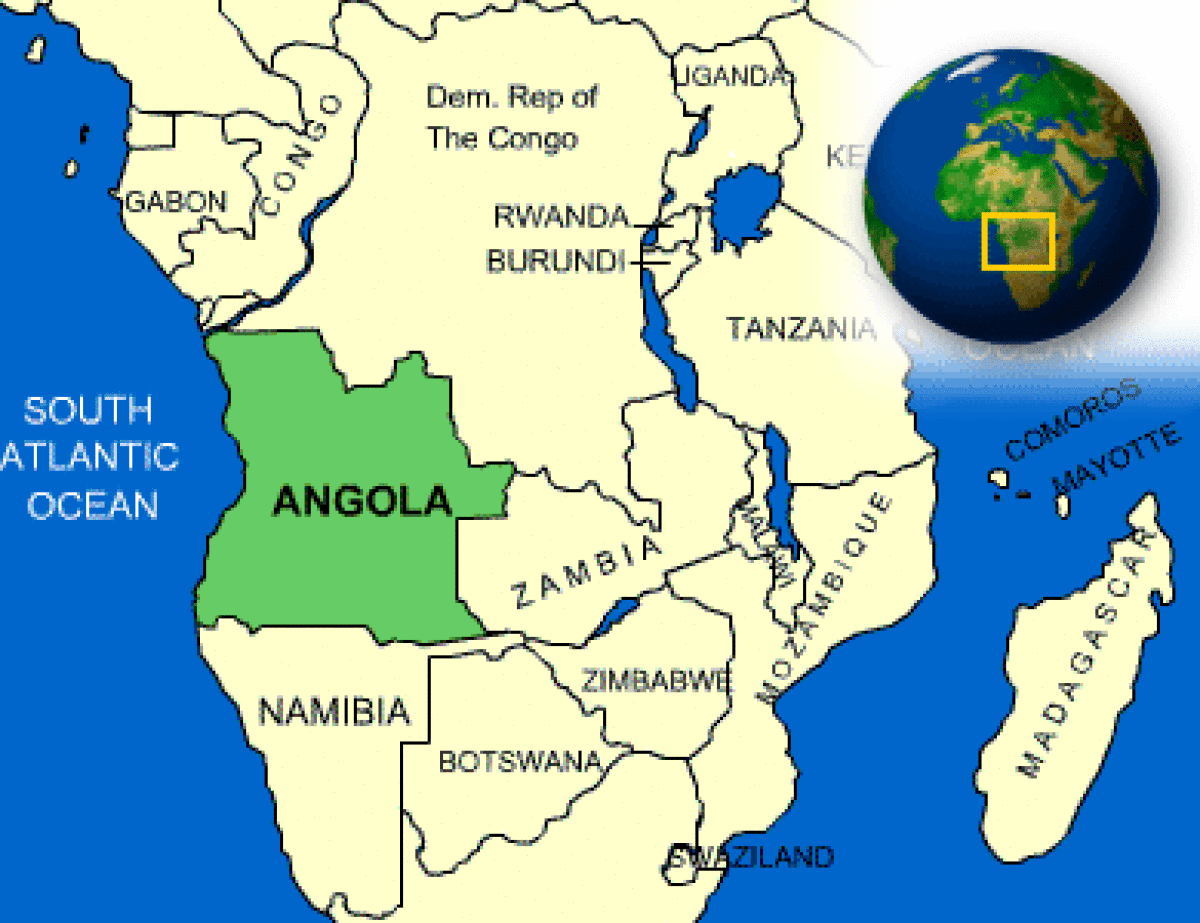
Where is Angola located?
What countries border Angola?
Angola Weather
What is the current weather in Angola?
Angola Facts and Culture
What is Angola famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: In Angola, a regional or tribal sense of identity is often more important than the national sense. Angola's people are... More
- Family: Most of the people in Angola live in simple wooden or clay houses. In the towns and villages, modern... More
- Personal Apperance: Angolans express their artistic sense by creating beautiful hairstyles and headdresses. Western-style of clothing is common although in the villages... More
- Recreation: The most popular sport in Angola is soccer. Boys of all ages play soccer in the streets, often with... More
- Diet: The traditional diet in Angola is influenced by its diverse cultural heritage and availability of local ingredients. The country's cuisine... More
- Food and Recipes: Cassava is the most important food in Angola. It can be made into flour, bread, tapioca, or even alcohol. Fuba... More
- Visiting: When visiting Angola and interacting with the local people, it's helpful to keep the following points in mind to ensure... More
- Dating: In the countryside, it is not uncommon for Angolan parents to suggest a possible partner for their son or daughter.... More
Angola Facts
What is the capital of Angola?
| Capital | Luanda |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | Angola Kwanza (AOA) |
| Total Area |
481,351 Square Miles 1,246,700 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southern Africa, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Namibia and the Democratic Republic of the Congo |
| Language | Portuguese (official), Bantu and other African languages |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $6,800.00 (USD) |
Angola Demographics
What is the population of Angola?
| Ethnic Groups | Ovimbundu 37%, Kimbundu 25%, Bakongo 13%, Mestico (mixed European and native African) 2%, European 1%, other 22% |
| Language - note | Portuguese is the official language used in government business and in major cities. Portuguese as a second language after the language of their native tribe or ethnic group. “Umbundu” is the language most commonly used and understood in central and southern Angola. In Northwest Angola “Kikongo” is spoken. |
| Languages | Portuguese 71.2% (official), Umbundu 23%, Kikongo 8.2%, Kimbundu 7.8%, Chokwe 6.5%, Nhaneca 3.4%, Nganguela 3.1%, Fiote 2.4%, Kwanhama 2.3%, Muhumbi 2.1%, Luvale 1%, other 3.6%; note - data represent most widely spoken languages; shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Angolan(s) adjective: Angolan |
| Population | 37,202,061 |
| Population Growth Rate | 3.33% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 9.292 million LUANDA (capital), 959,000 Lubango, 905,000 Cabinda, 809,000 Benguela, 783,000 Malanje |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 68.7% of total population rate of urbanization: 4.04% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 18,196,058 female: 19,006,003 |
Angola Government
What type of government does Angola have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Joao Manuel Goncalves LOURENCO (since 26 September 2017); Vice President Esperanca Francisco DA COSTA (since 15 September 2022); note - the president is both chief of state and head of government head of government: President Joao Manuel Goncalves LOURENCO (since 15 September 2022); Vice President Esperanca Francisco DA COSTA (since 15 September 2022) cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president elections/appointments: the candidate of the winning party or coalition in the last legislative election becomes the president; president serves a 5-year term (eligible for a second consecutive or discontinuous term); last held on 24 August 2022 (next to be held in 2027) election results: Joao Manuel Goncalves LOURENCO (MPLA) elected president by then winning party following the 24 August 2022 general election |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Angola dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 11 November (1975) |
| Constitution |
history: previous 1975, 1992; latest passed by National Assembly 21 January 2010, adopted 5 February 2010 amendments: proposed by the president of the republic or supported by at least one third of the National Assembly membership; passage requires at least two-thirds majority vote of the Assembly subject to prior Constitutional Court review if requested by the president of the republic |
| Independence | 11 November 1975 (from Portugal) |
Angola Video
YouTube: Christie Cherian Overview of Angola - Economy, Tourism & More
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Angola Geography
What environmental issues does Angola have?
| Overview | Angola is located on the southwestern coast of Africa (South Atlantic Ocean). The coastline extends a distance of nearly 1,000 miles from Angola’s oil-rich enclave of Cabinda north of the mouth of the Zaire River and is separated from the rest of the country by the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the border of Namibia. The country stretches inland for some 950 miles, a third of the way across Africa. The terrain features a narrow coastal plain, which rises abruptly to a vast inland plateau. Angola’s interior elevations range from 3,000–7,000 feet, with the upland region forming one of Africa’s largest watersheds. |
| Climate |
The climate is semiarid in the south and along the coast of Luanda. The north has a cool dry season (May to October) and a hot rainy season (November to April). Natural hazards are locally heavy rainfall, which causes periodic flooding. In Luanda during the January to April hot season, the temperature is often in the upper 90s; the sun is quite intense, and the humidity is very high. During the winter months, June through September, the days are pleasant, with high temperatures around 80°F, with mild evenings. Skies are often hazy, a condition called "cacimbo." Generally, there are light rains during November and December, with heavy rains falling in March and April. |
| Border Countries | The Democratic Republic of the Congo 2,511 km (of which 225 km is the boundary of discontiguous Cabinda Province), Republic of the Congo 201 km, Namibia 1,376 km, Zambia 1,110 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Overuse of pastures and subsequent soil erosion attributable to population pressures; desertification; deforestation of the tropical rain forests, in response to both international demand for tropical timber and to domestic use as fuel, resulting in loss of biodiversity; soil erosion contributing to water pollution and siltation of rivers and dams; inadequate supplies of potable water |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party To: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | A narrow coastal plain rises abruptly to a vast interior plateau |
Angola Economy
How big is the Angola economy?
| Economic Overview |
Angola's economy is overwhelmingly driven by its oil sector. Oil production and its supporting activities contribute about 50% of GDP, more than 70% of government revenue, and more than 90% of the country's exports; Angola is an OPEC member and is subject to its direction regarding oil production levels. Diamonds contribute an additional 5% to exports. Subsistence agriculture provides the main livelihood for most people, but half of the country's food is still imported. Increased oil production supported growth averaging more than 17% per year from 2004 to 2008. A postwar reconstruction boom and resettlement of displaced persons led to high rates of growth in construction and agriculture as well. Some of the country's infrastructure is still damaged or undeveloped from the 27-year-long civil war (1975-2002). However, since 2005 the government has used billions of dollars in credit from China, Brazil, Portugal, Germany, Spain, and the EU to help rebuild Angola's public infrastructure. Land mines left from the war still mar the countryside, and as a result, the national military, international partners, and private Angolan firms all continue to remove them. The global recession that started in 2008 stalled Angola’s economic growth and many construction projects stopped because Luanda accrued billions in arrears to foreign construction companies when government revenue fell. Lower prices for oil and diamonds also resulted in GDP falling 0.7% in 2016. Angola formally abandoned its currency peg in 2009 but reinstituted it in April 2016 and maintains an overvalued exchange rate. In late 2016, Angola lost the last of its correspondent relationships with foreign banks, further exacerbating hard currency problems. Since 2013 the central bank has consistently spent down reserves to defend the kwanza, gradually allowing a 40% depreciation since late 2014. Consumer inflation declined from 325% in 2000 to less than 9% in 2014, before rising again to above 30% from 2015-2017. Continued low oil prices, the depreciation of the kwanza, and slower than expected growth in non-oil GDP have reduced growth prospects, although several major international oil companies remain in Angola. Corruption, especially in the extractive sectors, is a major long-term challenge that poses an additional threat to the economy. |
| Industries | Petroleum; diamonds, iron ore, phosphates, feldspar, bauxite, uranium, and gold; cement; basic metal products; fish processing; food processing, brewing, tobacco products, sugar; textiles; ship repair |
| Currency Name and Code | Angola Kwanza (AOA) |
| Export Partners | China 43.8%, India 9.6%, United States 7.7%, Spain 6.2%, South Africa 4.8%, France 4.4% |
| Import Partners | China 22.1%, Portugal 13.8%, South Korea 11%, United States 6.9%, South Africa 5%, UK 4.1%, France 4% |
Angola News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Angola?
Source: Google News
Angola Travel Information
What makes Angola a unique country to travel to?
Languages
Portuguese 71.2% (official), Umbundu 23%, Kikongo 8.2%, Kimbundu 7.8%, Chokwe 6.5%, Nhaneca 3.4%, Nganguela 3.1%, Fiote 2.4%, Kwanhama 2.3%, Muhumbi 2.1%, Luvale 1%, other 3.6%; note - data represent most widely spoken languages; shares sum to more than 100% because some respondents gave more than one answer on the census
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
