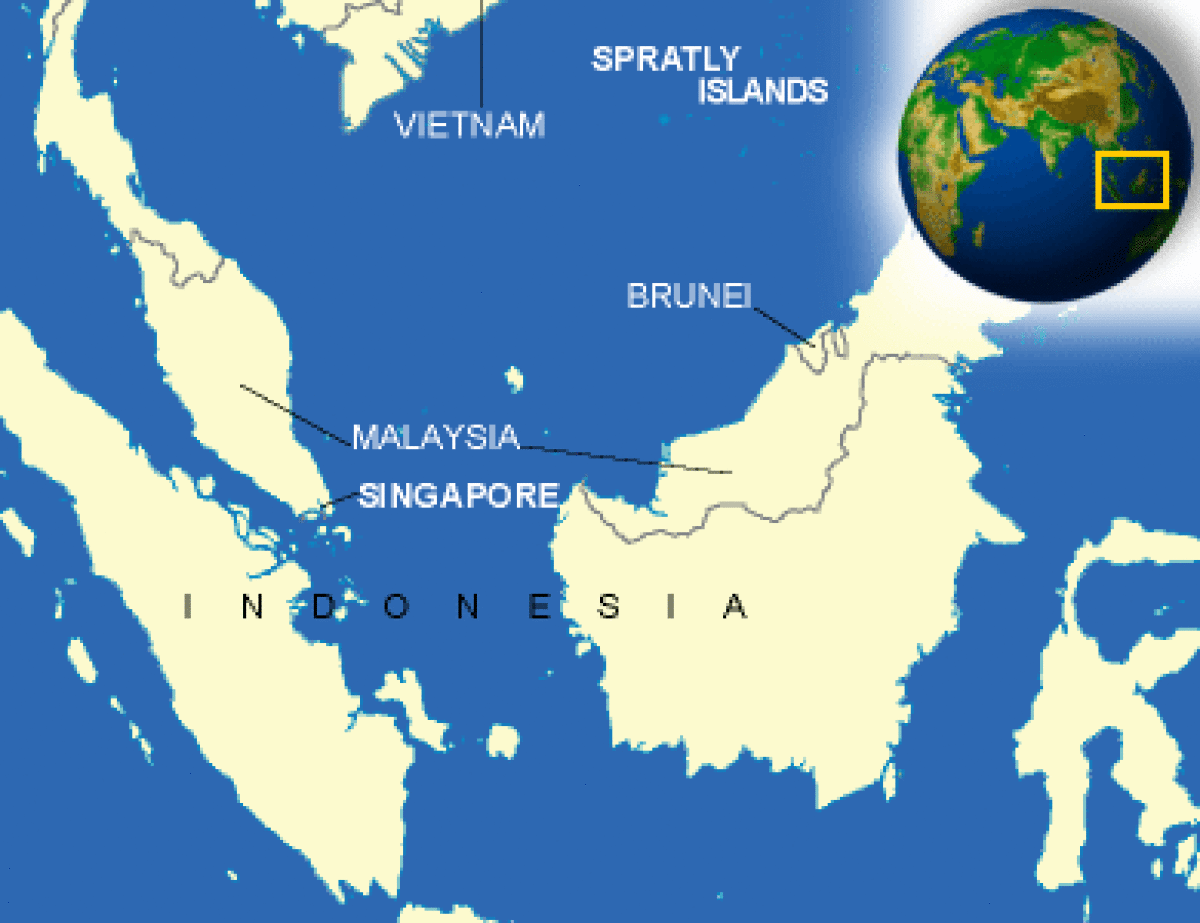
Where is Singapore located?
What countries border Singapore?
Singapore Weather
What is the current weather in Singapore?
Singapore Facts and Culture
What is Singapore famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: People in Singapore do not use first names except with close friends. They also do not talk openly about feelings... More
- Family: Singapore is an urban society and most people live with their immediate families in apartments. Today, about 78% of families... More
- Personal Apperance: Standard business attire is quite formal but can be tailored to suit Singapore's hot, tropical climate. Men should wear a... More
- Recreation: There are sports facilities throughout Singapore. Regional sports and fitness centers promote Sport For Life, a national program encouraging everyone... More
- Diet: The food of Singapore reflects its multi-ethnic society. Chinese, Malay, Peranakan, and Indian food are widely available, and Western food... More
- Food and Recipes: When Singaporeans serve food at home, they usually place dishes in the center of the table at the beginning of... More
- Dating: Arranged marriages are still common, especially among Indians and Malays. Young people may rely on parents or matchmakers to choose... More
Singapore Facts
What is the capital of Singapore?
| Capital | Singapore |
| Government Type | parliamentary republic |
| Currency | Singapore Dollar (SGD) |
| Total Area |
269 Square Miles 697 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southeastern Asia, islands between Malaysia and Indonesia |
| Language | Chinese (official), Malay (official and national), Tamil (official), English (official) |
| GDP - real growth rate | 2.2% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $85,700.00 (USD) |
Singapore Demographics
What is the population of Singapore?
| Ethnic Groups | Chinese 76.7%, Malay 14%, Indian 7.9%, other 1.4% |
| Nationality Noun | Singaporean(s) |
| Population | 6,209,660 |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.96% |
| Urban Population | 100.000000 |
Singapore Government
What type of government does Singapore have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President THARMAN Shanmugaratnam (since 14 September 2023) head of government: Prime Minister LEE Hsien Loong (since 12 August 2004) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president on the advice of the prime minister; Cabinet responsible to Parliament elections/appointments: president directly elected by simple majority popular vote for a 6-year term (no term limits); election last held on 1 September 2023 (next to be held in 2029); following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition appointed prime minister by the president; deputy prime ministers appointed by the president election results: 2023: THARMAN Shanmugaratnam elected president; percent of vote - THARMAN Shanmugaratnam (independent) 70.4%, NG Kok Song (independent) 15.7%, TAN Kin Lian (independent) 13.9% 2017: HALIMAH Yacob declared president on 13 September 2017, being the only eligible candidate 2011: Tony TAN Keng Yam elected president; percent of vote - Tony TAN Keng Yam (independent) 35.2%, TAN Cheng Bock (independent) 34.9%, TAN Jee Say (independent) 25%, TAN Kin Lian (independent) 4.9% |
| Suffrage | 21 years of age; universal and compulsory |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Singapore dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years |
| National Holiday | National Day, 9 August (1965) |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest adopted 22 December 1965 amendments: proposed by Parliament; passage requires two-thirds majority vote in the second and third readings by the elected Parliament membership and assent of the president of the republic; passage of amendments affecting sovereignty or control of the Police Force or the Armed Forces requires at least two-thirds majority vote in a referendum; amended many times, last in 2020 |
| Independence | 9 August 1965 (from Malaysian Federation) |
Singapore Video
YouTube, Expoza Travel Singapore Guide
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Singapore Geography
What environmental issues does Singapore have?
| Overview | The Republic of Singapore is a small city/state island located at the tip of the Malay Peninsula, 85 miles north of the Equator. It is a flat country of 250 square miles (641 square miles) with a maximum elevation of 581 feet. At its widest points it measures 26 miles from east to west and 14 miles north to south. |
| Climate | Vegetation is lush and tropical. Seasons are nonexistent. In this "Land of Eternal Summer," the mean high temperature is 90ºF and varies little from month to month. Humidity is high (average 70%) and annual rainfall is about 96 inches. Wet and dry seasons are not distinct, but November through February is wetter and cooler than other months. |
| Environment - Current Issues | industrial pollution; limited natural fresh water resources; limited land availability presents waste disposal problems; seasonal smoke/haze resulting from forest fires in Indonesia |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | lowland; gently undulating central plateau contains water catchment area and nature preserve |
Singapore Economy
How big is the Singapore economy?
| Economic Overview |
General economic overview of Singapore. 1. Economic Structure: Singapore has a highly developed and diversified economy, characterized by a strong emphasis on trade, finance, and technology. The country has successfully transitioned from a labor-intensive industrial economy to a knowledge-based and innovation-driven one. 2. GDP and Growth: Singapore has a high GDP per capita, making it one of the wealthiest nations in the world. The economy experienced robust growth for several decades, driven by its strategic location, open trade policies, and pro-business environment. However, growth slowed in recent years due to global economic challenges, including trade tensions and the COVID-19 pandemic. 3. Trade and Investment: Singapore is a major global hub for trade and investment. The country's open and export-oriented economy relies heavily on international trade. It has a well-developed port and serves as a regional financial and business center. Singapore has been actively promoting itself as a hub for technology and innovation, attracting foreign investment in these sectors. 4. Financial Sector: Singapore has a sophisticated and stable financial sector. The country is a global financial hub with a strong banking system, a thriving stock exchange (Singapore Exchange), and a rapidly growing fintech sector. The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) plays a crucial role in maintaining monetary stability and financial supervision. 5. Technology and Innovation: Singapore places a strong emphasis on technology and innovation. The government has implemented policies to encourage research and development, entrepreneurship, and the adoption of digital technologies. The country aims to position itself as a Smart Nation, leveraging technology for economic growth and societal improvements. 6. Government Policies: Singapore's government has a history of implementing prudent economic policies, emphasizing fiscal discipline and free-market principles. The country has also been proactive in diversifying its economy and investing in human capital through education and training. 7. Challenges: While Singapore has enjoyed economic success, it faces challenges such as an aging population, which may impact labor force dynamics and healthcare expenditures. The country is also susceptible to global economic uncertainties, given its reliance on international trade. |
| Industries | electronics, chemicals, financial services, oil drilling equipment, petroleum refining, rubber processing and rubber products, processed food and beverages, ship repair, offshore platform construction, life sciences, entrepot trade |
| Currency Name and Code | Singapore Dollar (SGD) |
| Export Partners | Malaysia 17.4%, US 15.3%, Hong Kong 9.2%, Japan 7.1%, China 5.5%, Taiwan 4.9%, Thailand 4.6%, South Korea 4.2% |
| Import Partners | Malaysia 18.2%, US 14.3%, Japan 12.5%, China 7.6%, Thailand 4.6%, Taiwan 4.6% |
Singapore News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Singapore?
Source: Google News
Singapore Travel Information
What makes Singapore a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Singapore is a small, stable, highly developed country with an elected parliamentary system of government. Tourist facilities are modern and widely available. Singapore's resident population of over five million inhabitants comprises 75% Chinese, 14% Malay, 9% Indian, and 2% others. English is widely spoken. Criminal penalties are strict and law enforcement rigorous; see sections on Entry/Exit Requirements, Special Circumstances, and Criminal Penalties below for further details.
Crime
The crime rate in Singapore is generally low. Even so, you should exercise caution when in congested areas and pay particular attention to personal belongings while in crowded shopping malls and markets, at the airport, and while traveling on public transportation. To avoid falling victim to credit card fraud, you should not carry multiple credit cards on your person, not allow credit cards to be removed from your sight, avoid giving credit card information over the phone, and use only secure Internet connections for financial transactions.Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, as not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them, you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own. While you are traveling in Singapore, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. If you break local laws in Singapore, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not in Singapore. In Singapore, you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you. Driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. In Singapore, you can be arrested for jaywalking, littering, or spitting. Commercial disputes that may be handled as civil suits in the United States can escalate to criminal cases in Singapore and may result in heavy fines and prison sentences. There are also some things that might be legal in Singapore but still illegal in the United States. You can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States.Mandatory Caning Sentences: Singapore has a mandatory caning sentence for vandalism offenses. Authorities in Singapore may also impose caning for immigration violations and other offenses. Singaporean authorities do impose these sentences on foreign nationals, including U.S. citizens. Males over the age of 50 and women are not subject to caning.
Mandatory Death Penalty for Many Narcotics Offenses: Singapore police have the authority to compel both residents and non-residents to submit to random drug analysis. They do not distinguish between drugs consumed before or after entering Singapore in applying local laws. In Singapore, detained U.S. citizens have been surprised when they were arrested for violations that would not have resulted in arrest in the United States.
There are no jury trials in Singapore. Judges hear cases and decide sentencing. The Government of Singapore does not provide legal assistance except in capital cases; legal assistance may be available in some other cases through the Law Society.
Carrying Firearms: There are very strict penalties for those who possess or carry arms, or who commit crimes with arms. Singaporean authorities define “arm” as any firearm, air-gun, air-pistol, automatic gun, automatic pistol, and any other kind of gun or pistol from which any shot, bullet, or other projectiles can be discharged or from which noxious liquid, flame, or fumes can be emitted, and any component thereof. This definition also includes any bomb or grenade and any component thereof. The unlawful possession of any arm or ammunition, including a single bullet in your luggage as you transit the airport, could result in imprisonment and caning. If you are convicted of committing a crime with an arm, you could receive punishment which could result in the maximum penalty of imprisonment for life and caning.
Engaging in sexual conduct: In Singapore, local law prohibits causing or encouraging prostitution of, or engaging in sexual relations with, a female below the age of 18. An indecent assault against anyone, male or female, regardless of age, is also prohibited. If you are convicted of facilitating or abetting the prostitution of any woman or girl, you could be sentenced to imprisonment of up to five years and a fine, or both. If the crime involves a female below the age of 16, you face an additional charge carrying a possible sentence of imprisonment of up to three years and a fine, or both.
Singapore enforces strict laws pertaining to the propriety of behavior between people and the modesty of individuals. The Singaporean law “Outrage of Modesty” is defined as an assault or use of criminal force on any person with the intent to, or the knowledge that it may, outrage the modesty of that person. Penalties may include imprisonment for up to two years, a fine, caning, or a combination thereof. Men are sometimes accused of inappropriately touching other people, often women, resulting in their prosecution and punishment under this Singaporean law. Scams involving a claim of outrage of modesty are thought to exist, and male travelers should be very cautious when frequenting popular nightspots.
Arrest notifications in Singapore: If you are arrested in Singapore, authorities of Singapore are required to notify the U.S. Embassy of your arrest. If you are concerned the Embassy may not be aware of your situation, you should request the police or prison officials to notify the Embassy of your arrest.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Good medical care is widely available in Singapore. Doctors and hospitals expect immediate payment for health services by credit card or cash and generally do not accept U.S. health insurance. Hospitals may require a substantial deposit before admitting you into the hospital for any major medical treatment. The U.S. Embassy cannot provide a letter of guarantee for payment. Recipients of health care should be aware that Ministry of Health auditors in certain circumstances may be granted access to patient medical records without the consent of the patient, and in certain circumstances physicians may be required to provide information relating to the diagnosis or treatment without the patient's consent.Despite vigorous mosquito eradication efforts, Singapore has had occasional outbreaks of mosquito-transmitted illnesses, such as dengue fever and the viral disease Chikungunya. For the most current health information regarding disease outbreaks in Singapore, visit the CDC’s website.
If you visit Singapore during a pandemic such as the 2009 H1N1 pandemic, you should expect that the Singapore government may order you to quarantine if you exhibit symptoms or have had contact with someone who has exhibited symptoms. Also, you should expect that you may be subject to quarantine if you were seated within several rows of a potentially infected person on a plane or public area or have recently traveled to countries more affected by the pandemic. You should also expect to encounter screening in public facilities such as the airport, hospitals, and museums. Please visit Singapore's Ministry of Health website for the most up-to-date information on infectious diseases in Singapore.
During the summer months, Singapore frequently experiences haze and air pollution caused by forest fires and the burning of agricultural waste in neighboring countries. Air pollution during these periods can reach levels considered hazardous to health. Please visit the website of Singapore’s National Environment Agency for the latest information on air pollution level.
Safety and Security
Threats of Terrorism: In 2001, plots were uncovered whereby Jemaah Islamiyah (JI), a terrorist organization with links to Al Qaeda, identified several Singapore government and private targets associated with the United States for possible attacks. These plans were disrupted, and the JI organization in Singapore was largely dismantled. While there have been no attacks against U.S. facilities or citizens in Singapore or against Singaporean government facilities, extremist groups in Southeast Asia have launched attacks in neighboring countries and U.S. citizens traveling in the region should closely monitor the Bureau of Consular Affairs website for the latest Travel Warnings and Travel Alerts. The Department of State remains concerned, however, that terrorist groups in the region could conduct attacks against locations where Westerners are known to congregate. Terrorist groups do not distinguish between official and civilian targets, and U.S. citizens residing in or traveling to Singapore and neighboring countries should therefore exercise caution and remain vigilant about their surroundings, particularly in areas where U.S. citizens and other Westerners live, work, congregate, shop, or visit.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Singapore, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Singapore is provided for general reference only and may not be completely accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Singapore has a highly developed and well-maintained road and highway network. Driving is done on the left-hand side of the road. Motorists should be particularly aware of motorcyclists, who often ignore lane markings. Public transportation and taxis are abundant, inexpensive, and reliable. All bus stops and trains have panels indicating all routes and stops. You should consider using these forms of transportation. The Automobile Association (AA) of Singapore provides roadside assistance, and the Land Transport Authority has rescue vehicles on the road at all hours. In addition, closed circuit cameras monitor all major roads. As with all laws in Singapore, those involving traffic rules, vehicle registration, and liability in case of accident are strictly enforced, and failure to follow them may result in criminal penalties.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
