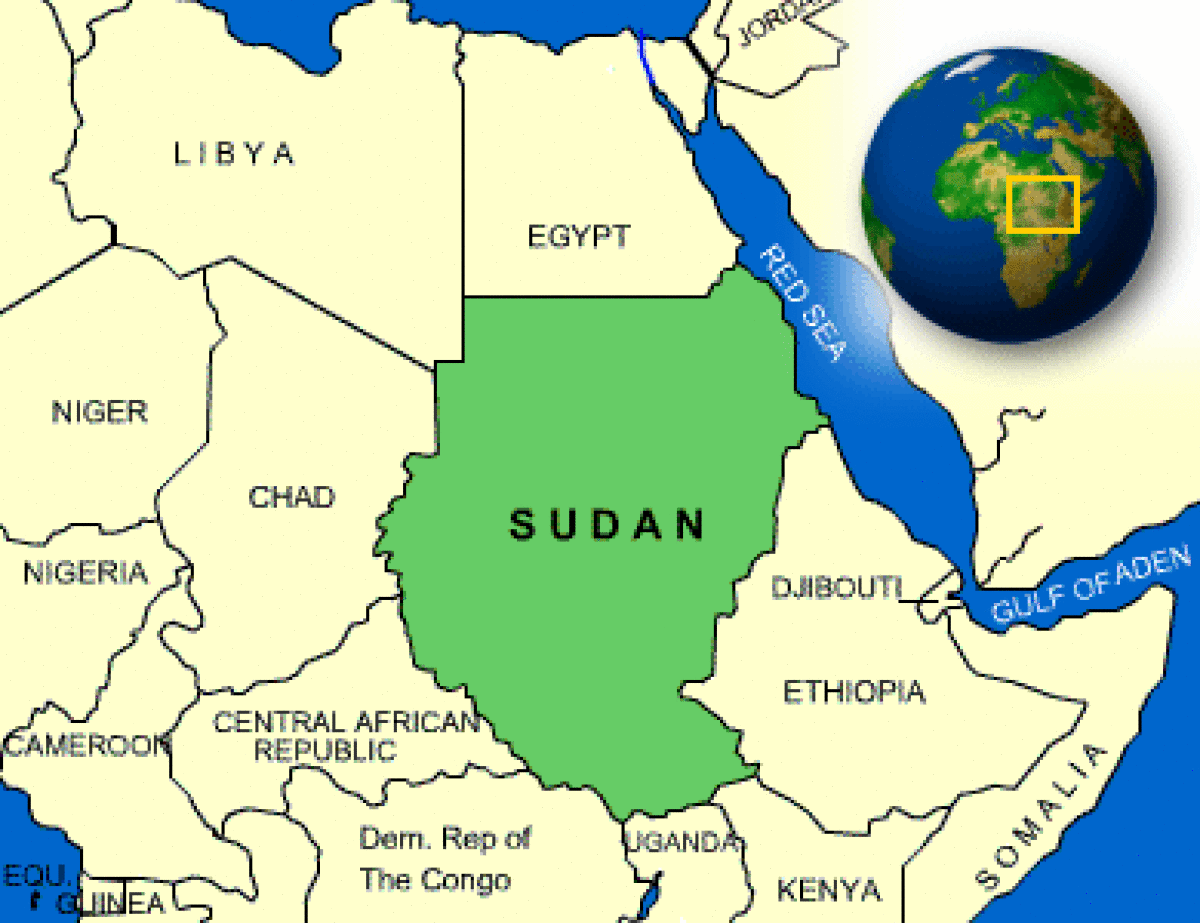
Where is Sudan located?
What countries border Sudan?
Sudan Weather
What is the current weather in Sudan?
Sudan Facts and Culture
What is Sudan famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Sudanese from the north are inclined to be polite, reserved, and cautious. They view whatever happens as the will of... More
- Family: The Sudanese family is based around the extended family and is headed by males. Men are responsible for the... More
- Personal Apperance: Southern men and women usually wear Western attire, and jewelry is a sign of affluence. Women frequently wear attractive... More
- Recreation: Soccer is popular in Sudan. Volleyball and basketball are also played. Popular traditional sports are wrestling and a kind of... More
- Diet: Locally grown foods may include grapes, okra, guavas, bananas, onions, tomatoes, cucumbers, and pineapples. A thinly layered food made from... More
- Food and Recipes: Two meals a day is the norm in Sudan. Dinner (evening) is the main meal, and it is shared by... More
- Visiting: Visiting usually takes place in the home, with close friends and family visiting spontaneously. Arrangements are made if the person... More
- Dating: Northern marriages are still arranged between cousins within families. A couple may usually, however, refuse the match. The groom's family... More
Sudan Facts
What is the capital of Sudan?
| Capital | Khartoum |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | Sudanese Point (SDG) |
| Total Area |
718,719 Square Miles 1,861,484 Square Kilometers |
| Location | north-eastern Africa, bordering the Red Sea, between Egypt and Eritrea |
| Language | Arabic (official), Nubian, Ta Bedawie, diverse dialects of Nilotic, Nilo-Hamitic, Sudanic languages, English |
| GDP - real growth rate | 3.5% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $4,500.00 (USD) |
Sudan Demographics
What is the population of Sudan?
| Ethnic Groups | black 52%, Arab 39%, Beja 6%, foreigners 2%, other 1% |
| Languages | Arabic is spoken by about half the people, but it is the official language. Many dialects are spoken throughout the country. Arabic Juba is a unique dialect used in southern urban areas for communicating between different ethnic groups. Other languages spoken are Nubian, Dinka, Azanda, Bari, Nuer and Shilluk. Those with education speak good English. |
| Nationality Noun | Sudanese (singular and plural) |
| Population | 45,561,556 |
| Population Growth Rate | 1.83% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | KHARTOUM (capital) 4.632 million |
| Urban Population | 33.200000 |
Sudan Government
What type of government does Sudan have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: Sovereign Council Chair and Commander-in-Chief of the Sudanese Armed Forces General Abd-al-Fatah al-BURHAN Abd-al-Rahman; note – the 2019 Constitutional Declaration established a collective chief of state of the "Sovereign Council," which was chaired by al-BURHAN; on 25 October 2021, al-BURHAN dissolved the Sovereign Council but reinstated it on 11 November 2021, replacing its civilian members (previously selected by the umbrella civilian coalition the Forces for Freedom and Change) with civilians of the military’s choosing but then relieved the newly appointed civilian members of their duties on 6 July 2022; note - Sovereign Council currently consists of only the 5 generals head of government: Sovereign Council Chair and Commander-in-Chief of the Sudanese Armed Forces General Abd-al-Fatah al-BURHAN Abd-al-Rahman; Acting Prime Minister Osman HUSSEIN (since 19 January 2022); note - former Prime Minister Abdallah HAMDOUK resigned on 2 January 2022; HAMDOUK served as prime minister from August 2019 to October 2019 before he was kidnapped; he was later freed and reinstated as prime minister on 21 November 2021 cabinet: most members of the Council of Ministers were forced from office in October 2021 by the military and subsequently resigned in November 2021; the military allowed a handful of ministers appointed by former armed opposition groups to retain their posts; at present, most of the members of the Council are senior civil servants serving in an acting minister capacity appointed either by Prime Minister HAMDOUK prior to his resignation or by the military elections/appointments: the 2019 Constitutional Declaration originally called for elections to be held in late 2022 at the end of the transitional period; that date was pushed back to late 2023 by the Juba Peace Agreement; the methodology for future elections has not yet been defined; according to the 2019 Constitutional Declaration, civilian members of the Sovereign Council and the prime minister were to have been nominated by an umbrella coalition of civilian actors known as the Forces for Freedom and Change; this methodology was followed in selecting HAMDOUK as prime minister in August 2019; the military purports to have suspended this provision of the 2019 Constitutional Declaration in October 2021; Prime Minister HAMDOUK’s restoration to office in November 2021 was the result of an agreement signed between him and Sovereign Council Chair BURHAN; military members of the Sovereign Council are selected by the leadership of the security forces; representatives of former armed groups to the Sovereign Council are selected by the signatories of the Juba Peace Agreement election results: NA |
| Suffrage | 17 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: the father must be a citizen of Sudan dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 1 January (1956) |
| Constitution |
history: previous 1973, 1998, 2005 (interim constitution, which was suspended in April 2019); latest initial draft completed by Transitional Military Council in May 2019; revised draft known as the "Draft Constitutional Charter for the 2019 Transitional Period," or “2019 Constitutional Declaration” was signed by the Council and opposition coalition on 4 August 2019 amendments: amended 2020 to incorporate the Juba Agreement for Peace in Sudan; the military suspended several provisions of the Constitutional Declaration in October 2021 |
| Independence | 1 January 1956 (from Egypt and the UK) |
Sudan Video
YouTube, Zann Parker Special Sudanese culture and Beja Tribe | Port Sudan
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Sudan Geography
What environmental issues does Sudan have?
| Overview |
Sudan, a vast, sun-baked land, gained independence in 1956, following the end of the Anglo-Egyptian condominium. It is the largest country in all Africa, stretching almost one million square miles. To the north are the Libyan and Nubian Deserts. In mid-country, a band of rocky semi-desert reaches from the Chad border eastward to encompass the range of arid mountains along the Red Sea coast and the Ethiopian border. The southern half consists of savanna and swampland grading into semitropical forests along the Democratic Republic of Congo and Uganda borders. Although arable, fertile land is available (37 %), but little (1.5 %) is cultivated because of inadequate irrigation. Through these diverse regions flow the White and Blue Niles, which converge at Khartoum. The Nile system, with its major tributaries-the Bahr al Ghazal, Sobat, and Atbara-is the primary water supply for northeastern Africa. Most cultivation in the north of Sudan depends on these rivers, but farther south, rainfall is sufficient for cultivation and grazing. The river is navigable only in certain areas. The Bahr al-Arab, flowing west to east, forms a natural frontier. Another, more formidable obstacle to the south is the Sudd, an immense 12,000 square miles of swamp floating vegetation into which the White Nile expands before reverting to river again. |
| Climate | Khartoum is usually hot and dusty. During May, June, and July, daily high temperatures average around 100 F or higher, with frequent dust storms called "haboobs." July, August, and part of September are not as hot, with rare but heavy rainstorms (average 8 inches yearly) and continuing haboobs. From November until April, daily temperatures range around 95 F; nights, around 70 F, are pleasant. Cool weather at night and in the early mornings sometimes requires light sweaters or blankets. |
| Border Countries | Central African Republic 1,165 km, Chad 1,360 km, Democratic Republic of the Congo 628 km, Egypt 1,273 km, Eritrea 605 km, Ethiopia 1,606 km, Kenya 232 km, Libya 383 km, Uganda 435 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | inadequate supplies of potable water; wildlife populations threatened by excessive hunting; soil erosion; desertification; periodic drought |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | generally flat, featureless plain; mountains in far south, northeast and west; desert dominates the north |
Sudan Economy
How big is the Sudan economy?
| Economic Overview |
Sudan is a country located in northeastern Africa with a population of over 44 million people. Its economy is characterized by agriculture, oil production, and small-scale industries. However, the country has faced significant economic challenges, including political instability, external debt, and economic sanctions, which have hindered its growth and development. Key Economic Indicators: GDP Growth: Sudan's GDP growth has been fluctuating in recent years due to various factors, including economic reforms, political instability, and external pressures. In 2020, the country experienced negative GDP growth due to the COVID-19 pandemic and ongoing economic challenges. Inflation: Inflation rates in Sudan have historically been high, leading to a decrease in purchasing power for citizens. The country has faced bouts of hyperinflation, causing significant economic hardships for its population. Agriculture: Agriculture is a vital sector in Sudan's economy, employing a large portion of the population. The country is known for its production of crops like sorghum, millet, and wheat. Additionally, Sudan is a major exporter of crops such as gum arabic, which is used in various industries. Oil Production: Sudan is also an oil-producing country, with oil being a crucial revenue source for the government. However, fluctuations in oil prices and the loss of significant oil-producing regions following South Sudan's secession in 2011 have impacted the sector. External Debt: Sudan has been burdened with a substantial external debt, making it challenging for the government to allocate resources effectively and invest in critical infrastructure and social programs. Economic Sanctions: Sudan has been under economic sanctions by the United States for decades due to its involvement in conflicts and human rights violations. These sanctions have restricted Sudan's access to international markets and financial institutions. Poverty and Unemployment: Sudan has faced persistent issues of poverty and high unemployment rates. The lack of job opportunities and economic opportunities has contributed to a significant informal economy. Economic Reforms: The Sudanese government has initiated economic reforms to address the country's economic challenges. This includes attempts to stabilize the currency, reduce subsidies, and attract foreign investment. |
| Industries | oil, cotton ginning, textiles, cement, edible oils, sugar, soap distilling, shoes, petroleum refining, pharmaceuticals, armaments, automobile/light truck assembly |
| Currency Name and Code | Sudanese Point (SDG) |
| Export Partners | China 53.3%, Japan 13.4%, South Africa 4.9%, Saudi Arabia 4.7% |
| Import Partners | China 20.1%, Saudi Arabia 7.5%, India 5.6%, UK 5.4%, Germany 5.4%, Indonesia 4.7%, Australia 4% |
Sudan News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Sudan?
Source: Google News
Sudan Travel Information
What makes Sudan a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Sudan is a diverse, developing country in northeastern Africa. The capital city is Khartoum. In July 2011, Sudan divided into two nations as a part of a peace agreement signed in 2005. The new nation of South Sudan was formed following a referendum on secession held in January 2011. A multi-party conflict continues in the Darfur region in western Sudan. Security conditions are adverse in Darfur and in the states of South Kordofan and Blue Nile. Transportation networks and other forms of infrastructure are poor and do not meet western standards. Even where available, water and electric services suffer frequent outages.
Crime
There is a high risk of crime in certain areas of Sudan, particularly in the Darfur and border regions. Crimes against persons or property are infrequent in Khartoum and the surrounding area, but you should follow common-sense security measures, such as keeping an eye on backpacks or hand luggage.You should try to avoid crowded public areas and public gatherings, and avoid traveling alone outside of Khartoum if possible. Report instances of anti-U.S. acts or crimes targeting westerners to the U.S. Embassy, and report all incidents of crime to the Sudanese police.
When flying, you should maintain constant contact with your baggage and ensure it does not contain illicit items, such as alcohol, pornography, or military ordinance. U.S. citizens have been removed from international airlines and detained when suspect items have been detected in checked baggage.
Carjackings and armed robberies occur in western Sudan. Sexual assault is more prevalent in areas of armed conflict. Travelers who do not use the services of reputable travel firms or knowledgeable guides or drivers are especially at risk. Travel outside of Khartoum should be undertaken with a minimum of two vehicles so that there is a backup in case of mechanical failure or other emergency. Solo camping is always risky.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Sudan you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In some places you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you. The possession or consumption of alcohol is prohibited by law in Sudan. Sudan has strict laws concerning matters of morality; for example, men and women cannot cohabitate (including staying in a hotel together) unless they are married to each other.All travelers, including journalists, must obtain a photography permit before taking any photographs. Even with a photography permit, photographing military facilities, bridges, drainage stations, broadcast stations, public utilities, slum areas, and beggars is prohibited.
If you break local laws in Sudan, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. Authorities have been known to hold a foreigner’s passports during investigations, which can take weeks or months to conclude. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not while you’re in Sudan. Persons violating Sudan’s laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Sudan are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. Attempting to convert Muslims to another religion is illegal in Sudan, and it is a crime punishable by imprisonment and even death.
There are also some acts that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States.
Based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements with certain countries, and customary international law, if you are arrested in Sudan, you have the option to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate of your arrest, and to have communications from you forwarded to the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate. However, it is not unusual that the U.S. Embassy is not notified by the Government of Sudan of the arrest of a U.S. citizen. Even if notified, the U.S. Embassy is often not allowed access to arrested/detained U.S. citizens.
Dual-nationals must be aware that the Sudanese government may not recognize your U.S. citizenship, and if detained/arrested, you may be considered a Sudanese citizen only.
Languages
Arabic is spoken by about half the people, but it is the official language. Many dialects are spoken throughout the country. Arabic Juba is a unique dialect used in southern urban areas for communicating between different ethnic groups. Other languages spoken are Nubian, Dinka, Azanda, Bari, Nuer and Shilluk. Those with education speak good English.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Persons with conditions which may require medical treatment are strongly discouraged from traveling to Sudan. Medical facilities in Khartoum fall short of U.S. standards; outside the capital, few facilities exist and hospitals and clinics are poorly equipped. Emergency medical treatment is provided without cost for the first 24 hours, but after that, payment will be required. For all other non-emergent medical treatment, payment in cash must be made in advance. Ambulance services are not available outside Khartoum. Medicines are available only intermittently; you should bring sufficient supplies of needed medicines in clearly marked containers.Malaria is prevalent in all areas of Sudan. The strain is resistant to chloroquine and can be fatal. In 2012, there was a large outbreak of Yellow Fever in Darfur, which resulted in 171 deaths. Consult a health practitioner before traveling, obtain suitable anti-malarial drugs, ensure that all your vaccines are up to date, and use protective measures, such as insect repellent, protective clothing, and mosquito nets. If you become ill with a fever or a flu-like illness while in Sudan, or within a year after departure, you should promptly seek medical care and inform your physician of your travel history and the kind of anti-malarial drugs used.
Safety and Security
The Department of State has issued a Travel Warning for Sudan advising U.S. citizens of the risks of travel to Sudan, urging U.S. citizens to avoid all travel to the Darfur region of Sudan, the Blue Nile, and Southern Kordofan States, and advising U.S. citizens to consider carefully the risks of travel in other areas of Sudan.On January 1, 2008, a group of assailants shot and killed two U.S. Embassy employees – a USAID officer and a Sudanese national driver. The attack was found to be ideologically motivated, and the assailants were convicted and sentenced under Sudanese law in 2009. The four men have since escaped from prison and two are still at large.
Aid workers and government employees from Western countries have been the targets of kidnappings in the Darfur region. In May 2010, a U.S. citizen employed by a humanitarian relief organization was kidnapped in Darfur, and was held for several months before being released.
Since June 2012, there have been increased incidents of anti-government protests, resulting in the arrest of at least one U.S. citizen. U.S. citizens should avoid crowds and demonstrations as they can become confrontational and quickly escalate into violence. Demonstrations may also occur in other areas of the country, and we recommend U.S. citizens throughout Sudan exercise caution.
Terrorist groups are known to operate in Sudan, and these groups seek opportunities to carry out attacks against U.S. and European interests. Terrorist actions may include suicide operations, bombings, or kidnappings. You should be aware of the risk of indiscriminate attacks on civilian targets in public places, including tourist sites and locations where westerners are known to congregate, and commercial operations associated with U.S. or Western interests. Terrorists are known to have targeted both official facilities and residential compounds. You should exercise utmost caution at all times.
The Embassy’s ability to provide consular services outside of the Khartoum area, including emergency assistance, is severely limited.Many areas of Sudan are extremely difficult to access, and travel in these areas is hazardous. Outside the major cities infrastructure is extremely poor, medical care is limited, and there are few facilities for tourists.
Conflict among various armed groups and government forces continues throughout the entire Darfur region. Banditry and lawlessness are prevalent in all of Darfur. Over one and a half million Darfuris live in camps for internally displaced persons, and receive humanitarian assistance for basic needs such as food, water, and shelter. Expatriate humanitarian workers have been the targets of kidnappings, carjackings, and burglaries.
Occasional clashes between armed groups representing communal interests continue to occur in areas of central and eastern Sudan. Banditry also occurs. Sudan is Africa’s third-largest country in physical area, and shares porous land borders with Chad, the Central African Republic, Uganda, Democratic Republic of Congo, South Sudan, Egypt, Ethiopia, and Eritrea. Conflict in these countries occasionally spills over into Sudan.
The secession of South Sudan in July 2011 has been accompanied by an increase in armed violence in states on the South Sudan border, particularly in Abyei, Southern Kordofan, and Blue Nile. In ongoing disputes in these regions, the Sudanese Armed Forces have conducted airstrikes throughout the region, and have engaged in ground clashes with the Sudanese People’s Liberation Army - Northern Sector. Non-governmental organizations have been expelled from the areas, and the United Nations operates with minimal staffing in government-controlled areas only.
U.S. citizens considering sea travel in Sudan's coastal waters should exercise caution as there have been incidents of armed attacks and robberies by unknown groups in recent years, including one involving U.S. vessels. Exercise extreme caution, as these groups are considered armed and dangerous. When transiting in and around the Horn of Africa and/or in the Red Sea near Yemen, vessels should convoy in groups and maintain good communications contact at all times. Marine channels 13 and 16 VHF-FM are international call-up and emergency channels, and are commonly monitored by ships at sea. 2182 MHz is the HF international call-up and emergency channel. Wherever possible, travel in trafficked sea-lanes, and avoid loitering in or transiting isolated or remote areas. In case of emergency, contact the nearest U.S. Embassy or Consulate. In the event of an attack, consider activating Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacons.
The United States Maritime Administration (MARAD) has advised that elevated regional tensions have increased the risk of maritime attacks being conducted by extremist to vessels operating in the Gulf of Oman, North Arabian Sea, Gulf of Aden, and the Bab el Mandeb regions.
MARAD recommends vessels at anchor, operating in restricted maneuvering environments, or at slow speeds should be especially vigilant, and report suspicious activity. U.S. flag vessels that observe suspicious activity in the area are advised to report such suspicious activity or any hostile or potentially hostile action to COMUSNAVCENT battlewatch captain at phone number 011-973-1785-3879. All suspicious activities and events are also to be reported to the U.S. Coast Guard National Response Center at the following toll free telephone: 1-800-424-8802, direct telephone 202-267-2675, or TDD 202-267-4477. The complete advisory is available on the MARAD website at www.MARAD.DOT.gov.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Sudan, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States.Road conditions throughout Sudan are hazardous due to erratic driver behavior, pedestrians, and animals in the roadways, and vehicles that are overloaded or lack basic safety equipment. Only major highways and some streets in the cities are paved; many roads are narrow, rutted, and poorly maintained. While there are functioning traffic signals on major streets in Khartoum, there are virtually none in other parts of the country. Local drivers often do not observe conventions for the right-of-way, stop on the road without warning, and frequently exceed safe speeds for road, traffic, and weather conditions. Driving at night is dangerous and should be avoided if possible; many vehicles operate without lights.
In northern and western Sudan, dust and sand storms, known as haboobs, greatly reduce visibility when they occur. Roads in these areas can be quickly covered with shifting sand at any season of the year. Roads in southern Sudan are often impassable during the rainy season which usually lasts from March to October. Spare tires, parts, and fuel should be taken when traveling in remote areas, as service stations are separated by long distances.
U.S. citizens are subject to the laws of the country in which they are traveling, including traffic laws. In Sudan, vehicles have the steering wheel on the left side and drivers use the right side of the road.
Traffic from side streets on the right has the right-of-way when entering a cross street, including fast-moving main streets. Traffic on the right has the right-of-way at stops. Right turns on a red light are prohibited. Speed limits are not posted, but the legal speed limit for passenger cars on inter-city highways is 120 kph (about 75 mph), while in most urban areas, the limit is 60 kph (about 35 mph). The speed limit in congested areas and school zones is 40 kph (about 25 mph).
Many local drivers carry no insurance despite the legal requirement that all motor vehicle operators purchase third-party liability insurance from the government. Persons involved in an accident resulting in death or injury must report the incident to the nearest police station or police officer as soon as possible. Persons found at fault can expect fines, revocation of driving privileges, and jail sentences, depending on the nature and extent of the accident. Persons convicted of driving under the influence of alcohol face fines, jail sentences, and flogging.
U.S. citizens may use their U.S. driver's license for up to 90 days after arrival in Sudan, and then must carry either an International Driving Permit (IDP) or a Sudanese driver's license. There are no restrictions on vehicle types, including motorcycles and motorized tricycles.
Public transportation exists in cities and between major urban areas. Passenger facilities are basic and crowded, especially during rush hours and periods of seasonal travel. Schedules are unpublished and subject to change without notice. There is routine passenger trainservice on the route from Khartoum to Wadi Halfa (on the border with Egypt) and to Port Sudan (on the Red Sea). Bus service between major cities is regular and inexpensive. Intra-city bus service in the major urban areas is by small and large buses, and vans. Many drivers of these vehicles have little training and are reckless, and the vehicles are often poorly maintained. Most buses and bus stops are privately operated and unmarked. Taxis are available in the major cities at hotels, tourist sites, and government offices. Motorized rickshaws, in common use in Khartoum, are unsafe. Travelers are encouraged to hire cars and drivers from reputable sources with qualified drivers and safe vehicles. While there is some public transit to rural communities by irregularly scheduled mini-buses, many areas lack any public transportation.
You should be extremely careful in crossing roads in Sudan. Crosswalks do not exist, and incidents of cars striking pedestrians do occur.
