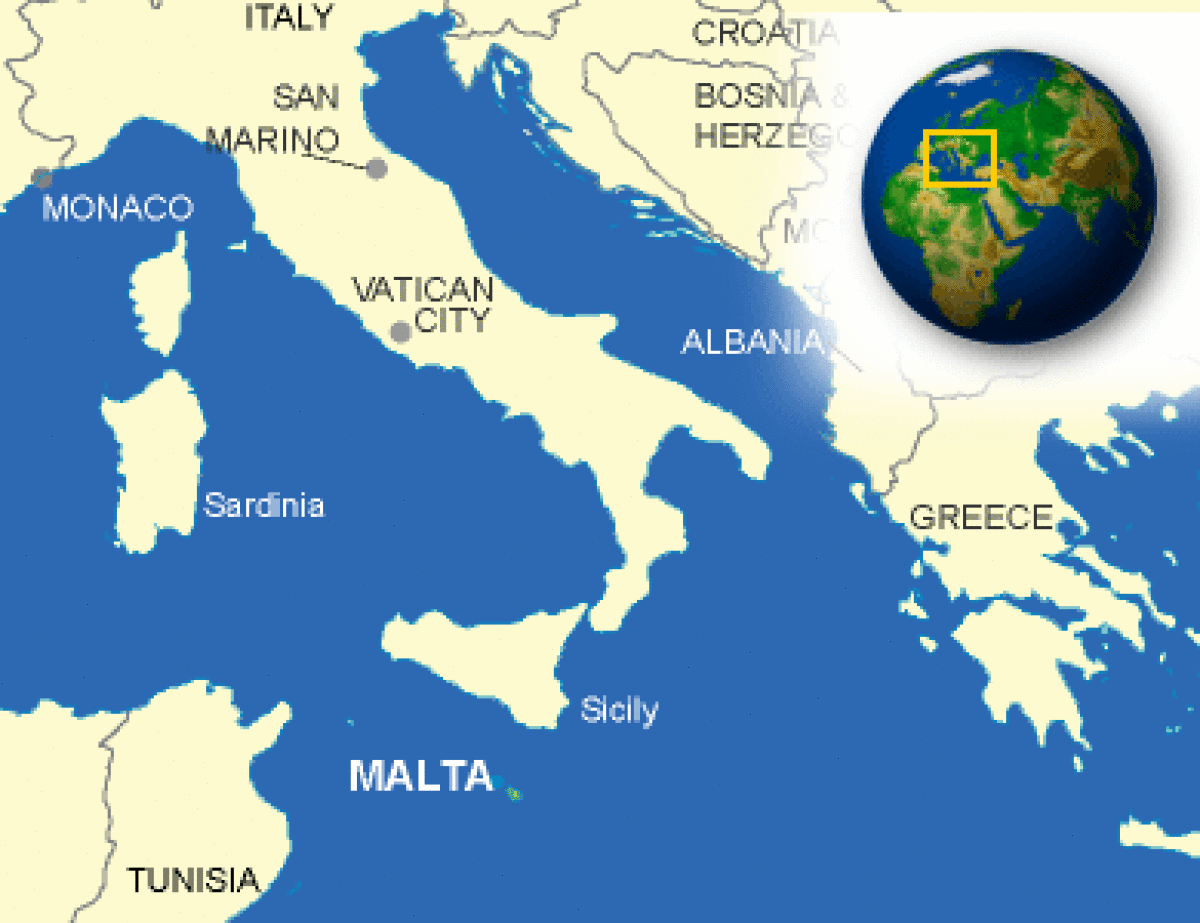
Where is Malta located?
What countries border Malta?
Malta Weather
What is the current weather in Malta?
Malta Facts and Culture
What is Malta famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: The Maltese are known for their hospitality, and generosity. The family is of great importance, and children stay in close... More
- Family: The man is the head of the family, but women often exercise power in home. For example, women usually control... More
- Personal Apperance: Style and quality of clothing define social status. The Maltese follow European fashions. People pay attention to hairstyle, and avoid... More
- Recreation: Soccer is the most popular sport in Malta. More
- Diet: The Maltese diet often combines Italian and British foods. Breakfast ranges from toast, cereal, and tea to full fried breakfast.... More
- Food and Recipes: Most families like to eat together. Breakfast and lunch are light meals, with lunch often consisting of a salad or... More
- Visiting: Going out to socialize is a favorite activity for most Maltese. It is polite to arrange a visit in advance. More
- Dating: Dating starts between age fourteen and sixteen, but are only 'going steady' when parents have been formally introduced. Engagements usually... More
Malta Facts
What is the capital of Malta?
| Capital | Valletta |
| Government Type | parliamentary republic |
| Currency | Euros (EUR) |
| Total Area |
122 Square Miles 316 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southern Europe, islands in the Mediterranean Sea, south of Sicily (Italy) |
| Language | Maltese (official), English (official) |
| GDP - real growth rate | 3.4% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $34,700.00 (USD) |
Malta Demographics
What is the population of Malta?
| Ethnic Groups | Maltese (descendants of ancient Carthaginians and Phoenicians, with strong elements of Italian and other Mediterranean stock) |
| Languages | The Maltese language has a Semitic structure derived from a early form of Arabic. Both Maltese and English are official languages. The written form of Maltese is a Latin script, and it is used in commerce, education and business. However, English is a second language that is taught in school. |
| Nationality Noun | Maltese (singular and plural) |
| Population | 457,267 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.34% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | VALLETTA (capital) 198,000 |
| Urban Population | 94.800000 |
Malta Government
What type of government does Malta have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President George VELLA (since 4 April 2019) head of government: Prime Minister Robert ABELA (13 January 2020) cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the president on the advice of the prime minister elections/appointments: president indirectly elected by the House of Representatives for a single 5-year term; election last held on 2 April 2019 (next to be held by April 2024); following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the president for a 5-year term; deputy prime minister appointed by the president on the advice of the prime minister election results: 2024: Myriam SPITERI DEBONO elected president; House of representatives vote - unanimous; SPITERI DEBONO takes office on 4 April 2024 2020: Robert ABELA (PL) appointed prime minister 2019: George VELLA (PL) elected president; House of Representatives vote - unanimous |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age (16 in local council elections); universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Malta dual citizenship recognized: no residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 21 September (1964); Republic Day, 13 December (1974) |
| Constitution |
history: many previous; latest adopted 21 September 1964 amendments: proposals (Acts of Parliament) require at least two-thirds majority vote by the House of Representatives; passage of Acts requires majority vote by referendum, followed by final majority vote by the House and assent of the president of the republic; amended many times, last in 2020 |
| Independence | 21 September 1964 (from the UK) |
Malta Video
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Malta Geography
What environmental issues does Malta have?
| Overview |
Malta is a small archipelago of six islands and islets in the center of the Mediterranean and takes its name from the main island in the group. Malta (95 sq. mi.) is the largest island of the group, followed by Gozo (26 sq. mi.) and Comino (1 sq. mi.). Malta, Gozo, and Comino are inhabited, while Cominotto, Filfla, and St. Paul's are small, uninhabited islets. The longest distance on Malta is about 17 miles, from southeast to northwest; the widest part is 9 miles from east to west. The same figures for Gozo are 9 miles and 4-1/2 miles. Gozo lies northwest of Malta across a narrow channel. Malta's shoreline is 85 miles; Gozo's is 27. The islands are formed of soft limestone which is the characteristic construction material used in most Maltese buildings. The terrain consists of low hills with terraced fields on slopes, with two small seasonal lakes and a few seasonal streams. Northern Malta is a series of ridges, valleys, bays, and promontories. The western side of the island is dominated by 800-foot high cliffs. Shorelines are very rocky, but a few sandy beaches exist. The soil on the islands is generally thin and rocky, although in some valleys it is terraced and farmed. Gozo has more arable land than Malta, and Comino is almost completely barren. In summer, the landscape is brown and arid, but soon after fall the rains begin, and the countryside turns green. Malta lies near the center of the Mediterranean Sea, 58 miles south of Sicily, 180 miles from the North African coast. Gibraltar is 1,141 miles to the west, and Alexandria (Egypt) 944 miles to the east. |
| Climate | The climate is subtropical in the summer, temperate the rest of the year, with occasional fog and rare frosts. Temperatures range from 35°F in winter to 95°F in summer, with brief periods above 100°F in August and early September. The driest months are May and July. Annual rainfall averages 19-22 inches, but fluctuates to less than 10 inches. The rains are heaviest from November to January and ease off slightly in February and March. Summer is hot and humid, with almost cloudless skies. The "scirocco," a warm humid southeast wind, occurs in spring and from mid-September to mid-October. The "gregale," a cold wind from the east and northeast in the winter, occasionally reaches gale forces of 70 miles per hour. Winter is chilly and damp with occasional heavy downpours, but also with many fine sunny days. |
| Environment - Current Issues | very limited natural fresh water resources; increasing reliance on desalination |
| Environment - International Agreements |
party to: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | mostly low, rocky, flat to dissected plains; many coastal cliffs |
Malta Economy
How big is the Malta economy?
| Economic Overview |
Malta’s free market economy – the smallest economy in the euro-zone – relies heavily on trade in both goods and services, principally with Europe. Malta produces less than a quarter of its food needs, has limited fresh water supplies, and has few domestic energy sources. Malta's economy is dependent on foreign trade, manufacturing, and tourism. Malta joined the EU in 2004 and adopted the euro on 1 January 2008. Malta has weathered the euro-zone crisis better than most EU member states due to a low debt-to-GDP ratio and financially sound banking sector. It maintains one of the lowest unemployment rates in Europe, and growth has fully recovered since the 2009 recession. In 2014 through 2016, Malta led the euro zone in growth, expanding more than 4.5% per year. Malta’s services sector continues to grow, with sustained growth in the financial services and online gaming sectors. Advantageous tax schemes remained attractive to foreign investors, though EU discussions of anti-tax avoidance measures have raised concerns among Malta’s financial services and insurance providers, as the measures could have a significant impact on those sectors. The tourism sector also continued to grow, with 2016 showing record-breaking numbers of both air and cruise passenger arrivals. Malta’s GDP growth remains strong and is supported by a strong labor market. The government has implemented new programs, including free childcare, to encourage increased labor participation. The high cost of borrowing and small labor market remain potential constraints to future economic growth. Increasingly, other EU and European migrants are relocating to Malta for employment, though wages have remained low compared to other European countries. Inflation remains low. |
| Industries | tourism; electronics, ship building and repair, construction; food and beverages, textiles, footwear, clothing, tobacco |
| Currency Name and Code | Euros (EUR) |
| Export Partners | Singapore 17.3%, US 11.4%, UK 9.4%, Germany 9.2%, France 7.3%, China 6.5%, Italy 5.9% |
| Import Partners | Italy 18.2%, France 12%, South Korea 11.3%, UK 7.5%, Germany 5.3%, Singapore 5.3%, Japan 4.9%, US 4.6%, Spain 4.2% |
Malta News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Malta?
Source: Google News
Malta Travel Information
What makes Malta a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Malta is a small, developed, democratic Mediterranean island nation, positioned as a cultural stepping-stone between Europe and North Africa. Malta became a member of the European Union in 2004, and became a full member of the Schengen Area in 2008. Tourist facilities of all categories are widely available.
Crime
Malta is rated Medium for crime by the Department of State. Most reported incidents are crimes of opportunity for immediate gain, such as simple assault, pick-pocketing, and petty theft. In general, criminals in Malta have avoided using violence in order to achieve their objective. However, while armed robberies, sexual assaults, and homicides are not as common as in some major U.S. cities, they do occur. . Practice the same good, common-sense personal security precautions that are part of everyday life in urban areas within the United States, particularly when spending time in areas frequented by tourists. Secure your valuables and be aware of pickpockets and purse snatchers; such criminals focus on areas and establishments frequented by tourists. You should be careful in the Paceville nightclub area, where excessive drinking and poor crowd control can lead to violence, including some that appears to be racially motivated. Theft of unattended personal property and car stereos from vehicles is also a common problem. Panhandling is almost non-existent in Malta.Don’t buy counterfeit or pirated goods, even if they are widely available. The bootlegs are illegal to bring back into the United States, and if you purchase them, you are also breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Malta, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own, and criminal penalties vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in Malta, but still illegal in the United States. For example, you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is also a crime prosecutable in the United States.If you break local laws in Malta, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not in any country you visit. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Malta are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. Judicial proceedings in Malta typically last five to seven years and are characterized by lengthy and sometimes unpredictable delays between hearings. Foreign nationals can expect to be denied bail while a court case is ongoing, which can result in lengthy periods of pre-trial detention ranging from several months to several years. Obtaining no-fee legal aid can be a slow and difficult process, delaying already lengthy judicial proceedings.
IF ARRESTED: If you are arrested in Malta, authorities of Malta are required to notify the U.S. Embassy of your arrest. If you are concerned the Department of State may not be aware of your situation, you should request the police or prison officials to notify the U.S. Embassy of your arrest. Malta’s laws on rights of arrestees are different from the United States. For example, once you have contacted a lawyer, you lose your right to remain silent.
Languages
The Maltese language has a Semitic structure derived from a early form of Arabic. Both Maltese and English are official languages. The written form of Maltese is a Latin script, and it is used in commerce, education and business. However, English is a second language that is taught in school.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical care is available through public and private hospitals. The quality of medical care in Malta ranges from adequate to good. Medical Specialists are few with many choosing to work in other countries. Private hospitals generally offer a higher standard of service than the public hospitals. One public hospital in Malta has adequate emergency room and trauma facilities, but its capacity is limited.
Safety and Security
o indigenous terrorist or extremist groups are known to be active in Malta and no foreign terrorist organization has carried out an attack against U.S. interests in Malta in recent years. Due to its geographic location and status as an EU-member country, Malta could be used as a possible staging point for terrorists desiring to enter other EU countries or as a refuge for terrorists attempting to evade detection. U.S. citizens are reminded to remain alert and aware of their immediate surroundings and exercise caution when out and about in Malta.
