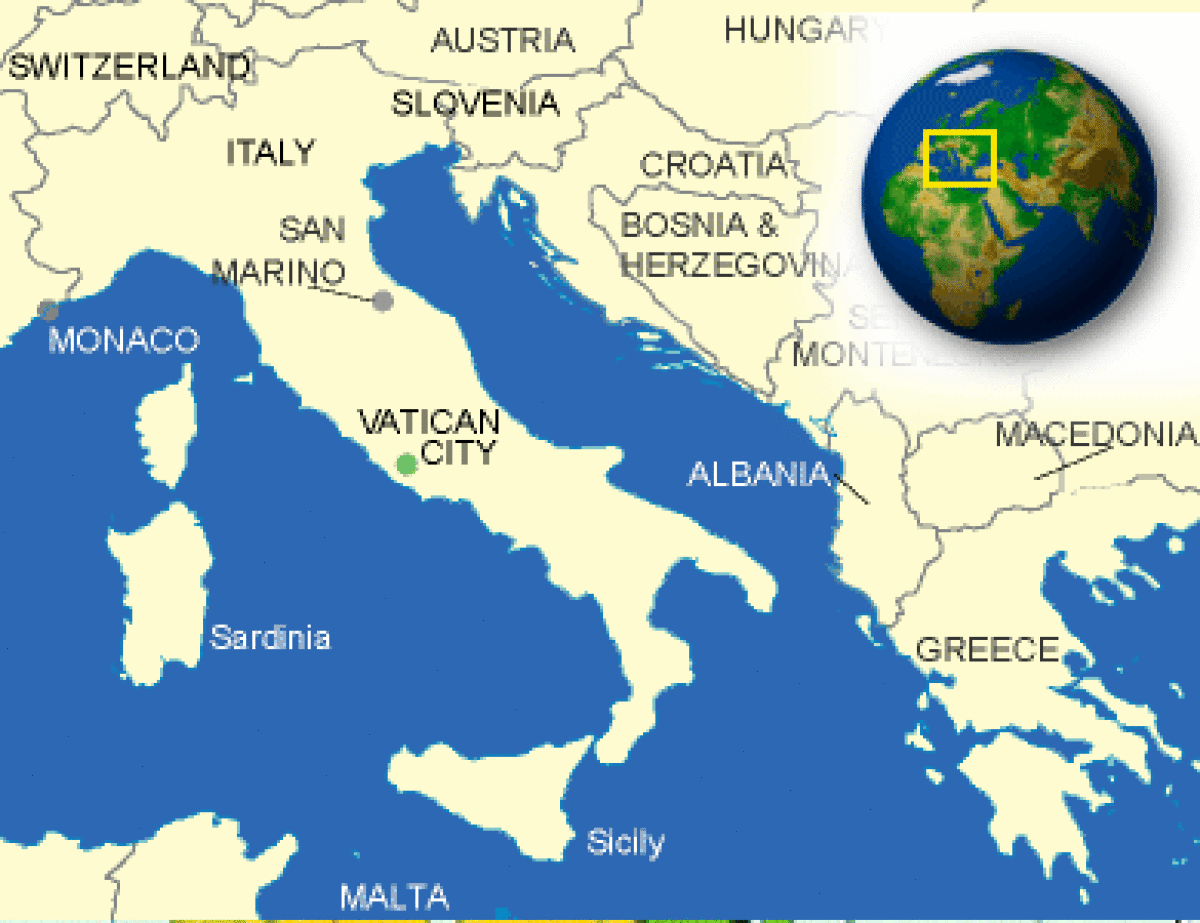
Where is Holy See located?
What countries border Holy See?
Holy See Facts
What is the capital of Holy See?
| Capital | Vatican City |
| Government Type | Ecclesiastical elective monarchy; self-described as an "absolute monarchy" |
| Currency | Euro (EUR) |
| Total Area |
0 Square Miles 0 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southern Europe, an enclave of Rome (Italy) |
| Language | Italian, Latin, French, various other languages |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $0.00 (USD) |
Holy See Demographics
What is the population of Holy See?
| Nationality Noun | None |
| Population | 1,000 |
| Urban Population | 0.000000 |
Holy See Government
What type of government does Holy See have?
| Executive Branch |
Chief of State: Pope FRANCIS (since 13 March 2013) Dead of Government: President of the Pontifical Commission for the State of Vatican City and President of the Governorate of the Vatican City State is Fernando VERGEZ ALZAGA (since 1 October 2021) Cabinet: Pontifical Commission for the State of Vatican City appointed by the pope Elections/Appointments: pope elected by the College of Cardinals, usually for life or until voluntary resignation; election last held on 13 March 2013 after the resignation of Pope BENEDICT XVI (next to be held after the death or resignation of the current pope); Secretary of State appointed by the pope Election results: 2013: Jorge Mario BERGOGLIO, former Archbishop of Buenos Aires, elected Pope FRANCIS |
| Suffrage | Election of the pope is limited to cardinals less than 80 years old |
| Citizenship |
Citizenship by birth: No Citizenship by descent only: No Dual citizenship recognized: No Residency requirement for naturalization: Not applicable Note: In the Holy See, citizenship is acquired by law, ex iure, or by adminstrative decision; in the first instance, citizenship is a function of holding office within the Holy See as in the case of cardinals resident in Vatican City or diplomats of the Holy See; in the second instance, citizenship may be requested in a limited set of circumstances for those who reside within Vatican City under papal authorization, as a function of their office or service, or as the spouses and children of current citizens; citizenship is lost once an individual no longer permanently resides in Vatican City, normally reverting to the citizenship previously held |
| National Holiday | Election Day of Pope FRANCIS, 13 March (2013) |
| Constitution |
History: Previous 1929, 1963; latest promulgated November 2000, effective 22 February 2001 (Fundamental Law of Vatican City State, the main governing document of the Vatican's civil entities); the Roman Curia is the administrative apparatus – the departments and ministries – used by the pontiff in governing the church; note - Pope Francis in October 2013, instituted a 9-member Council of Cardinal Advisers to reform the Roman Curia to include writing a new constitution; in June 2018, Pope Francis approved the Council of Cardinals' first draft of the new apostolic constitution, Predicate Evangelium (Preach the Gospel); it became effective 5 June 2022, replacing Pastor Bonus, the previous governing document of the Roman Curia Amendments: Note - although the Fundamental Law of Vatican City State makes no mention of amendments, Article Four (drafting laws), states that this legislative responsibility resides with the Pontifical Commission for Vatican City State; draft legislation is submitted through the Secretariat of State and considered by the pope |
| Independence | 11 February 1929; note - the three treaties signed with Italy on 11 February 1929 acknowledged, among other things, the full sovereignty of the Holy See and established its territorial extent; however, the origin of the Papal States, which over centuries varied considerably in extent, may be traced back to A.D. 754 |
Holy See Video
YouTube, Devin Graham Italy Takeover! Rome, Pisa & Vatican City
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Holy See Geography
What environmental issues does Holy See have?
| Overview | The state of Vatican City is the smallest sovereign state in the world. A tiny enclave within the city of Rome, it occupies 109 acres and is almost completely surrounded by medieval walls. As a result of the Lateran Pacts of 1929, the Italian Government granted St. Peter’s Basilica and Square and the surrounding area within the Vatican walls as the Holy See’s sovereign and independent territorial base. Besides St. Peter’s, Vatican City also includes the Apostolic Palace, administrative and residential buildings, museums, archives, and libraries, a cemetery, and gardens covering almost one-third of the entire area. Thirteen other buildings in Rome, as well as the Pope’s summer residence at nearby Castel Gandolfo, enjoy extraterritoriality under the terms of the Lateran Pacts. |
| Climate | Rome's climate is mild and the area is noted for its frequent sunny days. Summers are hot (and sometimes humid) and winters are cold (overcoats necessary). |
| Border Countries | Italy 3.2 km |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party to: Ozone Layer Protection Signed, but not ratified: Air Pollution, Environmental Modification |
Holy See Economy
How big is the Holy See economy?
| Economic Overview |
The Holy See is supported financially by a variety of sources, including investments, real estate income, and donations from Catholic individuals, dioceses, and institutions; these help fund the Roman Curia (Vatican bureaucracy), diplomatic missions, and media outlets. Moreover, an annual collection taken up in dioceses and from direct donations go to a non-budgetary fund, known as Peter's Pence, which is used directly by the pope for charity, disaster relief, and aid to churches in developing nations. The separate Vatican City State budget includes the Vatican museums and post office and is supported financially by the sale of stamps, coins, medals, and tourist mementos as well as fees for admission to museums and publication sales. Revenues increased between 2010 and 2011 because of expanded operating hours and a growing number of visitors. However, the Holy See did not escape the financial difficulties experienced by other European countries; in 2012, it started a spending review to determine where to cut costs to reverse its 2011 budget deficit of $20 million. The Holy See generated a modest surplus in 2012 before recording a $32 million deficit in 2013, driven primarily by the decreasing value of gold. The incomes and living standards of lay workers are comparable to those of counterparts who work in the city of Rome so most public expenditures go to wages and other personnel costs;. In February 2014, Pope FRANCIS created the Secretariat of the Economy to oversee financial and administrative operations of the Holy See, part of a broader campaign to reform the Holy See’s finances. |
| Currency Name and Code | Euro (EUR) |
Holy See News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Holy See?
Source: Google News
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
