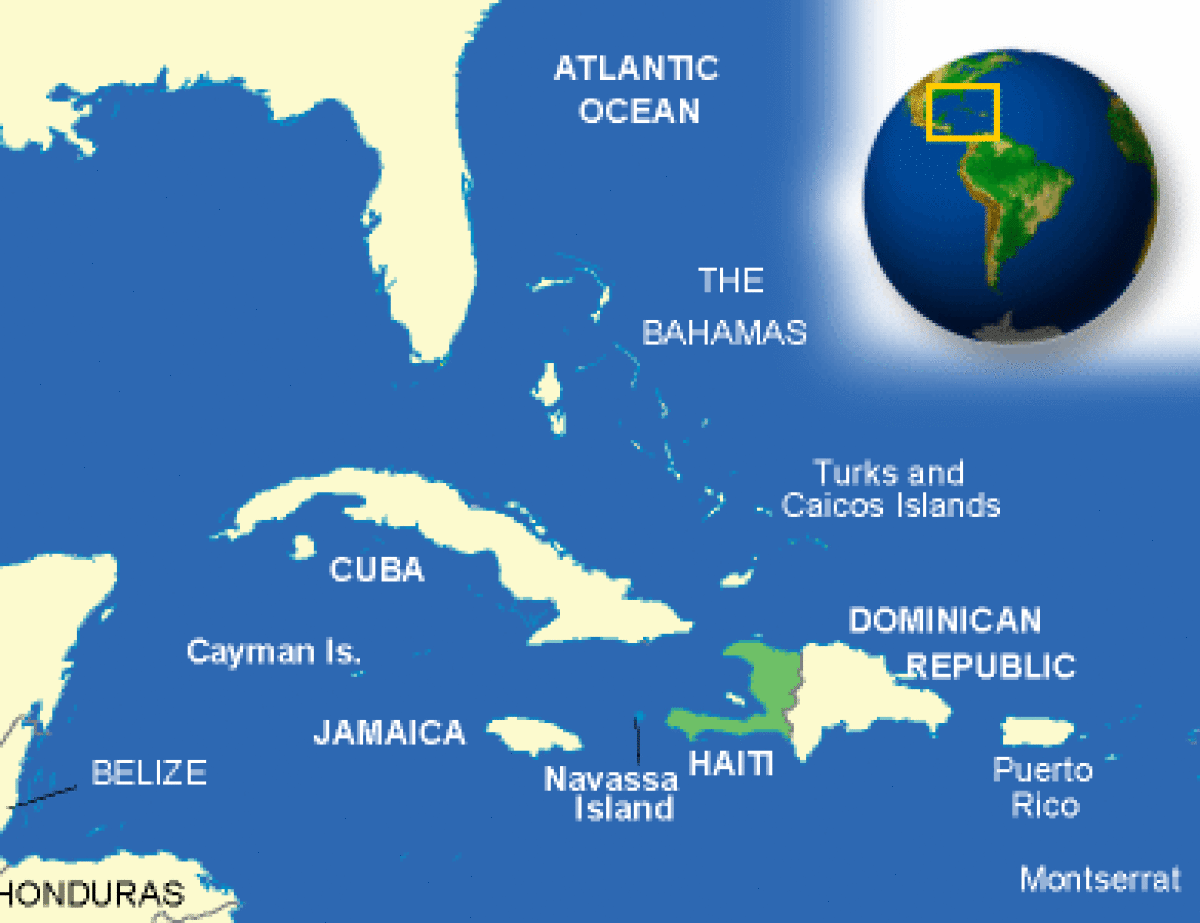
Where is Haiti located?
What countries border Haiti?
Haiti Weather
What is the current weather in Haiti?
Click for weather forecast
Haiti Facts and Culture
What is Haiti famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Haitians are friendly, generous and proud of their history and culture. More
- Family: Haitian society is matriarchal, especially where child-rearing and family life is concerned. Haitian families consist of parents and children. In... More
- Personal Apperance: Casual warm weather clothing is traditional in Haiti. Western Style clothing is worn in Urban areas. Tee-Shirts and shorts or... More
- Recreation: Soccer is the national sport of Haiti. Cockfighting is also popular. In the Haitian streets you can watch a version of... More
- Diet: The main elements of the Haitian diet are corn, cassava, millet, rice and fruit. Tropical fruits such as pineapples, mangoes,... More
- Visiting: Haitians express their love of music and dance in “bamboches”. Bamboches are social gatherings where the dancing is pou' plaisi'... More
Haiti Facts
What is the capital of Haiti?
| Capital | Port-au-Prince |
| Government Type | Semi-presidential republic |
| Currency | Haitian Gourde (HTG) and US Dollar (USD) |
| Total Area |
10,714 Square Miles 27,750 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Caribbean, western one-third of the island of Hispaniola, between the Caribbean Sea and the North Atlantic Ocean, west of the Dominican Republic |
| Language | French (official), Creole (official) |
| GDP - real growth rate | 2.5% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $1,800.00 (USD) |
Haiti Demographics
What is the population of Haiti?
| Ethnic Groups | Black 95%, mulatto and white 5% |
| Nationality Noun | Haitian(s) |
| Population | 11,067,777 |
| Population - note | Note: Estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.99% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | PORT-AU-PRINCE (capital) 2.207 million |
| Urban Population | 53.400000 |
Haiti Government
What type of government does Haiti have?
| Executive Branch |
Chief of State: President (vacant); note - Acting Prime Minister Ariel HENRY assumed executive responsibilities, including naming Cabinet members, following the assassination of President MOISE on 7 July 2021 Head of Government: Acting Prime Minister Ariel HENRY (since 20 July 2021) Cabinet: Cabinet chosen by the prime minister in consultation with the president; parliament must ratify the Cabinet and Prime Minister's governing policy eEections/Appointments: President directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a single non-consecutive term); last election was 20 November 2016; new elections have been delayed in 2022 and 2023 but have not been scheduled by Acting Prime Minister HENRY Election results: 2016: Jovenel MOISE elected president in first round; percent of vote - Jovenel MOISE (PHTK) 55.6%, Jude CELESTIN (LAPEH) 19.6%, Jean-Charles MOISE (PPD) 11%, Maryse NARCISSE (FL) 9%; other 4.8% 2011: Michel MARTELLY elected president in second round; percent of vote in second round - Michel MARTELLY (Peasant's Response) 68%, Mirlande MANIGAT (RDNP) 32% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
Citizenship by birth: No Citizenship by descent only: At least one parent must be a native-born citizen of Haiti Dual citizenship recognized: Yes Residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 1 January (1804) |
| Constitution |
History: Many previous; latest adopted 10 March 1987, with substantial revisions in June 2012; note – the constitution is commonly referred to as the “amended 1987 constitution” Amendments: Proposed by the executive branch or by either the Senate or the Chamber of Deputies; consideration of proposed amendments requires support by at least two-thirds majority of both houses; passage requires at least two-thirds majority of the membership present and at least two-thirds majority of the votes cast; approved amendments enter into force after installation of the next president of the republic; constitutional articles on the democratic and republican form of government cannot be amended; amended many times, last in 2012 |
| Independence | 1 January 1804 (from France) |
Haiti Video
YouTube: Walter James Haitian Kitchen
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Haiti Geography
What environmental issues does Haiti have?
| Overview | Eighteenth-century Haiti, famed for its wealth and productivity, was known to the colonial world as the Pearl of the Antilles. Located in the Caribbean Sea on the western third of the island of Hispaniola, Haiti is a 10,700-square-mile area of primarily mountainous terrain, some of which rise above 8,000 feet, and 850 miles of spectacular coastline. Haiti shares the island of Hispaniola with the Dominican Republic, which occupies the eastern two-thirds. |
| Climate | Haiti's tropical climate produces seasonal rainfall, although large areas of the country are semiarid. Temperatures year round range from 70°F to 90°F with humidity sometimes high along the coast. Average annual rainfall varies from nearly zero in some areas to 53 inches in Port-au-Prince. The two rainy seasons that Port-au-Prince experiences are from April to June and from August to mid-November. Rain and accompanying thunder/lightning storms usually occur at dusk and at night, but the days remain clear and sunny. There is a crisp dry season from December to April. Surrounding mountains generally protect Port-au-Prince from Caribbean hurricanes. |
| Border Countries | Dominican Republic 360 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Extensive deforestation (much of the remaining forested land is being cleared for agriculture and used as fuel); soil erosion; inadequate supplies of potable water |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection Signed, but not ratified: Hazardous Wastes |
| Terrain | Mostly rough and mountainous |
Haiti Economy
How big is the Haiti economy?
| Economic Overview |
Haiti is a free market economy with low labor costs and tariff-free access to the US for many of its exports. Two-fifths of all Haitians depend on the agricultural sector, mainly small-scale subsistence farming, which remains vulnerable to damage from frequent natural disasters. Poverty, corruption, vulnerability to natural disasters, and low levels of education for much of the population represent some of the most serious impediments to Haiti’s economic growth. Remittances are the primary source of foreign exchange, equivalent to more than a quarter of GDP, and nearly double the combined value of Haitian exports and foreign direct investment. Currently the poorest country in the Western Hemisphere, with close to 60% of the population living under the national poverty line, Haiti’s GDP growth rose to 5.5% in 2011 as the Haitian economy began recovering from the devastating January 2010 earthquake that destroyed much of its capital city, Port-au-Prince, and neighboring areas. However, growth slowed to below 2% in 2015 and 2016 as political uncertainty, drought conditions, decreasing foreign aid, and the depreciation of the national currency took a toll on investment and economic growth. Hurricane Matthew, the fiercest Caribbean storm in nearly a decade, made landfall in Haiti on 4 October 2016, with 140 mile-per-hour winds, creating a new humanitarian emergency. An estimated 2.1 million people were affected by the category 4 storm, which caused extensive damage to crops, houses, livestock, and infrastructure across Haiti’s southern peninsula. US economic engagement under the Caribbean Basin Trade Partnership Act (CBTPA) and the 2008 Haitian Hemispheric Opportunity through Partnership Encouragement Act (HOPE II) have contributed to an increase in apparel exports and investment by providing duty-free access to the US. The Haiti Economic Lift Program (HELP) Act of 2010 extended the CBTPA and HOPE II until 2020, while the Trade Preferences Extension Act of 2015 extended trade benefits provided to Haiti in the HOPE and HELP Acts through September 2025. Apparel sector exports in 2016 reached approximately $850 million and account for over 90% of Haitian exports and more than 10% of the GDP. Investment in Haiti is hampered by the difficulty of doing business and weak infrastructure, including access to electricity. Haiti's outstanding external debt was cancelled by donor countries following the 2010 earthquake, but has since risen to $2.6 billion as of December 2017, the majority of which is owed to Venezuela under the PetroCaribe program. Although the government has increased its revenue collection, it continues to rely on formal international economic assistance for fiscal sustainability, with over 20% of its annual budget coming from foreign aid or direct budget support. |
| Industries | Sugar refining, flour milling, textiles, cement, light assembly industries based on imported parts |
| Currency Name and Code | Haitian Gourde (HTG) and US Dollar (USD) |
| Export Partners | US 84.5%, Dominican Republic 6.7%, Canada 2.5%0 |
| Import Partners | US 52.5%, Dominican Republic 5.2%, Colombia 3.4% |
Haiti News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Haiti?
Source: Google News
Haiti Travel Information
What makes Haiti a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Haiti covers the western third of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola. The capital city is Port-au-Prince. The January 12, 2010, earthquake significantly damaged key infrastructure and reduced the capacity of Haiti’s medical facilities. While slowly improving, Haiti’s infrastructure remains in poor condition, unable to support normal activity, much less crisis situations While the Embassy's ability to provide emergency consular services has improved since the earthquake, it remains limited. The Haitian National Police (HNP), with assistance from the UN Stabilization Force for Haiti (MINUSTAH), is responsible for keeping the peace in Haiti and rendering assistance during times of civil unrest. The level of violent crime in Port-au-Prince, including murder and kidnapping, remains a concern and Haiti is considered a ‘critical threat’ post for crime.
Crime
Crimes such as kidnappings, death threats, murders, armed robberies, home break-ins and car-jacking are not uncommon in Haiti. Generally, these crimes are committed by Haitians against other Haitians, but foreigners and U.S. citizens have been victimized. The incidence of kidnapping in Haiti has diminished from its peak in 2006 when 60 U.S. citizens were reported kidnapped. In 2012 there were nine reported kidnappings of U.S. citizens, two homicides, seventeen aggravated assaults, one sexual assault, and 115 reported robberies. In recent years, some U.S. citizens who were kidnapped reported being beaten and/or raped by their hostage takers. Kidnapping remains the most critical security concern, and kidnappers have not been averse to targeting children in the past.It is important to exercise a high degree of caution throughout the country. Keep valuables well hidden, ensure possessions are not left in parked vehicles, use private transportation, alternate your travel routes, and keep doors and windows in homes and vehicles closed and locked. You should avoid all night-time travel due to poor road conditions and increased criminal activity after dark. Remain alert for suspicious onlookers when entering and exiting banks, as criminals often watch and subsequently attack bank customers. Withdrawals of large amounts of cash should be avoided.
Criminal perpetrators often operate in groups of two to four individuals, and may occasionally be confrontational and gratuitously violent. Criminals sometimes will seriously injure or kill those who resist their attempts to commit crime. In robberies or home invasions, it is not uncommon for the assailants to beat or shoot the victim in order to limit the victim's ability to resist. If an armed individual demands the surrender of a vehicle or other valuables, we recommend that you comply. This recommendation also applies in the event of a kidnapping. Exercise caution at all times and review basic personal security procedures frequently.
Avoid using public transportation, including "tap-taps" (private transportation used for commercial purposes). All public transportation is prohibited for Embassy personnel due to the safety and security risks associated with its use. When arriving to Haiti by air, arrange for someone you know to meet you at the airport.
You should decline all requests to carry items for others to or from Haiti. Traffickers of illegal drugs have duped unsuspecting travelers into helping transport narcotics aboard commercial airlines.
Avoid certain high-crime zones in the Port-au-Prince area, including Croix-des-Bouquets, Carrefour, Martissant, the port road (Boulevard La Saline), urban route Nationale #1, route Nationale #9, the airport road (Boulevard Toussaint L'Ouverture) and its adjoining connectors to the New ("American") Road via Route Nationale #1 (which should also be avoided). This latter area in particular has been the scene of numerous robberies, car-jackings, and murders. Embassy employees are prohibited from entering Cite Soleil and La Saline and their surrounding environs due to significant criminal activity. Neighborhoods in Port-au-Prince once considered relatively safe, such as the Delmas road area, Petionville, and Vivy Mitchel have been the scenes of an increasing number of violent crimes.
Cameras and video cameras should only be used with the permission of the subjects; violent incidents have followed unwelcome photography. Avoid photography/videography in high-crime areas.
Holiday periods, especially Christmas and Carnival, often bring a significant increase in criminal activity. Haiti's Carnival season is marked by street celebrations in the days leading up to Ash Wednesday. In recent years, Carnival has been accompanied by civil disturbances, altercations and severe traffic disruptions. People attending Carnival events or simply caught in the resulting celebrations have been injured and killed. Random stabbings during Carnival season have also occurred. Roving musical bands called “rah-rahs” operate during the period from New Year's Day through Carnival. Being caught in a rah-rah event may begin as an enjoyable experience, but the potential for injury and the destruction of property is high. A mob mentality can develop unexpectedly leaving people and cars engulfed and at risk. During Carnival, rah-rahs continuously form without warning; some rah-rahs have identified themselves with political entities, lending further potential for violence.
While the size of the Haitian National Police (HNP) is slowly increasing and its capabilities improving, it is still understaffed and under-equipped. As a result, it is unable to respond to all calls for assistance. There are continued allegations of police complicity in criminal activity. The response and enforcement capabilities of the HNP and the weakness of the judiciary often frustrate victims of crime in Haiti. In the past, U.S. citizens involved in business and property disputes in Haiti have been arrested and detained without charge and have been released only after intervention at high levels of the Haitian government.
Do not buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are pirated goods illegal in the United States, if you purchase them you may be also breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Haiti, you are subject to its laws. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different than our own. In some places you may be taken in for questioning if you don’t have your passport with you. In some places, it is illegal to take pictures of certain buildings. In some places driving under the influence could land you immediately in jail. These criminal penalties will vary from country to country. There are also some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States, and you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Haiti, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not where you are going.Persons violating Haiti's laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested or imprisoned. Penalties for possession, use, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Haiti are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines. The judicial process in Haiti can be extremely slow; progress is often dependent on considerations not related to the specific case, including personal disputes. Detainees have waited months or years for their cases to be heard before a judge or to have legal decisions acted upon by the authorities. Bond is not usually available to those arrested for serious crimes with the result that often suspects remain in custody for many months before formal indictment. Judges have more or less unfettered freedom to detain individuals for prolonged periods of time without the possibility of release or sanctions.
Based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements with certain countries, and customary international law, if you are arrested in Haiti, you have the option to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the U.S. Embassy of your arrest, and to have communications from you forwarded to the U.S. Embassy.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities in Haiti are scarce and for the most part sub-standard. Outside of the capital standards are often even lower than in Port-au-Prince. Medical care in Port-au-Prince is limited, and the level of community sanitation is extremely low. Life-threatening emergencies often require evacuation by air ambulance at the patient's expense. Doctors and hospitals often expect immediate cash payment in advance for health services. In the event of a medical emergency requiring evacuation, a list of air ambulance or charter flight services is available at the ACS web site.Incidents of cholera have declined significantly since a major outbreak in 2010 and travelers are generally not at high risk; however, cholera persists in many areas of Haiti. Prior to travel, U.S. citizens should obtain information about cholera and other health-related issues by visiting the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website.
Information on vaccinations and other health precautions, such as safe food and water precautions, malaria and insect bite protection, may be obtained from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s hotline for international travelers at 1-877-FYI-TRIP (1-877-394-8747) or via the CDC web site.
Safety and Security
While hundreds of thousands of U.S. citizens safely visit Haiti every year, the Department of State strongly urges U.S. citizens to consider carefully all travel to Haiti. Travel fully supported by organizations with solid infrastructure, evacuation options, and medical support systems in place is recommended.If you intend to work for an organization involved in humanitarian efforts in Haiti, be aware that living conditions are difficult. You should confirm that the organization has the capability to provide transportation and shelter for its paid and volunteer workers. All relief organizations should have a security plan in place for their personnel. Please note that space in hotels is extremely limited.
While most crime victims are residents of Haiti, temporary visitors share the risk of falling victim. There remains a persistent danger of violent crime, including armed robbery, homicide, rape, and kidnapping. While the size of the Haitian National Police (HNP) force has been growing and its capabilities improving, its ability to maintain citizen security is limited. The presence of MINUSTAH peacekeeping troops and UN-formed police units remain critical to maintaining an adequate level of security throughout the country. The limited capability of local law enforcement to respond to and investigate crimes further compounds the security threat to U.S. citizens. In particular, there have been cases in which travelers arriving in Port-au-Prince on flights from the United States were attacked and robbed after exiting the airport by car (two such cases involving U.S. citizens have been reported in the first six months of 2013). Police authorities believe criminals may be targeting travelers arriving on flights from the United States, following them, and attacking once they are out of the area. Use extra caution in arranging transportation from the airport. Most kidnappings are financial crimes of opportunity, and kidnappers make no distinctions of nationality, race, gender, or age. Some kidnap victims have been killed, shot, sexually assaulted, or physically abused.
While MINUSTAH remains fully deployed and is assisting the Government of Haiti in providing security, travel within Port-au-Prince can be hazardous. U.S. embassy personnel are under an embassy-imposed curfew of 1:00 a.m. to 5:00 a.m. and must remain in their homes or in U.S. government facilities during the curfew. Some areas are off-limits to Embassy staff after dark, including downtown Port-au-Prince, Cite Soleil, Martissant, Carrefour, Croix Des Bouquets, among other areas. The embassy restricts travel by its staff to some areas outside of Port-au-Prince because of the prevailing road, weather, or security conditions. This may constrain the embassy’s ability to provide emergency services to U.S. citizens outside Port-au-Prince. Demonstrations, which are common occurrences in Haiti and can become violent, may occasionally limit embassy operations to emergency services, even within Port-au-Prince.
We recommend that you avoid all large gatherings, as crowd behavior can be unpredictable. Visitors encountering roadblocks, demonstrations, or large crowds should remain calm and depart the area quickly and avoid confrontation. Assistance from Haitian authorities is often unavailable. Be particularly cautious on days when political activities are planned. Take common-sense precautions and avoid any event where crowds may congregate.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Haiti, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Haiti is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.Most of the main roads have been cleared of rubble following the January 2010 earthquake, although some rubble might remain in certain areas and impact traffic. A few roads remain impassable due to damage from the earthquake. People regularly walk on the side of the road and street-side vendors ply their wares on the existing sidewalks. Small animals (pigs, dogs, goats) are often encountered in the city and larger ones (cows and donkeys) will unexpectedly cross country roads. Cars are supposed to be driven on the right side of the road in Haiti, but few roads have lane indicators and drivers use whichever side of the road is open to them. Traffic is extremely congested in urban areas, and hours-long traffic jams develop throughout the country.
Driving in Haiti must be undertaken with extreme caution. Traffic is usually chaotic; those with no knowledge of Haitian roads and traffic customs should hire a driver through a local tour operator or hotel. Roads are generally unmarked, and detailed and accurate maps are not widely available. Lanes are not marked and signs indicating the direction of traffic flow seldom exist. Huge potholes may cause drivers to execute unpredictable and dangerous maneuvers in heavy traffic. The Haitian government lacks adequate resources to assist drivers in distress or to clear the road of accidents or broken-down vehicles blocking the flow of traffic. While drinking and driving is illegal in Haiti, people frequently drive after drinking, especially at night.
Public transportation in Haiti consists primarily of “tap-taps” that run regular routes within urban areas and between towns in the countryside. A handful of public buses exist in the capital. Neither is considered reliable nor safe. Regular marked taxis are nonexistent. We strongly discourage the use of “tap-taps,” public buses, and taxis. They pose the risk of vehicular accident - “tap-taps” in particular are hazardous because they are open and passengers are often ejected during an accident – and have been the site of numerous robberies and kidnappings in the past.
Never ride in open vehicles that lack seatbelts or on motorbikes without helmets. If you are visiting Haiti, to assist in humanitarian projects, you should confirm that your sponsoring organization has arranged to provide safe, reliable transportation during your stay. U.S. citizens have suffered life-threatening injuries and some have been killed after being thrown from open vehicles or motorbikes in accidents in Haiti. Those who drive in Haiti should do so defensively and conservatively, should avoid confrontations such as jockeying for position, and remain aware of the vehicles around them. Drivers should carry the phone numbers of people to call for assistance in an emergency, as Haitian authorities are unlikely to respond to requests for assistance. When traveling outside of Port-au-Prince, drivers should caravan with other vehicles to avoid being stranded in the event of an accident or breakdown.
Although Haitian law requires that applicants pass both a written and a driving test to qualify for a driver’s license, many Haitian drivers appear unaware of traffic laws. Signaling imminent actions is not widely practiced and not all drivers use turn indicators or international hand signals properly. For instance, many drivers use their left blinker for all actions, including turning right and stopping in the road, and others flap their left arm out the window to indicate that they will be taking an unspecified action. Drivers do not always verify that the road is clear before switching lanes, turning, or merging. When making a left-hand turn, drivers should be aware that traffic may pass on the left while they are attempting to turn. This is legal in Haiti. The driver passing on the left has the right of way even when the car being overtaken has its left-hand turn signal on and is attempting to turn left.
Speed limits are seldom posted and are generally ignored. Speeding is the cause of many fatal traffic accidents in Haiti, as are overloaded vehicles on winding, mountainous roads and vehicles without brakes. Poor maintenance and mechanical failures often cause accidents as well. Drivers should be particularly cautious at night, as unlighted vehicles can appear without warning.
Right of way is not widely observed in Haiti, and there are few operational traffic lights or traffic signs. It is advisable at most intersections to stop and verify that there is no oncoming traffic even if it appears that you have the right of way. Drivers can be quite aggressive and will seldom yield. Walls built to the edge of roads frequently make it impossible to see around corners, forcing drivers to edge their cars into the road at intersections to check for oncoming traffic.
In addition to vehicles, a variety of other objects may appear on the road in Haiti, such as wooden carts dragged by people or animals, small ice cream carts, animals, mechanics working on vehicles parked on the street, and vendors and their wares. Haiti’s unwritten rule of the road is that any vehicle that breaks down, must be left exactly where it stopped until it can be repaired, even if it creates an enormous backup of traffic. Cars often remain in the roadway for hours or days while often extensive repairs are carried out in-situ. Vehicles are often abandoned in the road or by the side of the road. These are often identified by tree branches extending from the rear of the vehicle. There are few marked crosswalks and sidewalks, and pedestrians often wend their way through traffic in urban areas. Additionally, motorcycles on Haitian roads tend to maneuver in between traffic on both the left and right sides of vehicles, as well as into on-coming traffic. Drivers should check all their rear view mirrors prior to changing lanes or making turns to avoid colliding with other traffic.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
