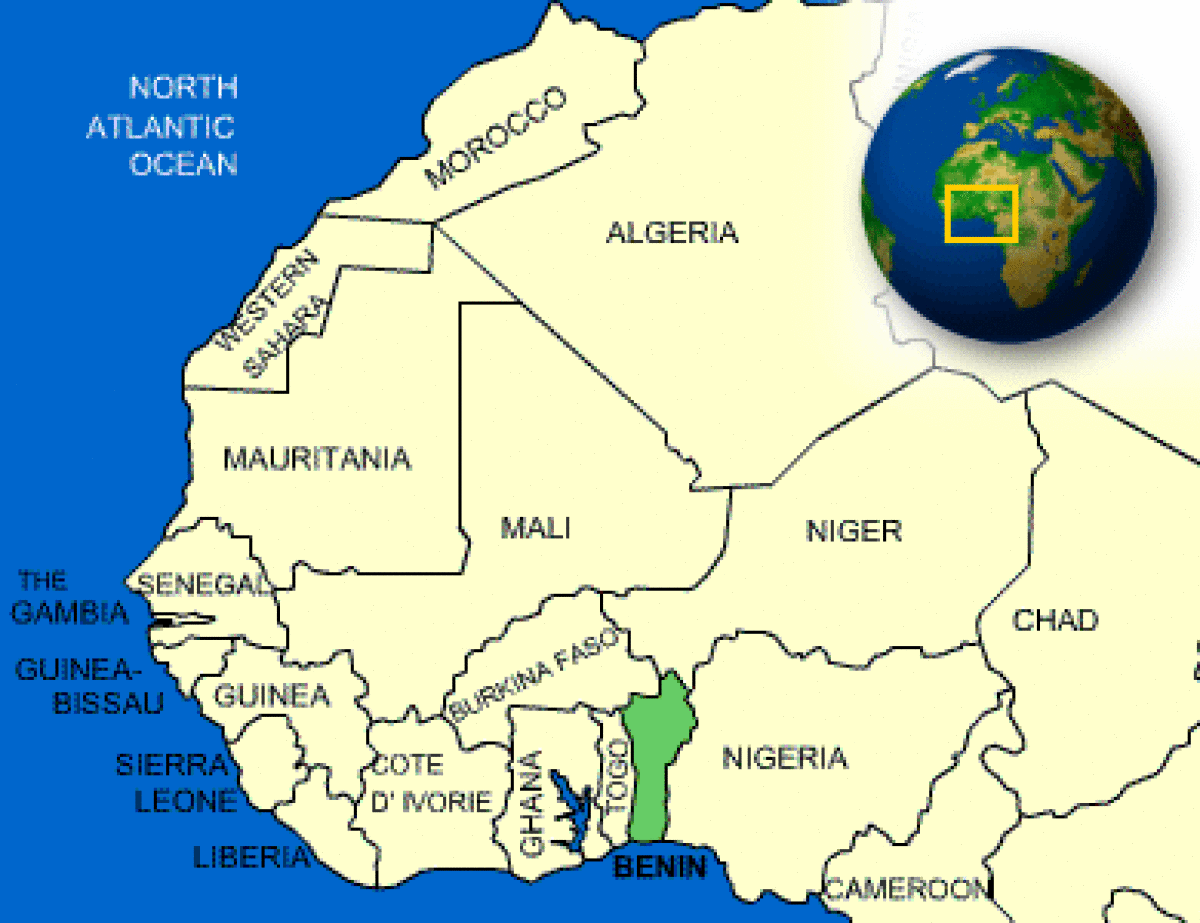
Where is Benin located?
What countries border Benin?
Benin Weather
What is the current weather in Benin?
Benin Facts and Culture
What is Benin famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: A proper greeting always precedes conversation. Benin has a mix of animist, Muslim, Christian, and secular holidays. Beninese place great... More
- Family: A marriage is considered the alliance of two families. In rural areas, the extended family lives in a compound of... More
- Personal Apperance: Urban residents wear western and traditional style clothes. Rural women often wear a pagne. The boubou... More
- Recreation: The national sport is soccer. Beninese enjoy traditional dancing. Electricity is not widely available in most villages - there people... More
- Diet: Beninese prefer hot and spicy foods. French cuisine is eaten in the north while fresh seafood is plentiful in the... More
- Food and Recipes: The main food is La Pate, bread made from various kinds of flour. La pate is... More
- Visiting: Men usually shake right hands, with the oldest person initiating the handshake. Women shake hands with men only if the... More
Benin Facts
What is the capital of Benin?
| Capital | Porto-Novo (constitutional capital); Cotonou (seat of government) |
| Government Type | presidential republic |
| Currency | Communaute Financiere Africaine francs (XOF) |
| Total Area |
43,483 Square Miles 112,622 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Western Africa, bordering the Bight of Benin, between Nigeria and Togo |
| Language | French (official), Fon and Yoruba (most common vernaculars in the south), tribal languages (at least six major ones in the north) |
| GDP - real growth rate | 4.6% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $2,200.00 (USD) |
Benin Demographics
What is the population of Benin?
| Ethnic Groups | African 99% (42 ethnic groups, most important being Fon, Adja, Yoruba, Bariba), Europeans 5,500 |
| Nationality Noun | Beninese (singular and plural) |
| Population | 12,864,634 |
| Population - note | Note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of the population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected |
| Population Growth Rate | 2.84% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | COTONOU (seat of government) 924,000; PORTO-NOVO (capital) 314,000 |
| Urban Population | 44.900000 |
Benin Government
What type of government does Benin have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Patrice TALON (since 6 April 2016); note - the president is both head of state and head of government head of government: President Patrice TALON (since 6 April 2016); prime minister position abolished cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); last held on 11 April 2021 (next to be held on 12 April 2026) election results: 2021: Patrice TALON reelected president in the ; percent of vote - Patrice TALON (independent) 86.3%, Alassane SOUMANOU (FCBE) 11.4%, Corentin KOHOUE (The Democrats) 2.3% 2016: Patrice TALON elected president in second round; percent of vote in first round - Lionel ZINSOU (FCBE) 28.4%, Patrice TALON (independent) 24.8%, Sebastien AJAVON (independent) 23%, Abdoulaye Bio TCHANE (ABT) 8.8%, Pascal KOUPAKI (NC) 5.9%, other 9.1%; percent of vote in second round - Patrice TALON 65.4%, Lionel ZINSOU 34.6% |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Benin dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 1 August (1960) |
| Constitution |
history: previous 1946, 1958 (preindependence); latest adopted by referendum 2 December 1990, promulgated 11 December 1990 amendments: proposed concurrently by the president of the republic (after a decision in the Council of Ministers) and the National Assembly; consideration of drafts or proposals requires at least three-fourths majority vote of the Assembly membership; passage requires approval in a referendum unless approved by at least four-fifths majority vote of the Assembly membership; constitutional articles affecting territorial sovereignty, the republican form of government, and secularity of Benin cannot be amended; amended 2019 |
| Independence | 1 August 1960 (from France) |
Benin Video
YouTube: Independent Television and Radio Uniqueness of Benin - Tradition and Culture Re-enacted during Ugie Mobo Celebration
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Benin Geography
What environmental issues does Benin have?
| Overview |
Benin, a narrow, north-south strip of land in West Africa, lies between the Equator and the Tropic of Cancer. Benin is bordered by Togo to the west, Burkina Faso and Niger to the north, Nigeria to the east, and the Bight of Benin to the south. With an area of 112,622 square kilometers, roughly the size of Pennsylvania, Benin extends from the Niger River in the north to the Atlantic Ocean in the south, a distance of 700 kilometers (about 500 miles). Although the coastline measures 121 kilometers (about 80 miles), the country measures about 325 kilometers (about 215 miles) at its widest east-west point. It is one of the smaller countries in West Africa: 8 times smaller than Nigeria, it's neighbor to the east. It is, however, twice as large as Togo, it's neighbor to the west. A relief map of Benin shows that it has little variation in elevation (average elevation of 200 meters). The country can be divided into four main areas from the south to the north. The low-lying, sandy, coastal plain (highest elevation 10 meters) is, at most, 10 kilometers wide. It is marshy and dotted with lakes and lagoons communicating with the ocean. The plateaus of southern Benin — between 20 and 200 meters in altitude — are split by valleys running north to south along the Couffo, Zou, and Oueme Rivers. An area of flat lands dotted with rocky hills whose altitude seldom reaches 400 meters extends around Nikki and Save. Finally, a range of mountains extends along the northwest border and into Togo: this is the Atacora, with the highest point, Mont Sokbaro, at 658 meters. Two types of landscape predominate in the south. Benin has fields of lying fallow, mangroves, and remnants of large sacred forests. In the rest of the country, the savanna is covered with thorny scrubs and dotted with huge baobab trees. Some forests line the banks of rivers. In the north and the northwest of Benin, the Reserve du W du Niger and Pendjari National Park attract tourists eager to see elephants, lions, antelopes, hippos, and monkeys. |
| Climate |
Benin's climate is hot and humid. Annual rainfall in the coastal area averages 36 centimeters (14 inches), not particularly high for coastal West Africa. Benin has two rainy and two dry seasons. The principal rainy season is from April to late July, with a shorter less intense rainy period from late September to November. The main dry season is from December to April with a short cooler dry season from late July to early September. Temperatures and humidity are high along the tropical coast. In Cotonou, the average maximum temperature is 31°C (89°F); the minimum is 24°C (75°F). Variations in temperature increase when moving north through a savanna and plateau toward the Sahel. A dry wind from the Sahara called the harmattan blows from December to March. Grass dries up, the vegetation turns reddish-brown, and a veil of fine dust hangs over the country, causing the skies to be overcast. |
| Border Countries | Burkina Faso 306 km, Niger 266 km, Nigeria 773 km, Togo 644 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Inadequate supplies of potable water; poaching threatens wildlife populations; deforestation; desertification |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party To: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Wetlands, Whaling Signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | Mostly flat to undulating plain; some hills and low mountains |
Benin Economy
How big is the Benin economy?
| Economic Overview |
The free market economy of Benin has grown consecutively for four years, though growth slowed in 2017, as its close trade links to Nigeria expose Benin to risks from volatile commodity prices. Cotton is a key export commodity, with export earnings significantly impacted by the price of cotton in the broader market. The economy began deflating in 2017, with the consumer price index falling 0.8%. During the first two years of President TALON’s administration, which began in April 2016, the government has followed an ambitious action plan to kickstart development through investments in infrastructure, education, agriculture, and governance. Electricity generation, which has constrained Benin’s economic growth, has increased and blackouts have been considerably reduced. Private foreign direct investment is small, and foreign aid accounts for a large proportion of investment in infrastructure projects. Benin has appealed for international assistance to mitigate piracy against commercial shipping in its territory and has used equipment from donors effectively against such piracy. Pilferage has significantly dropped at the Port of Cotonou, though the port is still struggling with the effective implementation of the International Ship and Port Facility Security (ISPS) Code. Projects included in Benin's $307 million Millennium Challenge Corporation (MCC) first compact (2006-11) were designed to increase investment and private sector activity by improving key institutional and physical infrastructure. The four projects focused on access to land, access to financial services, access to justice, and access to markets (including modernization of the port). The Port of Cotonou is a major contributor to Benin’s economy, with revenues projected to account for more than 40% of Benin’s national budget. Benin will need further efforts to upgrade infrastructure, stem corruption, and expand access to foreign markets to achieve its potential. In September 2015, Benin signed a second MCC Compact for $375 million that entered into force in June 2017 and is designed to strengthen the national utility service provider, attract private sector investment, fund infrastructure investments in electricity generation and distribution, and develop off-grid electrification for poor and unserved households. As part of the Government of Benin’s action plan to spur growth, Benin passed public-private partnership legislation in 2017 to attract more foreign investment, place more emphasis on tourism, facilitate the development of new food processing systems and agricultural products, encourage new information and communication technology, and establish Independent Power Producers. In April 2017, the IMF approved a three-year $150.4 million Extended Credit Facility agreement to maintain debt sustainability and boost donor confidence. |
| Industries | Textiles, food processing, construction materials, cement |
| Currency Name and Code | Communaute Financiere Africaine francs (XOF) |
| Export Partners | India 24.2%, Gabon 14.6%, China 7.2%, Niger 6%, Bangladesh 5%, Nigeria 4.9%, Vietnam 4.2% |
| Import Partners | China 42.1%, United States 8.9%, India 5.7%, Malaysia 4.8%, Thailand 4.3%, France 4% |
Benin News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Benin?
Source: Google News
Benin Travel Information
What makes Benin a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Benin is a developing country in West Africa. Its political capital is Porto Novo; however, its administrative capital, Cotonou, is Benin's largest city and the site of most government, commercial, and tourist activity.
Crime
Street crime is a significant problem in Cotonou. Robbery and muggings occur along the Boulevard de France (the beach road by the Marina and Novotel Hotels), on the beaches near hotels frequented by international visitors, and within the Haie Vive and Les Cocotiers neighborhoods (where many bars and restaurants frequented by expatriates are located), in addition to other parts of the city. Most of the reported incidents involve the use of force, often by armed persons, with an occasional minor injury to the victim. Travelers should avoid isolated and poorly lit areas and should not walk around the city or the beaches between dusk and dawn. U.S. diplomatic personnel are prohibited from visiting the Dantokpa market between the hours of dusk and dawn. Even during daylight hours, foreigners on the beach near Cotonou are frequently victims of robberies. When visiting the beach, travelers should not carry valuables and should carry only a photocopy of their passport. If you are a victim of a crime, you should contact the U.S. Embassy immediately.There has been a continued increase in the number of robberies after dark, both within metropolitan Cotonou and on highways and rural roads outside of major metropolitan areas. Motorists are urged to be wary of the risk of carjacking in both urban and rural areas. Keep the windows of your vehicle rolled up and the doors locked, and stay alert for signs of suspicious behavior by other motorists or pedestrians that may lead to carjacking, such as attempts to stop a moving vehicle for no obvious reason. Motorists should be aware of obstacles or obstructions, such as branches, tires, or ropes, that would-be robbers place in the roadway in an effort to ambush victims. Travelers should avoid driving outside the city of Cotonou after dark and should exercise extreme caution when driving inside of Cotonou after dark (see Traffic Safety and Road Conditions below). Overland travel to Nigeria is dangerous near the Benin/Nigeria border due to unofficial checkpoints and highway banditry.
Travelers should exercise extreme caution when using credit cards and automated teller machines (ATMs) in Benin due to a high rate of fraud. Perpetrators of business and other kinds of fraud often target foreigners, including U.S. citizens. While such fraud schemes in the past have been largely associated with Nigeria, they are now prevalent throughout West Africa, including Benin, and are more frequently perpetrated by Beninese criminals. Business scams are not always easy to recognize, and any unsolicited business proposal should be carefully scrutinized.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal in the United States, but if you purchase them you may also be breaking local law.
Over the previous three years, there have been numerous pirate attacks off the coast of Benin. The attacks have been focused on oil tanker ships, not container ships or other types of vessels. It is unlikely that any tourist would become a victim of piracy, but be cautious if approached by an unknown vessel while at sea. If you spot any suspected pirates, do not approach them; immediately contact port officials, local police, and the U.S. Embassy.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Benin, you are subject to its laws and regulations even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from those in the United States and may not afford the protections available to the individual under U.S. law. Penalties for breaking the law can be more severe than in the United States for similar offenses. Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States.While some countries will automatically notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate if a U.S. citizen is detained or arrested in a foreign country, that might not always be the case. To ensure that the United States is aware of your circumstances, request that the police and prison officials notify the nearest U.S. embassy or consulate as soon as you are arrested or detained overseas.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical facilities in Benin are limited and not all medicines are available. Travelers should carry their own supplies of prescription drugs and preventive medicines. Not all medicines and prescription drugs available in Benin are USFDA-approved. U.S. citizens should be prepared to pay for medical services, including consultations and tests before medical advice or treatment is received. Credit cards are not accepted.Information on vaccinations and other health precautions, such as safe food and water precautions and insect bite protection, may be obtained from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) hotline for international travelers at 1-877-FYI-TRIP (1-877-394-8747) or via the CDC website. For information about outbreaks of infectious diseases abroad, consult the infectious diseases section of the World Health Organization (WHO) website. The WHO website also contains additional health information for travelers, including detailed country-specific health information.
Malaria is a serious risk to travelers to Benin.
Safety and Security
U.S. citizens should avoid crowds, political rallies, and street demonstrations and maintain security awareness at all times.U.S. citizens should not walk on the beach, at any time of day, alone. The U.S. Mission recommends that U.S. citizens not carry a passport or valuables when walking in any part of the city. Instead, carry a notarized photocopy of the photo page of your passport (see Crime section). You should not walk around the city after dark and should take particular care to avoid the beach and isolated areas near the beach after dark.
The ocean currents along the coast are extremely strong and treacherous, with rough surf and a strong undertow, and several people drown each year. Swimming conditions along Benin’s coastline are notoriously dangerous due to strong and changeable tides, waves, and rip currents. There is no safe way to determine whether conditions on any given day are suitable for entering the water, in part because waves and rip currents can develop and intensify abruptly. The U.S. Mission strongly discourages beachgoers from entering the ocean, regardless of a person’s age, size, fitness level, or swimming ability.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Benin, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. The information below concerning Benin is provided for general reference only, and may not be totally accurate in a particular location or circumstance.With the exception of the road linking Cotonou in the south to Malanville on the border with Niger in the north, roads in Benin are generally in poor condition and are often impassable during the rainy season. Benin's unpaved roads vary widely in quality; deep sand and potholes are common. During the rainy season from mid-June to mid-September, dirt roads often become impassable. Four-wheel drive vehicles with full spare tires and emergency equipment are recommended.
Most of the main streets in Cotonou are paved, but side streets are often made of dirt and have deep potholes. Traffic moves on the right, as in the United States. Cotonou has a very limited public transportation system; many Beninese people rely on bicycles, mopeds, motorbikes, and zemidjans. U.S. Embassy personnel are required to wear safety helmets when on a motorcycle and are prohibited from using zemidjans. Travelers using zemidjans, particularly at night, are much more vulnerable to being mugged, assaulted, or robbed. Buses and bush taxis offer service in the interior.
Gasoline smuggled from Nigeria is widely available in glass bottles and jugs at informal roadside stands throughout Cotonou and much of the country. This gasoline is of unreliable quality, often containing water or other contaminants that can damage or disable your vehicle. Drivers should purchase fuel only from official service stations. There are periodic gas shortages, which can be particularly acute in the north of the country where there are few service stations.
U.S. citizens traveling by road should exercise extreme caution. Poorly maintained and overloaded transport and cargo vehicles frequently break down and cause accidents. Drivers often place branches or leaves in the road to indicate a broken-down vehicle is in the roadway. Undisciplined drivers move unpredictably through traffic. Construction work is often poorly indicated. Speed bumps, commonly used on paved roads in and near villages, are seldom indicated. Drivers must be on guard against people and livestock wandering into or across the roads. Nighttime driving is particularly hazardous as vehicles frequently lack headlights and/or taillights, and brake lights are often burned out.
With few exceptions, Cotonou and other cities lack street lighting, and lighting on roads between population centers is non-existent. The U.S. Embassy in Cotonou prohibits non-essential travel outside of metropolitan areas after dusk by diplomatic personnel and strongly urges all U.S. citizens to avoid night driving as well. There have been numerous carjackings and robberies on roads in Benin after dark, several of which resulted in murder when the driver refused to comply with the assailants' demands. The national police periodically conduct vehicle checks at provisional roadblocks in an effort to improve road safety and reduce the increasing number of carjackings. When stopped at such a roadblock, you must have all of the vehicle's documentation available to present to the authorities.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
