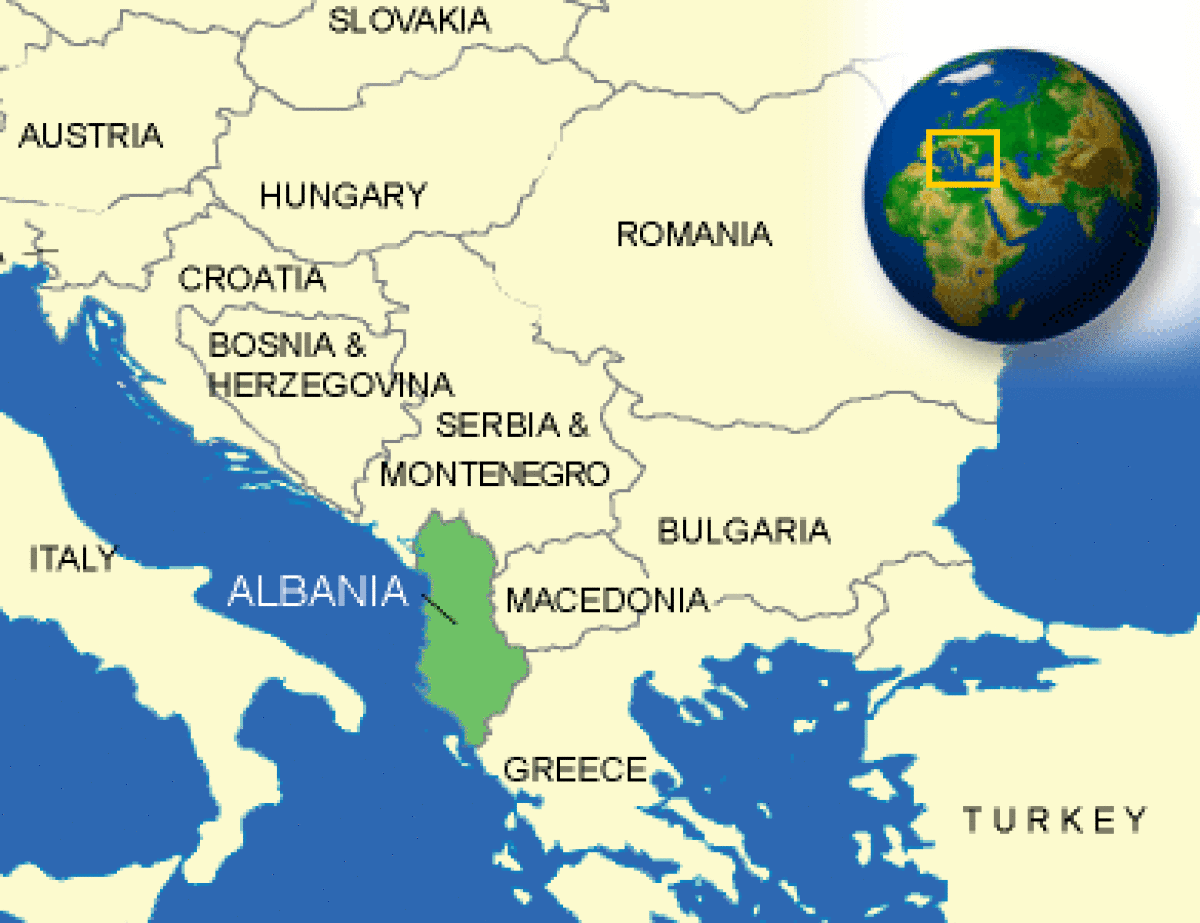
Where is Albania located?
What countries border Albania?
Albania Weather
What is the current weather in Albania?
Albania Facts and Culture
What is Albania famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Northern Albanians are known to be resourceful. They honor a tradition called the "besa", (truce). For Albanians, the... More
- Family: Men and women have equal social rights, and both parents usually work. Adult children often live with their parents and... More
- Personal Apperance: Young people wear Western-style clothing. Traditional, hand-made clothing is still worn in villages. Cotton and wool are preferred. Women... More
- Recreation: Soccer is the most popular sport in Albania. Swimming in the Adriatic Sea on hot summer days is a favorite... More
- Diet: The alcoholic drink "raki" is often served before the main meal, and wine is served during or after a meal.... More
- Food and Recipes: An Albanian breakfast often consists of bread, milk, eggs, jam, or cheese. Lunch is usually the main meal, (1-2 pm).... More
- Visiting: In Albania, there are several customs and cultural norms relating to visiting that reflect hospitality, respect, and social etiquette. Here... More
- Dating: Young people are able to select their own spouses. In some places, families are involved in the spouse selection.... More
Albania Facts
What is the capital of Albania?
| Capital | Tirana (Tirane) |
| Government Type | parliamentary republic |
| Currency | leke (ALL) |
| Total Area |
11,100 Square Miles 28,748 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Southeastern Europe, bordering the Adriatic Sea and the Ionian Sea, between Greece in the south and Montenegro and Kosovo to the north |
| Language | Albanian (official - Tosk is the official dialect), Greek |
| GDP - real growth rate | 3.8% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $12,500.00 (USD) |
Albania Demographics
What is the population of Albania?
| Ethnic Group - note | data represent population by ethnic and cultural affiliation |
| Ethnic Groups | Albanian 82.6%, Greek 0.9%, other 1% (including Vlach, Romani, Macedonian, Montenegrin, and Egyptian), unspecified 15.5% |
| Languages | Albanian 98.8% (official - derived from Tosk dialect), Greek 0.5%, other 0.6% (including Macedonian, Romani, Vlach, Turkish, Italian, and Serbo-Croatian), unspecified 0.1% |
| Nationality Noun |
noun: Albanian(s) adjective: Albanian |
| Population | 3,107,100 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.16% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | 520,000 TIRANA (capital) |
| Urban Population |
urban population: 64.6% of total population rate of urbanization: 1.29% annual rate of change |
| Population: Male/Female |
male: 1,531,063 female: 1,576,037 |
Albania Government
What type of government does Albania have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: President Bajram BEGAJ (since 24 July 2022) head of government: Prime Minister Edi RAMA (since 10 September 2013); Deputy Prime Minister Arben AHMETAJ (since 18 September 2021) cabinet: Council of Ministers proposed by the prime minister, nominated by the president, and approved by the Assembly elections/appointments: president indirectly elected by the Assembly for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); a candidate needs three-fifths majority vote of the Assembly in 1 of 3 rounds or a simple majority in 2 additional rounds to become president; election last held in 4 rounds on 16, 23, and 30 May and 4 June 2022 (next election to be held in 2027); prime minister appointed by the president on the proposal of the majority party or coalition of parties in the Assembly election results: 2022: Bajram BEGAJ elected president in the fourth round; Assembly vote - 78-4, opposition parties boycotted 2017: Ilir META elected president in the fourth round; Assembly vote - 87-2 |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Albania dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 5 years |
| National Holiday | Independence Day, 28 November (1912) also known as Flag Day |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest approved by the Assembly 21 October 1998, adopted by referendum 22 November 1998, promulgated 28 November 1998 amendments: proposed by at least one-fifth of the Assembly membership; passage requires at least a two-thirds majority vote by the Assembly; referendum required only if approved by two-thirds of the Assembly; amendments approved by referendum effective upon declaration by the president of the republic; amended several times, last in 2020 |
| Independence | 28 November 1912 (from the Ottoman Empire) |
Albania Video
YouTube, United Nations Harnessing Albania's Cultural Heritage
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Albania Geography
What environmental issues does Albania have?
| Overview |
Albania is located in the southwestern corner of the Balkan Peninsula, occupying 28,748 square kilometers. It is roughly the size of the state of Maryland with a maximum length of about 340-km and a maximum width of about 150-km. Much of the country is rugged and mountainous. The highest peak is Korabi in the northeast at 275-m. Albania has 1,094 km of borders, 30% of which is the shore of the Adriatic and Ionian Seas. Of Albania’s lakes, the Lake of Shkodra is the largest in the Balkans (368 sq. km) and the Lake of Ohrid is the deepest. The country has 152 rivers including the Shkumbini, which roughly divides the country into northern and southern regions. |
| Climate | The plain of Albania, where the capital city Tirana is located, has a typical Mediterranean climate with hot summers and generally mild winters with abundant rainfall. In the mountains, winters can be very severe with low temperatures and high snowfall. On average, temperatures range from -3°C in January to a maximum of 35°C in July. Parts of Albania are on a fault line and experience earthquakes and tremors. |
| Border Countries | Greece 282 km, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia 151 km, Serbia and Montenegro 287 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | Deforestation; soil erosion; water pollution from industrial and domestic effluents |
| Environment - International Agreements |
Party To: Air Pollution, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Wetlands signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | Mostly mountains and hills; small plains along the coast |
Albania Economy
How big is the Albania economy?
| Economic Overview |
Albania, a formerly closed, centrally-planned state, is a developing country with a modern open-market economy. Albania managed to weather the first waves of the global financial crisis but, the negative effects of the crisis caused a significant economic slowdown. Since 2014, Albania’s economy has steadily improved and economic growth reached 3.8% in 2017. However, close trade, remittance, and banking sector ties with Greece and Italy make Albania vulnerable to spillover effects of possible debt crises and weak growth in the euro zone. Remittances, a significant catalyst for economic growth, declined from 12-15% of GDP before the 2008 financial crisis to 5.8% of GDP in 2015, mostly from Albanians residing in Greece and Italy. The agricultural sector, which accounts for more than 40% of employment but less than one-quarter of GDP, is limited primarily to small family operations and subsistence farming, because of a lack of modern equipment, unclear property rights, and the prevalence of small, inefficient plots of land. Complex tax codes and licensing requirements, a weak judicial system, endemic corruption, poor enforcement of contracts and property issues, and antiquated infrastructure contribute to Albania's poor business environment making attracting foreign investment difficult. Since 2015, Albania has launched an ambitious program to increase tax compliance and bring more businesses into the formal economy. In July 2016, Albania passed constitutional amendments reforming the judicial system in order to strengthen the rule of law and reduce deeply entrenched corruption. Albania’s electricity supply is uneven despite upgraded transmission capacities with neighboring countries. However, the government has recently taken steps to stem non-technical losses and has begun to upgrade the distribution grid. Better enforcement of electricity contracts has improved the financial viability of the sector, decreasing its reliance on budget support. Also, with help from international donors, the government is taking steps to improve the poor road and rail networks, a long-standing barrier to sustained economic growth. Inward foreign direct investment has increased significantly in recent years as the government has embarked on an ambitious program to improve the business climate through fiscal and legislative reforms. The government is focused on the simplification of licensing requirements and tax codes, and it entered into a new arrangement with the IMF for additional financial and technical support. Albania’s three-year IMF program, an extended fund facility arrangement, was successfully concluded in February 2017. The Albanian Government has strengthened tax collection amid moderate public wage and pension increases in an effort to reduce its budget deficit. The country continues to face high public debt, exceeding its former statutory limit of 60% of GDP in 2013 and reaching 72% in 2016. |
| Industries | Food; footwear, apparel and clothing; lumber, oil, cement, chemicals, mining, basic metals, hydropower |
| Currency Name and Code | leke (ALL) |
| Export Partners | Italy 53.4%, Kosovo 7.7%, Spain 5.6%, Greece 4.2% |
| Import Partners | Italy 28.5%, Turkey 8.1%, Germany 8%, Greece 8%, China 7.9%, Serbia 4% |
Albania News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Albania?
Source: Google News
Albania Travel Information
What makes Albania a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
Albania is a parliamentary democracy with a market-oriented economic system. Albania's per capita income is among the lowest in Europe, but economic conditions in the country are improving steadily. Albania's economic integration into broader European markets is underway slowly and the Albanian economy continues to grow despite uncertainty in the region. Tourist facilities are not highly developed in much of the country, and some goods and services taken for granted in Western European countries are not widely available. Hotel accommodations are plentiful in Tirana and in other major cities but limited in smaller towns. Albanian is the official language; English is limited except for Tirana’s main tourist areas.
Crime
High unemployment and other economic factors encourage criminal activity. Use caution and protect your valuables in Tirana, just as you would in any major U.S. city. Violent crime aimed at U.S. citizens is rare and criminals do not appear to target U.S. citizens or other foreigners, but rather seek targets of opportunity, selecting those who appear to have anything of value. Crime statistics indicate a steady increase in violent crime has occurred throughout Albania since 2009. Organized crime is present in Albania; organized criminal activity occasionally results in violent confrontations between members of rival organizations.Pick-pocketing, theft, and other petty street crimes are widespread, particularly in areas where tourists and foreigners congregate. Pickpockets use various diversionary tactics to distract victims, and panhandlers – particularly children – may become aggressive. U.S. citizens have reported the theft of their passports and portable electronic devices by pick-pockets. Victims of pick-pocketing should report the crime to the police and cancel their credit cards as soon as possible. Exercise caution in bars and clubs in Tirana, where violent incidents, some involving the use of firearms, have occurred in the past.
Vehicle theft and theft from vehicles are not uncommon in Albania. Carjacking can also occur. You should avoid leaving valuables, including cell phones and electronic items, in plain view in unattended vehicles. You should lock the windows and doors of your residence securely when it is not occupied. In the event you are a victim of carjacking, you should surrender your vehicle without resistance.
Travelers should take standard safety precautions when using Automated Teller Machines (ATMs). Try to use ATMs located inside banks and check for any evidence of tampering with the machine before use. Be cautious when using publicly available Internet terminals, such as in Internet cafes, as sensitive personal information, account passwords, etc., may be subject to compromise. Theft of personal items from hotel rooms can also occur.
Do not buy counterfeit and pirated goods. Doing so is illegal in both the United States and Albania.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Albania, you are subject to its laws even if you are a U.S. citizen. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own. For instance, it is illegal to take pictures of certain physical structures in Albania. Be alert for signage and guidance by security personnel.There are some things that might be legal in the country you visit, but still illegal in the United States. If you break local laws in Albania your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what’s legal and what’s not wherever you go.
In Albania, you may be taken in for questioning if you are not carrying your passport. We encourage U.S. citizens to carry a copy of their U.S. passport with them at all times to show proof of identity and U.S. citizenship if questioned by local officials.
Engaging in sexual conduct with children or using or disseminating child pornography in a foreign country is a crime prosecutable in the United States. Engaging in sexual conduct with children is also a crime in Albania, as is the production and distribution of child pornography.
Under Albanian law, police can detain any individual for up to 10 hours without filing formal charges. Although this is not a common occurrence reported by U.S. citizens, the possibility remains. Persons violating Albanian laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking illegal drugs in Albania are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines.
Languages
Albanian 98.8% (official - derived from Tosk dialect), Greek 0.5%, other 0.6% (including Macedonian, Romani, Vlach, Turkish, Italian, and Serbo-Croatian), unspecified 0.1%
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Medical care at private hospitals and clinics in Tirana has improved in recent years but still remains below western standards. Medical facilities outside Tirana have very limited capabilities. Emergency and major medical care requiring surgery and hospital care outside Tirana are often inadequate because of a lack of medical specialists, diagnostic aids, medical supplies, and prescription drugs. There are very few ambulances in Albania; therefore, injured or seriously ill U.S. citizens may be required to take taxis or other immediately available vehicles to the nearest major hospital rather than waiting for ambulances to arrive. If you have been previously diagnosed with (a) medical condition(s), you may wish to consult your personal health care provider before travel. As some prescription drugs may not be available locally, you may also wish to bring extra supplies of required medications.Electricity shortages result in sporadic blackouts throughout the country, which can affect the food storage capabilities of restaurants and shops. While some restaurants and food stores have generators to store food properly, you should take care that food is cooked thoroughly to reduce the risk of food-borne illness. Tap water is not considered potable or safe to drink. You should purchase bottled water or drinks while in-country. Air pollution is also a problem throughout Albania, particularly in Tirana. Travelers should consult their doctor prior to travel and consider the impact seasonal smog and heavy particulate pollution may have on them.
Safety and Security
Public demonstrations occur throughout Albania, often with little or no notice, and can cause serious traffic disruptions. Although most demonstrations are peaceful, a demonstration in January 2011 turned violent and resulted in four deaths and injuries to many others, including Albania State Police Officers. Travelers should avoid areas where demonstrations are taking place. The use of roadblocks and/or the blocking of public facilities has occurred. U.S. citizens should stay up to date with media coverage of local events and be aware of their surroundings at all times. Information regarding demonstrations in Albania can be found on the U.S. Embassy Tirana website.Organized criminal activity occurs in many regions of Albania. Corruption is also a concern in many areas. Police and news outlets often report small-scale, sporadic incidents of violence. Although there is no direct prohibition on the travel of U.S. Government employees within Albania, we encourage all travelers to avoid the southern town of Lazarat, where Albanian State Police and armed marijuana growers have recently engaged in violent altercations. Police ability to protect and assist travelers in and near Lazarat is limited.
Power outages occur frequently throughout Albania. Regular outages may also disrupt other public utilities, including water service, and interfere with traffic lights and the provision of normal business and public services.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Albania you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States.The most dangerous aspect of living and working in Albania is the unsafe driving regularly encountered on roads nationwide, and the generally poor condition of the roads. Road conditions are especially poor in rural areas in the winter months and at other times of inclement weather. Sporadic electricity shortages sometimes result in blackouts affecting road lighting and traffic signals. Traveling at night and outside the main urban areas is particularly dangerous as road hazards are unpredictable and can be more difficult to see. Disregarding traffic laws is widespread. Traffic accidents are frequent occurrences and often result in serious injury or death. If you choose to drive in Albania, please exercise strong caution and drive as defensively as possible.
Buses travel between most major cities almost exclusively during the day, but they do not always run according to schedule and can be uncomfortable relative to buses in the United States. No public bus routes exist between cities; travelers seeking intra-city transit may use privately owned vans, which function as an unofficial system of bus routes and operate almost entirely without schedules or set fares. These privately owned vehicles may not have permission to operate as a bus service and may not adhere to accepted safety and maintenance standards or driver training; you should consider the condition of the van before you choose to travel in one. In January 2013, vans carrying passengers were robbed at gunpoint near the city of Tepelene on the route from Saranda to Tirana. Personal vehicles have been robbed in the same fashion. There are no commercial domestic flights and the rail conditions are poor, connections limited, and service unreliable.
You can only use an international driver’s license for one year in Albania. If you wish to drive in Albania for a period of time in excess of one year, you must apply for an Albanian driver’s license.
It is illegal to drive under the influence of alcohol and, if caught, the police may seize your driver’s license and vehicle and impose additional penalties such as a fine or up to six months in prison.
Using a cell phone while driving is only permitted when the driver utilizes a Bluetooth or other hands-free device and failure to use such a device can result in a fine.
World Regions
All Countries
Afghanistan
Akrotiri
Albania
Algeria
American Samoa
Andorra
Angola
Anguilla
Antarctica
Antigua and Barbuda
Argentina
Armenia
Aruba
Australia
Austria
Azerbaijan
Bahamas
Bahrain
Bangladesh
Barbados
Belarus
Belgium
Belize
Benin
Bermuda
Bhutan
Bolivia
Bosnia and Herzegovina
Botswana
Brazil
British Indian Ocean Territory
British Virgin Islands
Brunei
Bulgaria
Burkina Faso
Burma
Burundi
Cabo Verde
Cambodia
Cameroon
Canada
Cayman Islands
Central African Republic
Chad
Chile
China
Christmas Island
Clipperton Island
Cocos (Keeling) Islands
Colombia
Comoros
Congo, Democratic Republic of the
Congo, Republic of the
Cook Islands
Coral Sea Islands
Costa Rica
Cote d’Ivoire
Croatia
Cuba
Curacao
Cyprus
Czech Republic
Denmark
Dhekelia
Djibouti
Dominica
Dominican Republic
Ecuador
Egypt
El Salvador
Equatorial Guinea
Eritrea
Estonia
Eswatini
Ethiopia
Falkland Islands
Faroe Islands
Fiji
Finland
France
French Guiana
French Polynesia
Gabon
Gambia, The
Gaza Strip
Georgia
Germany
Ghana
Gibraltar
Greece
Greenland
Grenada
Guadeloupe
Guam
Guatemala
Guernsey
Guinea
Guinea-Bissau
Guyana
Haiti
Holy See
Honduras
Hong Kong
Hungary
Iceland
India
Indonesia
Iran
Iraq
Ireland
Isle of Man
Israel
Italy
Jamaica
Jan Mayen
Japan
Jersey
Jordan
Kazakhstan
Kenya
Kiribati
Korea, North
Korea, South
Kosovo
Kuwait
Kyrgyzstan
Laos
Latvia
Lebanon
Lesotho
Liberia
Libya
Liechtenstein
Lithuania
Luxembourg
Macau
Madagascar
Malawi
Malaysia
Maldives
Mali
Malta
Marshall Islands
Martinique
Mauritania
Mauritius
Mayotte
Mexico
Micronesia
Moldova
Monaco
Mongolia
Montenegro
Montserrat
Morocco
Mozambique
Namibia
Nauru
Nepal
Netherlands
New Caledonia
New Zealand
Nicaragua
Niger
Nigeria
Niue
Norfolk Island
North Macedonia
Northern Mariana Islands
Norway
Oman
Pakistan
Palau
Panama
Papua New Guinea
Paraguay
Peru
Philippines
Pitcairn Islands
Poland
Portugal
Puerto Rico
Qatar
Reunion
Romania
Russia
Rwanda
Saint Helena, Ascension, and Tristan da Cunha
Saint Kitts and Nevis
Saint Lucia
Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
Samoa
San Marino
Sao Tome and Principe
Saudi Arabia
Senegal
Serbia
Seychelles
Sierra Leone
Singapore
Slovakia
Slovenia
Solomon Islands
Somalia
South Africa
Spain
Sri Lanka
Sudan
Sudan, South
Suriname
Svalbard
Sweden
Switzerland
Syria
Taiwan
Tajikistan
Tanzania
Thailand
Timor-Leste
Togo
Tokelau
Tonga
Trinidad and Tobago
Tunisia
Turkey
Turkmenistan
Turks and Caicos Islands
Tuvalu
Uganda
Ukraine
United Arab Emirates
United Kingdom
United States (US)
Uruguay
Uzbekistan
Vanuatu
Venezuela
Vietnam
Virgin Islands
Wake Island
Wallis and Futuna
West Bank
Western Sahara
World
Yemen
Zambia
Zimbabwe
