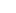Where is Denmark located?
What countries border Denmark?
Denmark Weather
What is the current weather in Denmark?
Denmark Facts and Culture
What is Denmark famous for?
- Cultural Attributes: Danish people are informal and friendly. They appreciate courtesy in all interactions. Danes live very much "by the clock." They... More
- Family: Danish society is built on respect for the individual and responsibility for the common good, both at the family and... More
- Personal Apperance: Danes follow general European fashion trends, frequently changing with the year or season. Because of the cool, rainy climate and... More
- Recreation: Most schoolchildren play football (soccer). Volunteer clubs are dedicated to turning young players into pros. Other popular activities include rugby,... More
- Diet: Danes eat in continental style, with a fork in the left hand and a knife in the right. At family... More
- Food and Recipes: Denmark is famous for its pastries. In Danish folklore, the next one to get married is believed to be the... More
- Visiting: In Denmark, people celebrate all kinds of occasions with parties: weddings, baptisms, confirmations, birthdays, religious festivals, when someone moves into... More
Denmark Facts
What is the capital of Denmark?
| Capital | Copenhagen |
| Government Type | parliamentary constitutional monarchy |
| Currency | Danish kroner (DKK) |
| Total Area |
16,639 Square Miles 43,094 Square Kilometers |
| Location | Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea and the North Sea, on a peninsula north of Germany (Jutland); also includes several major islands (Sjaelland, Fyn, and Bornholm) |
| Language |
Danish, Faroese, Greenlandic (an Inuit dialect), German (small minority) note: English is the predominant second language |
| GDP - real growth rate | 1% |
| GDP - per capita (PPP) | $46,600.00 (USD) |
Denmark Demographics
What is the population of Denmark?
| Ethnic Groups | Scandinavian, Inuit, Faroese, German, Turkish, Iranian, Somali |
| Languages |
The Danish alphabet has a total of 29 letters: 9 vowels (a,e,i,o,u,y,æ,ø,å) and 20 consonant. |
| Nationality Noun | Dane(s) |
| Population | 5,869,410 |
| Population - note | note: Statistics Denmark estimates the country's total population to be 5,724,456 as of 2016 Q3 |
| Population Growth Rate | 0.23% |
| Population in Major Urban Areas | COPENHAGEN (capital) 1.206 million |
| Urban Population | 86.900000 |
Denmark Government
What type of government does Denmark have?
| Executive Branch |
chief of state: King FREDERIK X (since 14 January 2024); Heir Apparent Crown Prince CHRISTIAN (son of the king, born 15 October 2005); note - Queen MARGRETHE II abdicated on 14 January 2024, the first Danish monarch to voluntarily abdicate since King ERIC III in 1146 head of government: Prime Minister Mette FREDERIKSEN (since 27 June 2019) cabinet: Council of State appointed by the monarch elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the monarch |
| Suffrage | 18 years of age; universal |
| Citizenship |
citizenship by birth: no citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of Denmark dual citizenship recognized: yes residency requirement for naturalization: 7 years |
| National Holiday | Constitution Day, 5 June (1849); note - closest equivalent to a national holiday |
| Constitution |
history: several previous; latest adopted 5 June 1953 amendments: proposed by the Folketing with consent of the government; passage requires approval by the next Folketing following a general election, approval by simple majority vote of at least 40% of voters in a referendum, and assent of the chief of state; changed several times, last in 2009 (Danish Act of Succession) |
| Independence | ca. 965 (unified and Christianized under Harald I GORMSSON); 5 June 1849 (became a parliamentary constitutional monarchy) |
Denmark Video
YouTube: DJI Dutch flower fields near Keukenhof, The Netherlands drone footage
CountryReports YouTube Channel:
Join CountryReports YouTube Channel (Click Here)Denmark Geography
What environmental issues does Denmark have?
| Overview |
Denmark proper consists of the Jutland Peninsula and 406 islands, of which 79 are inhabited. The straits between these islands connect the Baltic and the North Seas. Greenland and the Faroe Islands, although self‑governing, are parts of Denmark. Greenland, the largest island in the world, is geographically part of North America. For many years, Denmark has been regarded traditionally as an agricultural country. However, dramatic changes have occurred in recent years, and today only about 3% of the population is employed in agriculture and fishing. The coastline is irregular and dotted with inlets, breaks, gently sloping fjords, and impressive cliffs. About 10% of the country is covered by woodland, including commercial forests. The public has access, as a right, to all the beaches in the country, including right of passage along privately owned shore. |
| Climate |
Because Denmark is almost entirely surrounded by the sea, it has a moderate, maritime climate. This, however, produces changeable weather, which makes forecasting an imperfect art. The average temperatures range from 32°F in February to 61°F in July. Temperatures vary slightly from day to night. Average rainfall is 24 inches. August and October are the wettest months. Days are short in winter, with about 6 hours of daylight in December and January. Daylight in summer lasts 18-20 hours. |
| Border Countries | Germany 68 km |
| Environment - Current Issues | air pollution, principally from vehicle and power plant emissions; nitrogen and phosphorus pollution of the North Sea; drinking and surface water becoming polluted from animal wastes and pesticides |
| Environment - International Agreements | party to: Air Pollution, Air Pollution-Nitrogen Oxides, Air Pollution-Persistent Organic Pollutants, Air Pollution-Sulfur 85, Air Pollution-Sulfur 94, Air Pollution-Volatile Organic Compounds, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements |
| Terrain | low and flat to gently rolling plains |
Denmark Economy
How big is the Denmark economy?
| Economic Overview |
Despite its relatively small size, Denmark has consistently ranked among the top countries in various global economic indicators, thanks to its stable political environment, innovative business landscape, and robust social infrastructure. Economic Stability: Denmark's economy is characterized by remarkable stability, supported by prudent fiscal policies, sound financial regulations, and a transparent business environment. The country weathered the storms of the global economic crisis with resilience, maintaining low levels of unemployment and inflation compared to many other European nations. Moreover, Denmark's commitment to maintaining a balanced budget and a relatively low national debt-to-GDP ratio has contributed to its economic resilience, fostering investor confidence and sustainable growth. Innovation and Technology: Denmark is renowned for its culture of innovation and technological advancement. The country consistently invests in research and development (R&D), fostering a conducive environment for startups and established businesses alike to thrive. Copenhagen, the capital city, has emerged as a vibrant hub for tech entrepreneurs and innovators, attracting talent from around the world. Notable sectors driving Denmark's innovation include renewable energy, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and information technology. Companies such as Novo Nordisk, Maersk, and Vestas exemplify Denmark's prowess in innovation, achieving global recognition for their contributions to their respective industries. Strong Social Welfare System: Denmark's social welfare system is often cited as a model for other nations. The Danish government prioritizes social inclusion, healthcare, education, and childcare, ensuring that citizens have access to essential services and support. The generous welfare programs, including universal healthcare and free education, contribute to a high standard of living and social cohesion. Moreover, Denmark's labor market policies, such as flexible working hours and strong protections for workers, promote a healthy work-life balance and employee satisfaction. Sustainable Development: Environmental sustainability is a core principle embedded in Denmark's economic policies. The country has made significant strides in transitioning towards renewable energy sources, with wind power playing a prominent role in its energy mix. Denmark's commitment to sustainability is not limited to energy; it extends to areas such as transportation, urban planning, and waste management. The government's ambitious targets for reducing carbon emissions and investing in green technologies underscore Denmark's leadership in the global fight against climate change. Global Trade and Investment: As a member of the European Union (EU) and a participant in international trade agreements, Denmark enjoys access to a vast market for its exports and attracts foreign investment. The country's strategic location at the crossroads of Northern Europe and its well-developed infrastructure facilitate trade and commerce. Danish companies are known for their global outlook, with many engaging in export-oriented industries such as manufacturing, agriculture, and maritime shipping. Moreover, Denmark's reputation for quality products and services enhances its competitiveness in the global marketplace. |
| Industries | iron, steel, nonferrous metals, chemicals, food processing, machinery and transportation equipment, textiles and clothing, electronics, construction, furniture and other wood products, shipbuilding and refurbishment, windmills, pharmaceuticals, medical equipment |
| Currency Name and Code | Danish kroner (DKK) |
| Export Partners | Germany 17.8%, Sweden 11.6%, US 8.4%, Norway 6.3%, UK 6.3%, Netherlands 4.4%, China 4.2% |
| Import Partners | Germany 20.4%, Sweden 12.3%, Netherlands 8.1%, China 7.3%, Norway 6.1%, UK 4.4% |
Denmark News and Current Events
What current events are happening in Denmark?
Source: Google News
Denmark Travel Information
What makes Denmark a unique country to travel to?
Country Description
The Kingdom of Denmark is a highly developed, stable democracy with a modern economy. Greenland is a self-governing part of the Kingdom of Denmark, and the Faroe Islands have home rule within the Kingdom of Denmark.
Crime
Denmark, Greenland, and the Faroes all have relatively low violent-crime rates. Muggings, sexual assault, and racially motivated violence are rare. Violent confrontations occasionally take place between various immigrant gangs and outlaw motorcycle gangs operating in Denmark, but do not typically affect tourists and law-abiding Danish citizens. However, there is always a possibility that travelers could be caught in the wrong place at the wrong time. Travelers should be aware of their surroundings and immediately leave the area if they feel threatened. Be particularly vigilant in the Nørrebro and Vesterbro areas of Copenhagen.Freetown Christiania, located in the Christianshavn area of Copenhagen, has been known to be a hostile environment for tourists. Historically, Christiania has been the site of illicit drug activity and recent drug enforcement efforts have resulted in violent clashes between the police and Christiania residents. Because of the illicit activity, Christiania residents have imposed a strict no-photography policy. Tourists have been assaulted and robbed for taking pictures in Christiania. Police and emergency services are limited in Christiania.
Pickpockets and purse-snatchers operate mainly at train stations -- the Copenhagen Central Station in particular -- and on crowded trains or buses, as well as in areas frequented by tourists. Sophisticated thieves target the Copenhagen Airport and cruise ship quays. The best precaution is to keep an eye on your belongings at all times. Do not put any bags containing valuables, such as your passport or credit cards, down on the ground or on the back of a chair. Watch your computer bag, which is particularly desirable. Popular tourist attractions, like shopping streets and restaurants, also attract pickpockets and thieves. Hotel lobbies and breakfast rooms attract professional, well-dressed criminals who blend in with guests and target purses and briefcases left unguarded by unsuspecting tourists and business travelers. Pickpockets and purse-snatchers often work in pairs or groups with one person distracting the victim while another grabs the valuables. Since car and home break-ins have become more prevalent in recent years, we strongly recommend that you not leave any valuables in parked vehicles.
Don’t buy counterfeit and pirated goods, even if they are widely available. Not only are the bootlegs illegal to bring back into the United States, if you purchase them, you may also be breaking local law.
Criminal Penalties
While you are traveling in Denmark, you are subject to Danish laws. Foreign laws and legal systems can be vastly different from our own. In Denmark, the police may take you in for questioning if you violate the law and don’t have proper identification with you. However, most forms of identification, such as student ID or a driver’s license, are acceptable, and there is no legal requirement for foreigners to carry their passports. Under Danish law, the police are permitted to detain someone for up to eight hours without charge. In addition, possessing knives with a locking blade longer than seven centimeters in a public place carries an immediate jail sentence. Some activities may be legal in Denmark, but are illegal in the United States. For instance, you can be prosecuted under U.S. law if you buy pirated goods. Engaging in sexual conduct with minors and using or disseminating child pornography are crimes prosecutable in the United States. If you break local laws in Denmark, your U.S. passport won’t help you avoid arrest or prosecution. It’s very important to know what activities are legally permissible at your travel destination.Greenland has very strict laws on the removal of natural resources, including precious and semi-precious metals, stones, and gemstones found there. Before attempting to extract or export any of these materials, make certain that doing so is not against the law.
Persons violating Denmark’s laws, even unknowingly, may be expelled, arrested, or imprisoned. Penalties for possessing, using, or trafficking in illegal drugs in Denmark are severe, and convicted offenders can expect long jail sentences and heavy fines, depending on the drug type. The possession of heroin, speed, ecstasy, cocaine, etc., will, in most cases, result in a jail sentence. A tourist’s possession of smaller amounts of marijuana or hashish for personal use will in most cases result in a warning or deportation. For larger quantities and trafficking, jail sentences are likely.
Based on the Vienna Convention on Consular Relations, bilateral agreements with certain countries, and customary international law, if you are arrested in Denmark, you have the option to request that the police, prison officials, or other authorities alert the U.S. Embassy of your arrest. You also have the right to have your communications forwarded to the Embassy.
Languages
The Danish alphabet has a total of 29 letters: 9 vowels (a,e,i,o,u,y,æ,ø,å) and20 consonant.
Medical Facilities and Health Information
Excellent medical facilities are widely available in Denmark. In Greenland and the Faroe Islands, medical facilities are limited, and evacuation is required for serious illness or injury. Although emergency medical treatment is free of charge, the patient is charged for follow-up care. There are modern, fully equipped hospitals throughout Denmark; the largest – also called University Hospitals – are located in Copenhagen, Odense, and Aarhus.
Safety and Security
Denmark remains largely free of terrorist incidents; however, like other Western European nations, Denmark faces an increased threat of terrorism. In 2011 and 2012, police arrested individuals accused of planning terrorist attacks in Denmark. In particular, the 2005 and 2010 publication in Denmark of cartoons depicting the Islamic Prophet Muhammad continues to impact Danish relations with the Muslim world and draw the attention of extremists. The Department of State recently re-issued the Worldwide Caution, which includes information about the potential for terrorist attacks in Europe.As with other countries in the Schengen area, Denmark’s open borders allow for the possibility of terrorist groups entering and exiting the country with anonymity. You are reminded to remain vigilant with regard to your personal security and to exercise caution. In general, Copenhagen is a safe city. However, certain areas pose more of a threat than others; for instance, you should avoid downtown Vesterbro and Nørrebro late at night.
Public demonstrations occasionally occur in Copenhagen and other cities, and are generally peaceful events. Prior police approval is required for public demonstrations, and police oversight is routinely provided to ensure adequate security for participants and passers-by. Nonetheless, as with any large crowd composed of diverse groups, situations may develop which could pose a threat to public safety. You should avoid areas where public demonstrations are taking place. Be aware that participation in illegal demonstrations or street riots may result in immediate imprisonment and long-term bans on re-entering Denmark.
Traffic Safety and Road Conditions
While in Denmark, you may encounter road conditions that differ significantly from those in the United States. You must be 18 years of age to drive a car in Denmark. U.S. tourists may use their state driver’s license in Denmark for up to 90 days. Long-term residents must obtain a valid Danish driver’s license. Driving in Denmark is on the right side of the road. Road signs use standard international symbols. Many urban streets have traffic lanes reserved for public transport only, and bicycle lanes are common. Unless otherwise noted on traffic signs, the speed limit is 50 km/h in urban areas, 80 km/h on open roads, and 130km/h on expressways.Use of seat belts is mandatory for drivers and all passengers. Children under three years of age or under 135 cm in height must be secured with approved safety equipment appropriate to the child’s age, size, and weight.
Driving any vehicle, including bicycles, under the influence of alcohol or drugs is considered a very serious offense. The rules are stringently enforced and violations can result in stiff fines and jail sentences. It is against to law to drive while using a hand-held cell phone.
Denmark has an extensive and efficient public transportation system. Trains, buses, and ferries connect Copenhagen with other major cities in Denmark and with Norway, Sweden, Poland, and Germany. Bicycles are also widely used in Denmark. Passengers exiting public or tourist buses, as well as tourists driving rental cars, should watch for bicycles in designated lanes and paths, which are usually located between the pedestrian sidewalk and the motor-vehicle lane.
Danish expressways, highways, and secondary roads are of high quality and connect all areas of the country. It is possible to drive from the northern tip of Denmark to the German border in the south in just four hours. Greenland has no established road system, and domestic travel is by foot, boat, or air. The majority of the Faroe Islands are interconnected by roads and tunnels as well as by boat, and on the large islands even small hamlets are accessible by road. On the smaller islands, travel is mostly done on foot. There is excellent mobile telephone coverage throughout the islands.